| [1] |
de FRANCHIS R, BOSCH J, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Baveno Ⅶ-Renewing consensus in portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(4): 959-974. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.022. |
| [2] |
LESMANA C, RAHARJO M, GANI RA. Managing liver cirrhotic complications: Overview of esophageal and gastric varices[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2020, 26(4): 444-460. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0022. |
| [3] |
PONS M, AUGUSTIN S, SCHEINER B, et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of portal hypertension in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2021, 116(4): 723-732. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000994. |
| [4] |
SHIN SU, LEE JM, YU MH, et al. Prediction of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis: usefulness of three-dimensional MR elastography with echo-planar imaging technique[J]. Radiology, 2014, 272(1): 143-153. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14130916. |
| [5] |
GARCIA-TSAO G, ABRALDES JG, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(1): 310-335. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
JAKAB SS, GARCIA-TSAO G. Evaluation and management of esophageal and gastric varices in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2020, 24(3): 335-350. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2020.04.011. |
| [8] |
ARDEVOL A, IBAÑEZ-SANZ G, PROFITOS J, et al. Survival of patients with cirrhosis and acute peptic ulcer bleeding compared with variceal bleeding using current first-line therapies[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(4): 1458-1471. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29370. |
| [9] |
CHAVEZ-TAPIA NC, BARRIENTOS-GUTIERREZ T, TELLEZ-AVILA F, et al. Meta-analysis: antibiotic prophylaxis for cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding - an updated Cochrane review[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 34(5): 509-518. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04746.x. |
| [10] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Endoscopy, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002. |
| [11] |
DAI C, LIU WX, JIANG M, et al. Endoscopic variceal ligation compared with endoscopic injection sclerotherapy for treatment of esophageal variceal hemorrhage: a meta-analysis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(8): 2534-2541. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2534. |
| [12] |
KANWAL F, TAPPER EB, HO C, et al. Development of quality measures in cirrhosis by the practice metrics committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(4): 1787-1797. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30489. |
| [13] |
AL-ALI J, PAWLOWSKA M, COSS A, et al. Endoscopic management of gastric variceal bleeding with cyanoacrylate glue injection: safety and efficacy in a Canadian population[J]. Can J Gastroenterol, 2010, 24(10): 593-596. DOI: 10.1155/2010/276273. |
| [14] |
KAHLOON A, CHALASANI N, DEWITT J, et al. Endoscopic therapy with 2-octyl-cyanoacrylate for the treatment of gastric varices[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59(9): 2178-2183. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-014-3148-9. |
| [15] |
RÍOS CASTELLANOS E, SERON P, GISBERT JP, et al. Endoscopic injection of cyanoacrylate glue versus other endoscopic procedures for acute bleeding gastric varices in people with portal hypertension[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2015, (5): CD010180. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010180.pub2. |
| [16] |
BHAT YM, WEILERT F, FREDRICK RT, et al. EUS-guided treatment of gastric fundal varices with combined injection of coils and cyanoacrylate glue: a large U.S. experience over 6 years (with video)[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2016, 83(6): 1164-1172. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.09.040. |
| [17] |
WEIL D, CERVONI JP, FARES N, et al. Management of gastric varices: a French national survey[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 28(5): 576-581. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000560. |
| [18] |
LEE HA, CHANG JM, GOH HG, et al. Prognosis of patients with gastric variceal bleeding after endoscopic variceal obturation according to the type of varices[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31(2): 211-217. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001271. |
| [19] |
IMAI Y, NAKAZAWA M, ANDO S, et al. Long-term outcome of 154 patients receiving balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for gastric fundal varices[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 31(11): 1844-1850. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13382. |
| [20] |
LEE SJ, KIM SU, KIM MD, et al. Comparison of treatment outcomes between balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for gastric variceal bleeding hemostasis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 32(8): 1487-1494. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13729. |
| [21] |
CHU HH, KIM M, KIM HC, et al. Long-term outcomes of balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for the treatment of gastric varices: a comparison of ethanolamine oleate and sodium tetradecyl sulfate[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2018, 41(4): 578-586. DOI: 10.1007/s00270-017-1869-9. |
| [22] |
STEIN DJ, SALINAS C, SABRI S, et al. Balloon retrograde transvenous obliteration versus endoscopic cyanoacrylate in bleeding gastric varices: comparison of rebleeding and mortality with extended follow-up[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2019, 30(2): 187-194. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2018.12.008. |
| [23] |
CHAU TN, PATCH D, CHAN YW, et al. "Salvage" transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: gastric fundal compared with esophageal variceal bleeding[J]. Gastroenterology, 1998, 114(5): 981-987. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)00640-4. |
| [24] |
LAKHOO J, BUI JT, LOKKEN RP, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation and variceal coil or plug embolization ineffectively attain gastric variceal decompression or occlusion: results of a 26-patient retrospective study[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2016, 27(7): 1001-1011. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.02.019. |
| [25] |
SAAD WE. Combining transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration or augmenting TIPS with variceal embolization for the management of gastric varices: an evolving middle ground?[J]. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2014, 31(3): 266-268. DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1382796. |
| [26] |
GARCÍA-PAGÁN JC, CACA K, BUREAU C, et al. Early use of TIPS in patients with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362(25): 2370-2379. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0910102. |
| [27] |
HERNÁNDEZ-GEA V, PROCOPET B, GIRÁLDEZ Á, et al. Preemptive-TIPS improves outcome in high-risk variceal bleeding: an observational study[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(1): 282-293. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30182. |
| [28] |
LV Y, YANG Z, LIU L, et al. Early TIPS with covered stents versus standard treatment for acute variceal bleeding in patients with advanced cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(8): 587-598. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30090-1. |
| [29] |
ALBILLOS A, ZAMORA J, MARTÍNEZ J, et al. Stratifying risk in the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage: Results of an individual patient meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(4): 1219-1231. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29267. |
| [30] |
FUKUDA T, HIROTA S, SUGIMURA K. Long-term results of balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for the treatment of gastric varices and hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2001, 12(3): 327-336. DOI: 10.1016/s1051-0443(07)61912-5. |
| [31] |
HUNG HH, CHANG CJ, HOU MC, et al. Efficacy of non-selective β-blockers as adjunct to endoscopic prophylactic treatment for gastric variceal bleeding: a randomized controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56(5): 1025-1032. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.021. |
| [32] |
LO GH, LIANG HL, CHEN WC, et al. A prospective, randomized controlled trial of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus cyanoacrylate injection in the prevention of gastric variceal rebleeding[J]. Endoscopy, 2007, 39(8): 679-685. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-966591. |
| [33] |
MISHRA SR, CHANDER SHARMA B, KUMAR A, et al. Endoscopic cyanoacrylate injection versus beta-blocker for secondary prophylaxis of gastric variceal bleed: a randomised controlled trial[J]. Gut, 2010, 59(6): 729-735. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2009.192039. |
| [34] |
LUO X, XIANG T, WU J, et al. Endoscopic cyanoacrylate injection versus balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for prevention of gastric variceal bleeding: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74(4): 2074-2084. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31718. |
| [35] |
MU YP, LIU CH, ZHANG H, et al. Theory of "asthenia and deficiency cause accumulation" in liver cirrhosis--Brief analysis on academic system of Professor Liu Ping[J]. Acta Univ Tradit Med Sin Pharmacol Shanghai, 2013, 27(2): 1-4. DOI: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2013.02.006. |
| [36] |
CHEN C, LYU Y, CHEN XL, et al. Effect of endoscopic ligation combined with traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation-based treatment in the secondary prevention of esophageal variceal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(5): 1075-1080. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.019. |
| [37] |
XIAO DH, GU J, CAI H, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled multicentre study of Fuzhenghuayu capsule for prevention of oesophageal variceal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2014, 22(8): 594-599. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2014.08.009. |
| [38] |
GARCIA-TSAO G, SANYAL AJ, GRACE ND, et al. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 46(3): 922-938. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21907. |
| [39] |
SARIN SK, KUMAR A, ANGUS PW, et al. Primary prophylaxis of gastroesophageal variceal bleeding: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver[J]. Hepatol Int, 2008, 2(4): 429-439. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-008-9096-8. |
| [40] |
GROSZMANN RJ, GARCIA-TSAO G, BOSCH J, et al. Beta-blockers to prevent gastroesophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2005, 353(21): 2254-2261. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa044456. |
| [41] |
MANDORFER M, BOTA S, SCHWABL P, et al. Nonselective β blockers increase risk for hepatorenal syndrome and death in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(7): 1680-1690. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.03.005. |
| [42] |
SERSTÉ T, MELOT C, FRANCOZ C, et al. Deleterious effects of beta-blockers on survival in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 52(3): 1017-1022. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23775. |
| [43] |
TERGAST TL, KIMMANN M, LASER H, et al. Systemic arterial blood pressure determines the therapeutic window of non-selective beta blockers in decompensated cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(6): 696-706. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15439. |
| [44] |
SHARMA M, SINGH S, DESAI V, et al. Comparison of therapies for primary prevention of esophageal variceal bleeding: A systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(4): 1657-1675. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30220. |
| [45] |
MISHRA SR, SHARMA BC, KUMAR A, et al. Primary prophylaxis of gastric variceal bleeding comparing cyanoacrylate injection and beta-blockers: a randomized controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 54(6): 1161-1167. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.09.031. |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
CHEN Y, YANG YP. The role of traditional Chinese medicine in blocking and reversing hepatic fibrosis: current status, hope, and challenge[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(4): 689-693. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.04.002. |



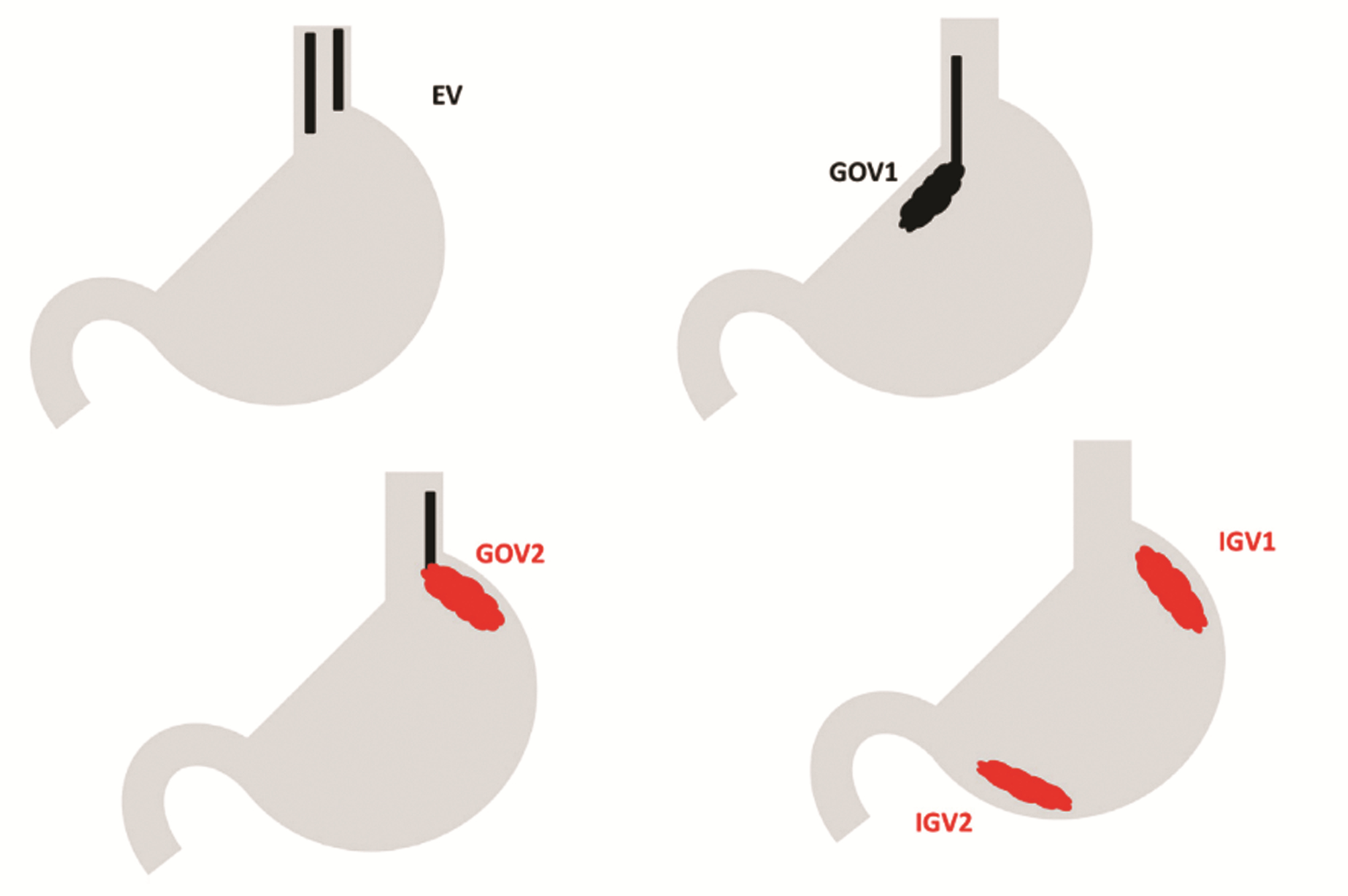




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: