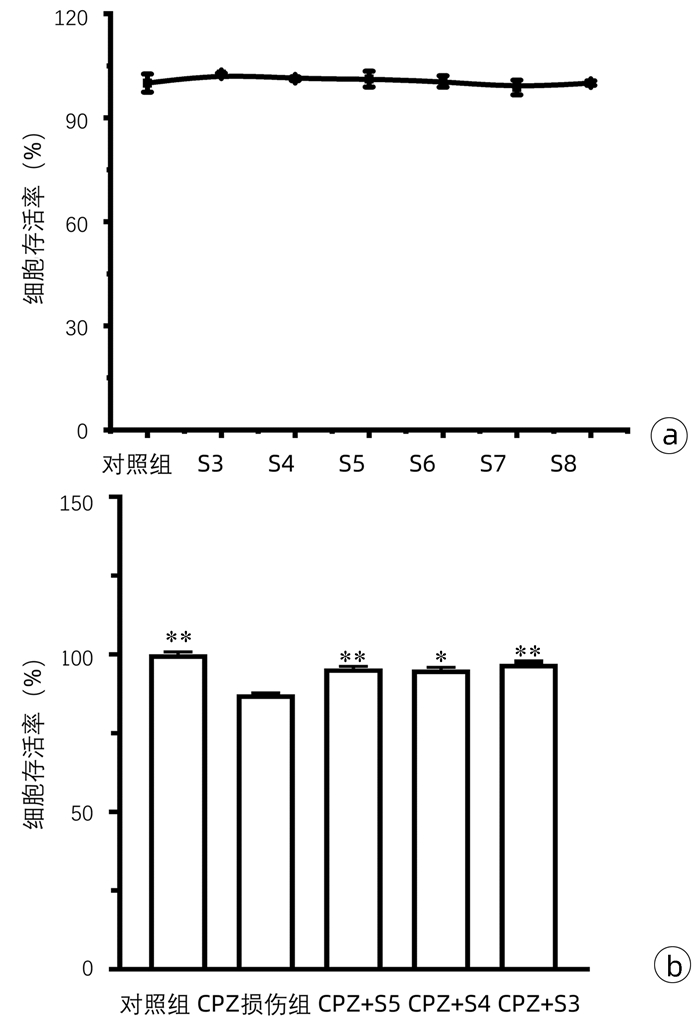
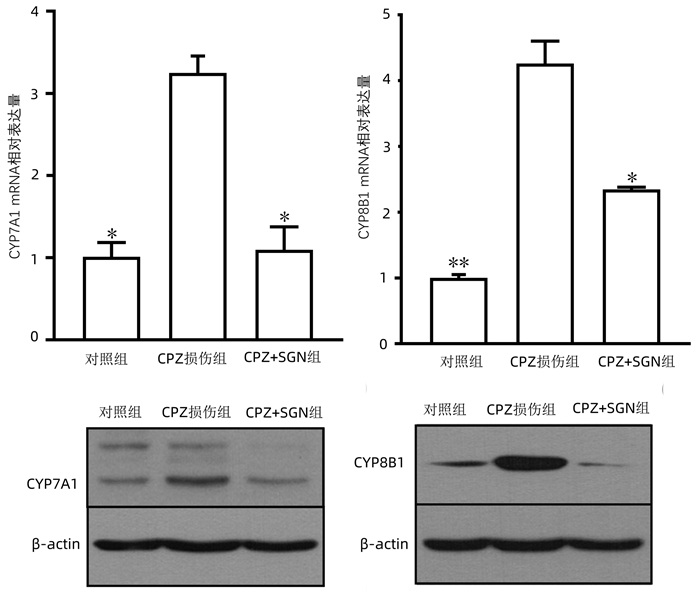
| [1] |
SHEN T, HUANG X, WANG YY, et al. Current status of epidemiological studies on drug-induced liver injury in China[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(6): 1152-1155. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn. 1001-5256.2018.06.002.
|
| [2] |
Drug-induced Liver Disease Study Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the management of drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(11): 1752-1769. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.11.002. |
| [3] |
ZENG LR, HUANG XM, YANG CY, et al. Safety, rationality and drug use of Shuganning injection[J]. Chin J Clin Ration Drug Use, 2021, 14(15): 35-37, 41. DOI: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2021.15.012. |
| [4] |
HENDRIKS DF, FREDRIKSSON PUIGVERT L, MESSNER S, et al. Hepatic 3D spheroid models for the detection and study of compounds with cholestatic liability[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 35434. DOI: 10.1038/srep35434. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
ANTHÉRIEU S, BACHOUR-EL AZZI P, DUMONT J, et al. Oxidative stress plays a major role in chlorpromazine-induced cholestasis in human HepaRG cells[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57(4): 1518-1529. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26160. |
| [7] |
COPPLE BL, JAESCHKE H, KLAASSEN CD. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of cholestasis[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2010, 30(2): 195-204. DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1253228. |
| [8] |
CHATTERJEE S, ANNAERT P. Drug-induced cholestasis: Mechanisms, models, and markers[J]. Curr Drug Metab, 2018, 19(10): 808-818. DOI: 10.2174/1389200219666180427165035. |
| [9] |
AI G, YAN YD, HUANG ZM. Research progress on Chinese materia medica in treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis based on FXR-mediated regulation[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drug, 2017, 48(19): 4077-4088. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2017.19.028. |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
LI YX, LI XP, GU J, et al. Study on protective mechanism of Tibetan medicine Ershiwuwei Songshi Pills on cholestatic liver injury in rats based on FXR signaling pathway[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2020, 45(21): 5273-5279. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200727.401. |
| [12] |
LU TT, REPA JJ, MANGELSDORF DJ. Orphan nuclear receptors as eLiXiRs and FiXeRs of sterol metabolism[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(41): 37735-37738. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R100035200. |
| [13] |
GOODWIN B, JONES SA, PRICE RR, et al. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis[J]. Mol Cell, 2000, 6(3): 517-526. DOI: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00051-4. |
| [14] |
ZOLLNER G, MARSCHALL HU, WAGNER M, et al. Role of nuclear receptors in the adaptive response to bile acids and cholestasis: Pathogenetic and therapeutic considerations[J]. Mol Pharm, 2006, 3(3): 231-251. DOI: 10.1021/mp060010s. |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
LEFEBVRE P, CARIOU B, LIEN F, et al. Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in metabolic regulation[J]. Physiol Rev, 2009, 89(1): 147-191. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00010.2008. |
| [17] |
XU LJ, JIANG SD, JI H, et al. Role of bile acid nuclear receptor FXR in cholestasis and related pharmacotherapy[J]. J Pharm Res, 2018, 37(3): 169-173. DOI: 10.13506/j.cnki.jpr.2018.03.011. |
| [18] |
MARIN JJ, MACIAS RI, BRIZ O, et al. Bile acids in physiology, pathology and pharmacology[J]. Curr Drug Metab, 2015, 17(1): 4-29. DOI: 10.2174/1389200216666151103115454. |



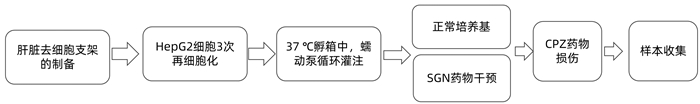




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: