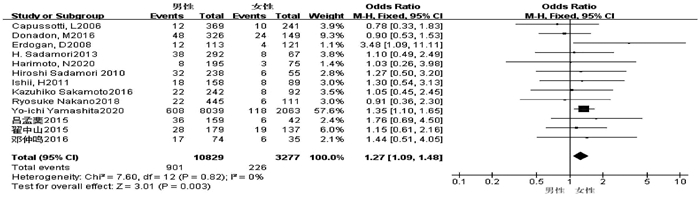
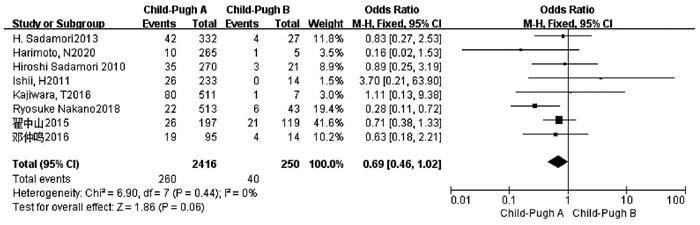
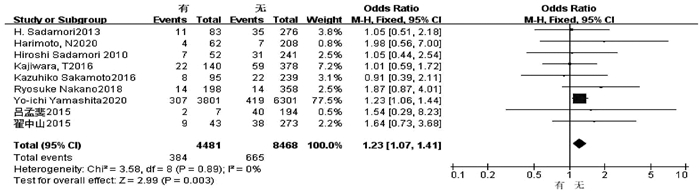
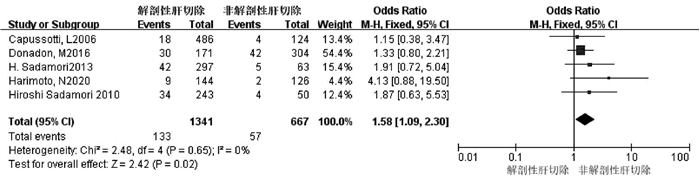
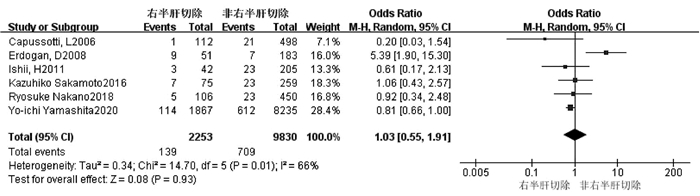
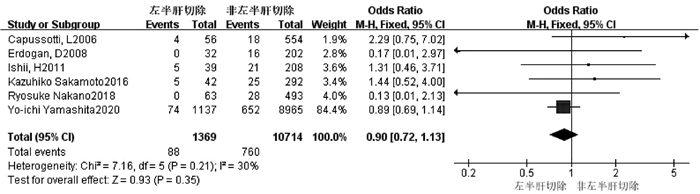
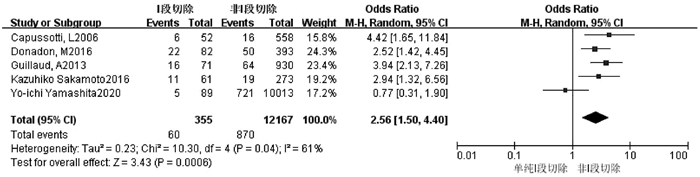
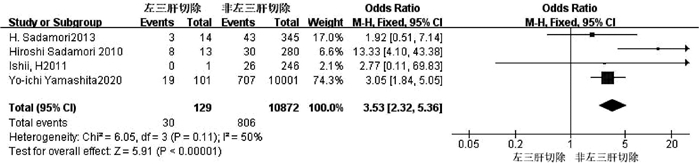
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
YAMASHITA YI, YAMAMOTO H, MIYATA H, et al. Risk factors for bile leakage: Latest analysis of 10 102 hepatectomies for hepatocellular carcinoma from the Japanese national clinical database[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2021, 28(7): 556-562. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.827. |
| [3] |
MIURA F, YAMAMOTO M, GOTOH M, et al. Validation of the board certification system for expert surgeons (hepato-biliary-pancreatic field) using the data of the National Clinical Database of Japan: Part 1 - Hepatectomy of more than one segment[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2016, 23(6): 313-323. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.344. |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
WEN Y, MIAO XY, HUANG SF, et al. The prevention and treatment of bile leakage after the hepatectomy[J]. J Clin Surg, 2005, 13(10): 639-640. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2005.10.021. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9): 603-605. DOI: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z. |
| [8] |
SAKAMOTO K, TAMESA T, YUKIO T, et al. Risk factors and managements of bile leakage after hepatectomy[J]. World J Surg, 2016, 40(1): 182-189. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-015-3156-8. |
| [9] |
SADAMORI H, YAGI T, SHINOURA S, et al. Risk factors for major morbidity after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Br J Surg, 2013, 100(1): 122-129. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.8957. |
| [10] |
PANARO F, HACINA L, BOUYABRINE H, et al. Risk factors for postoperative bile leakage: A retrospective single-center analysis of 411 hepatectomies[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2016, 15(1): 81-86. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(15)60424-6. |
| [11] |
NAKANO R, OHIRA M, KOBAYASHI T, et al. Independent risk factors that predict bile leakage after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Cohort study[J]. Int J Surg, 2018, 57: 1-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.07.005. |
| [12] |
CAPUSSOTTI L, FERRERO A, VIGANÔ L, et al. Bile leakage and liver resection: Where is the risk?[J]. Arch Surg, 2006, 141(7): 690-694; discussion 695. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.141.7.690. |
| [13] |
DONADON M, COSTA G, CIMINO M, et al. Diagnosis and management of bile leaks after hepatectomy: Resultsof a prospective analysis of 475 hepatectomies[J]. World J Surg, 2016, 40(1): 172-181. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-015-3143-0. |
| [14] |
ERDOGAN D, BUSCH OR, van DELDEN OM, et al. Incidence and management of bile leakage after partial liver resection[J]. Dig Surg, 2008, 25(1): 60-66. DOI: 10.1159/000118024. |
| [15] |
GUILLAUD A, PERY C, CAMPILLO B, et al. Incidence and predictive factors of clinically relevant bile leakage in the modern era of liver resections[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2013, 15(3): 224-229. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00580.x. |
| [16] |
HARIMOTO N, MURANUSHI R, HOSHINO K, et al. Albumin-Indocyanine Green Evaluation (ALICE) grade predicts bile leakage after hepatic resection[J]. Surg Today, 2020, 50(8): 849-854. DOI: 10.1007/s00595-020-01955-2. |
| [17] |
SADAMORI H, YAGI T, MATSUDA H, et al. Risk factors for major morbidity after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in 293 recent cases[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2010, 17(5): 709-718. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-010-0275-3. |
| [18] |
ISHⅡ H, OCHIAI T, MURAYAMA Y, et al. Risk factors and management of postoperative bile leakage after hepatectomy without bilioenteric anastomosis[J]. Dig Surg, 2011, 28(3): 198-204. DOI: 10.1159/000324042. |
| [19] |
KAJIWARA T, MIDORIKAWA Y, YAMAZAKI S, et al. Clinical score to predict the risk of bile leakage after liver resection[J]. BMC Surg, 2016, 16(1): 30. DOI: 10.1186/s12893-016-0147-0. |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
DENG ZM, SUN Q. Risk factors and measures of prevention and treatment for bile leakage after hepatectomy[J]. Chin J Clin Res, 2016, 29(2): 204-206. DOI: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2016.02.015. |
| [22] |
ZHAI ZS. Multivariate regression analysis of risk factors for biliary leakage after hepatic R0 resection[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2015, 20(5): 404-407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2015.05.017. |
| [23] |
KUBO N, SHIRABE K. Treatment strategy for isolated bile leakage after hepatectomy: Literature review[J]. Ann Gastroenterol Surg, 2020, 4(1): 47-55. DOI: 10.1002/ags3.12303. |
| [24] |
LIU ZY, JIN H, LIU M, et al. Role of bile leakage test in preventing bile leakage during partial liver resection[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2014, 13(2): 139-141. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2014.02.021. |
| [25] |
LO CM, FAN ST, LIU CL, et al. Biliary complications after hepatic resection: Risk factors, management, and outcome[J]. Arch Surg, 1998, 133(2): 156-161. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.133.2.156. |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
ZHENG SM, LI H, LI GC, et al. Risk factors, treatment and impact on outcomes of bile leakage after hemihepatectomy[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2017, 87(7-8): e26-e31. DOI: 10.1111/ans.13073. |
| [29] |
RAHBARI NN, ELBERS H, KOCH M, et al. Bilirubin level in the drainage fluid is an early and independent predictor of clinically relevant bile leakage after hepatic resection[J]. Surgery, 2012, 152(5): 821-831. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.03.012. |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
BAGDADE JD, STEWART M, WALTERS E. Impaired granulocyte adherence. A reversible defect in host defense in patients with poorly controlled diabetes[J]. Diabetes, 1978, 27(6): 677-681. DOI: 10.2337/diab.27.6.677. |
| [33] |
LI Q, WANG Y, MA T, et al. Clinical outcomes of patients with and without diabetes mellitus after hepatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0171129. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171129. |
| [34] |
INOUE Y, SUZUKI Y, YOKOHAMA K, et al. Diabetes mellitus does not influence results of hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Case control study[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn), 2020, 24(4): 211-215. DOI: 10.5114/wo.2020.102825. |
| [35] |
YAMAMOTO K, TAKADA Y, FUJIMOTO Y, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in donors for living donor liver transplantation[J]. Transplantation, 2007, 83(3): 257-262. DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000250671.06456.3f. |
| [36] |
FISCHER A, FUCHS J, STRAVODIMOS C, et al. Influence of diabetes on short-term outcome after major hepatectomy: An underestimated risk?[J]. BMC Surg, 2020, 20(1): 305. DOI: 10.1186/s12893-020-00971-w. |
| [37] |
INOUE Y, SUZUKI Y, YOKOHAMA K, et al. Diabetes mellitus does not influence results of hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Case control study[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn), 2020, 24(4): 211-215. DOI: 10.5114/wo.2020.102825. |
| [38] |
LIANG J, ARⅡZUMI SI, NAKANO M, et al. Diabetes mellitus and/or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma showed favorable surgical outcomes after hepatectomy[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39(10): 5639-5643. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.13760. |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
NAGANO Y, TOGO S, TANAKA K, et al. Risk factors and management of bile leakage after hepatic resection[J]. World J Surg, 2003, 27(6): 695-698. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-003-6907-x. |
| [42] |
FRVHLING P, HELLBERG K, EJDER P, et al. The prognostic value of C-reactive protein and albumin in patients undergoing resection of colorectal liver metastases. A retrospective cohort study[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2021, 23(6): 970-978. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.10.019. |
| [43] |
MA B, TANG GY, WANG L, et al. Prediction of independent risk factors for biliary leakage after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Medical Diet and Health, 2018, 12: 72.
马斌, 汤光耀, 王麟, 等. 预测肝细胞癌肝切除术后胆漏的独立危险因素[J]. 医学食疗与健康, 2018, 12: 72.
|
| [44] |
SPETZLER VN, SCHEPERS M, PINNSCHMIDT HO, et al. The incidence and severity of post-hepatectomy bile leaks is affected by surgical indications, preoperative chemotherapy, and surgical procedures[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2019, 8(2): 101-110. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.02.06. |
| [45] |
Chinese expert consensus and path management guideline for accelerated rehabilitation surgery (2018): Hepatobiliary surgery[J]. Chin J Anesthesiol, 2018, 38(1): 13-18. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1416.2018.01.101. |
| [46] |
COSTA G, DONADON M, TORZILLI G. Post-hepatectomy biliary fistula: From risk factors to the role of drain placement and management-still a lot to be answered[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2019, 8(4): 417-418. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.06.10. |









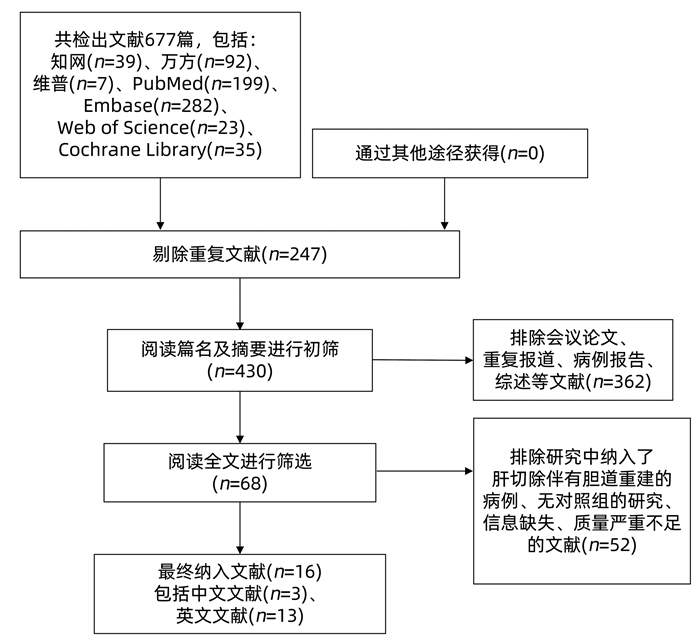




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: