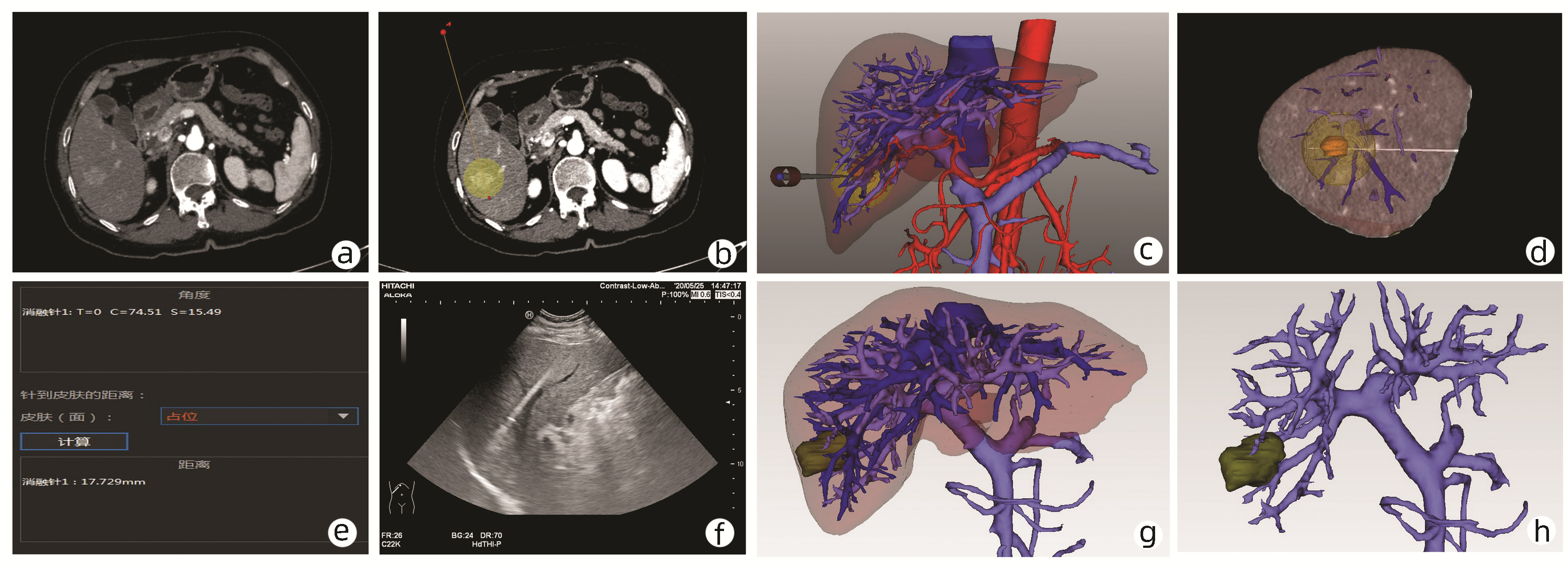
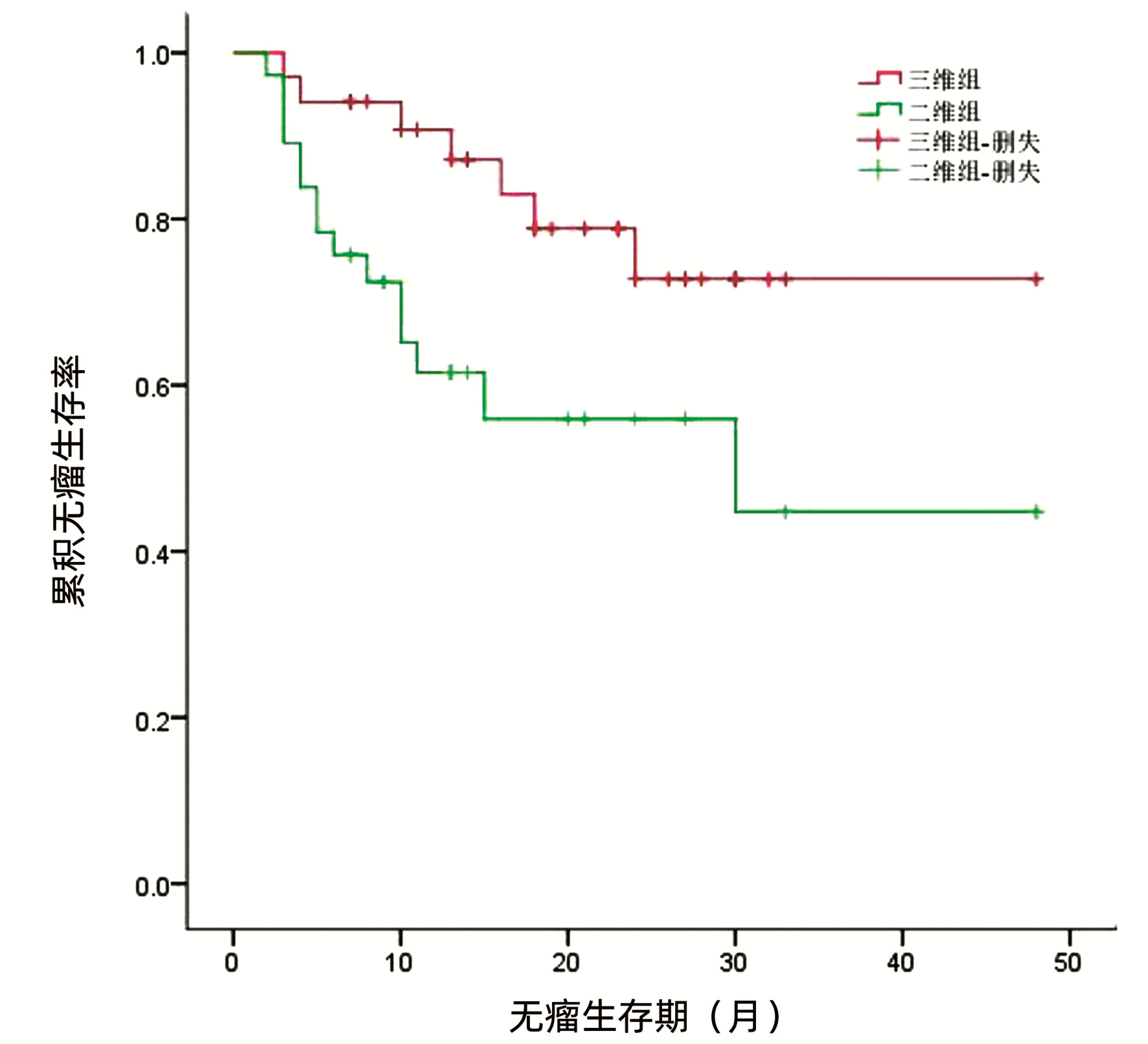
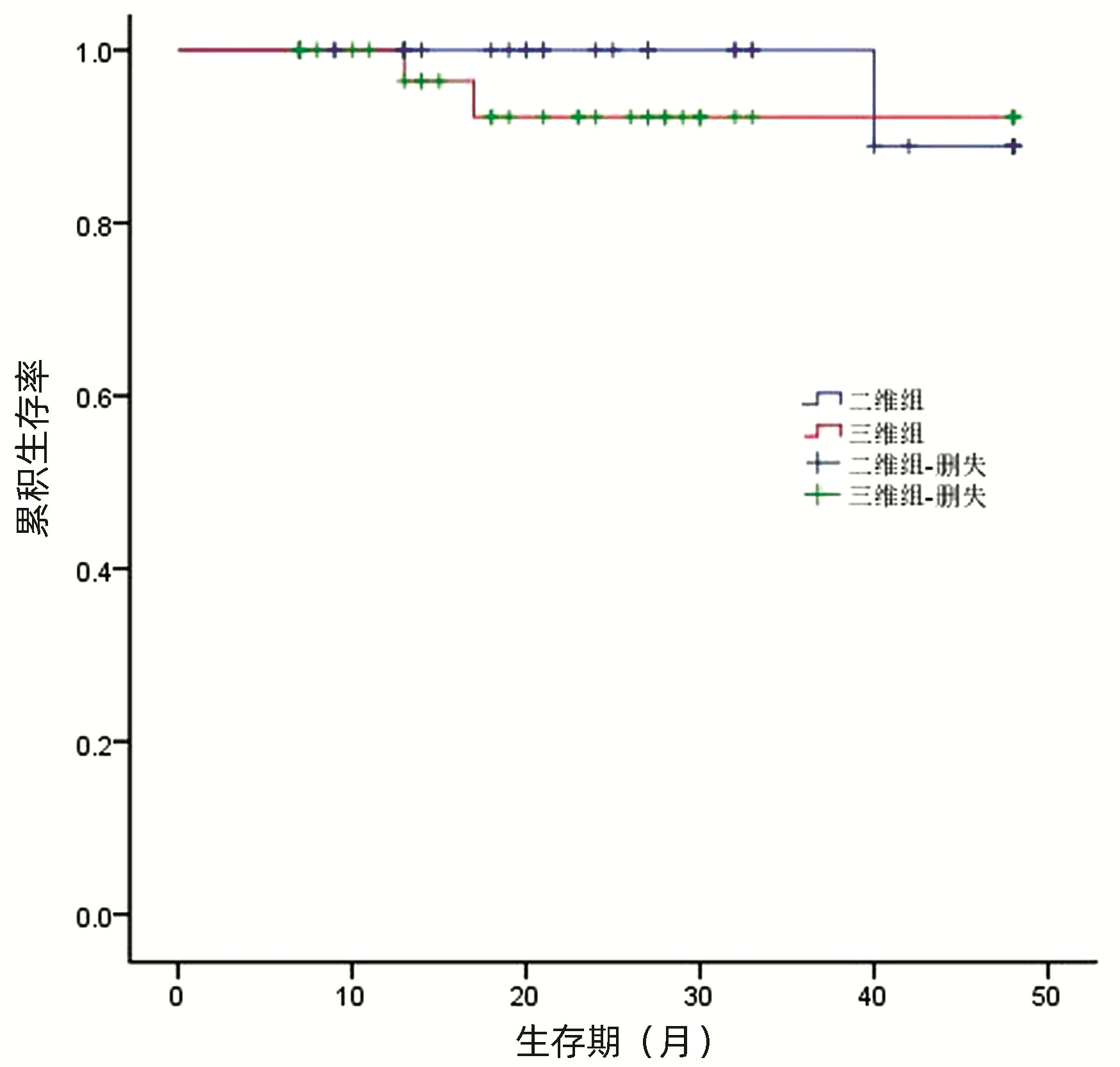
| [1] |
FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, DIKSHIT R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(5): E359- E386. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.29210. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
ZHOU M, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10204): 1145-1158. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1. |
| [4] |
Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China (2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(2): 277-292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007. |
| [5] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(1): 182-236. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019. |
| [6] |
ZHU F, RHIM H. Thermal ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: what's new in 2019[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2019, 8(6): 58. DOI: 10.21037/cco.2019.11.03. |
| [7] |
LI R, CHEN HP, WANG F, et al. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in treatment of liver cancer rupture and bleeding[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2020, 40(17): 3653-3656. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2020.17.021. |
| [8] |
ZHI-YU H, PING L, XIAO-LING Y, et al. A clinical study of thermal monitoring techniques of ultrasound-guided microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in high-risk locations[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 41246. DOI: 10.1038/srep41246. |
| [9] |
HUANG S, YU J, LIANG P, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to large vessels: a long-term follow-up[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2014, 83(3): 552-558. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.12.015. |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
HU H, CHEN GF, YUAN W, et al. Microwave ablation with chemoembolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2018, 34(8): 1351-1358. DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1462536. |
| [12] |
FANG CH, ZHANG P, ZHOU WP, et al. Efficacy of three-dimensional visualization technology in the precision diagnosis and treatment for primary liver cancer: a retrospective multicenter study of 1 665 cases in China[J]. Chin J Surg, 2020, 58(5): 375-382. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20200220-00105. |
| [13] |
BARI H, WADHWANI S, DASARI B. Role of artificial intelligence in hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2021, 13(1): 7-18. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i1.7. |
| [14] |
YEO CT, MACDONALD A, UNGI T, et al. Utility of 3D reconstruction of 2D liver computed tomography/magnetic resonance images as a surgical planning tool for residents in liver resection surgery[J]. J Surg Educ, 2018, 75(3): 792-797. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2017.07.031. |
| [15] |
LI SS, ZHANG K, CHENG SJ, et al. Current status and future perspectives of the application of medical 3D visualization technology in accurate surgery of liver tumors[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(5): 1114-1117. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.05.042. |
| [16] |
HU M, HU H, CAI W, et al. The safety and feasibility of three-dimensional visualization technology assisted right posterior lobe allied with part of V and VⅢ sectionectomy for right hepatic malignancy therapy[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A, 2018, 28(5): 586-594. DOI: 10.1089/lap.2017.0479. |
| [17] |
RENZULLI M, TOVOLI F, CLEMENTE A, et al. Ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: beyond the standard indications[J]. Med Oncol, 2020, 37(4): 23. DOI: 10.1007/s12032-020-01348-y. |
| [18] |
YOSHIDA S, KORNEK M, IKENAGA N, et al. Sublethal heat treatment promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances the malignant potential of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(5): 1667-1680. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26526. |
| [19] |
CROCETTI L, de BAÉRE T, PEREIRA PL, et al. CIRSE standards of practice on thermal ablation of liver tumours[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2020, 43(7): 951-962. DOI: 10.1007/s00270-020-02471-z. |
| [20] |
YANG JD, HAINAUT P, GORES GJ, et al. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(10): 589-604. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y. |









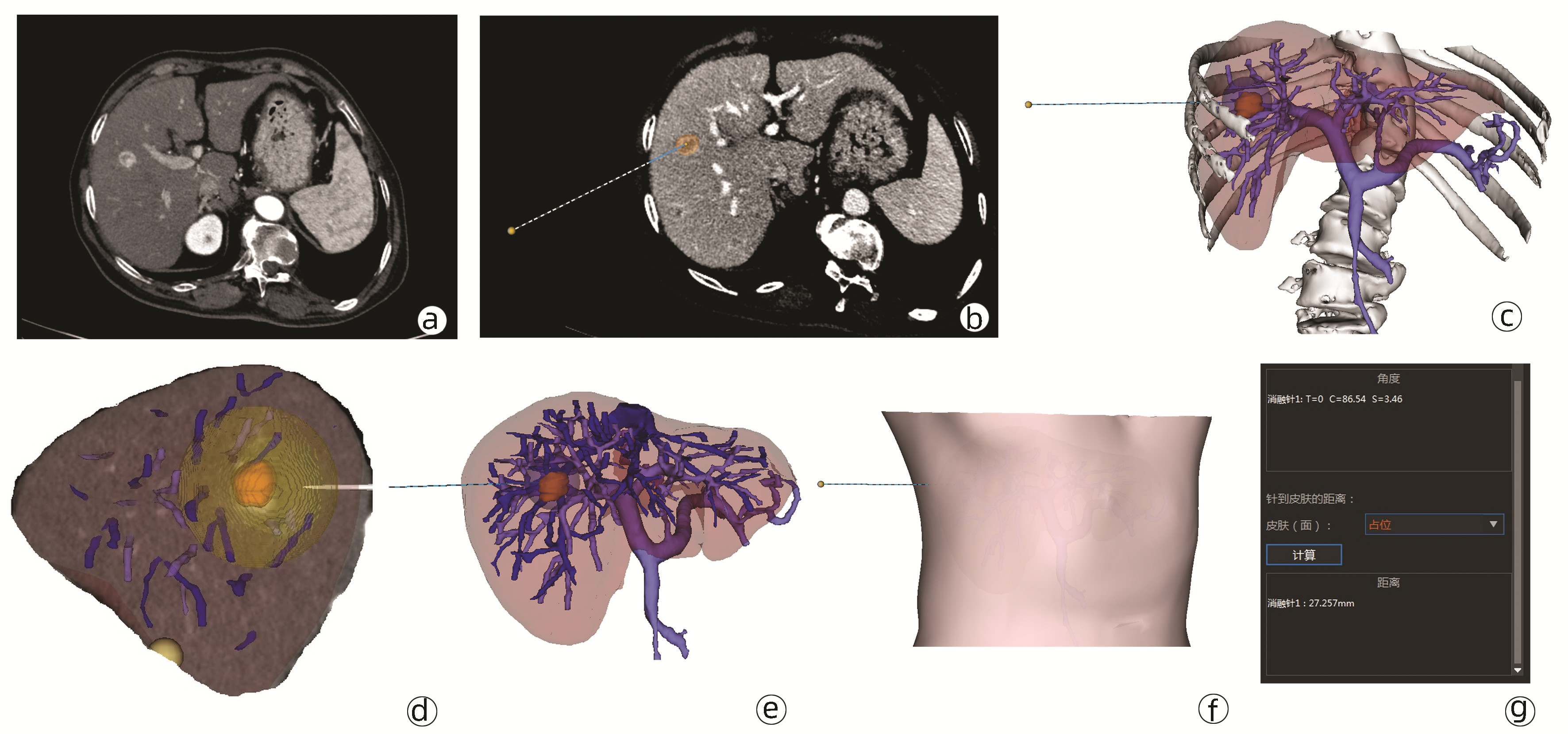




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: