| [1] |
SIMONETTO DA, LIU M, KAMATH PS. Portal hypertension and related complications: diagnosis and management[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2019, 94(4): 714-726. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.12.020. |
| [2] |
JIANG GQ, BAI DS, JIN SJ, et al. Modified vagus nerve-preserving versus conventional laparoscopic splenectomy and azygoportal disconnection for cirrhotic portal hypertension: a prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2020, 19(12): 1280-1285. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20201126-00741. |
| [3] |
HAN D, PENG JW, XIE HJ. Prevention of portal vein thrombosis in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension aftersplenectomy and devascularization[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2020, 23(3): 409-412. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.03.027. |
| [4] |
de FRANCHIS R, Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(3): 743-752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. |
| [5] |
SONG ZM, DAI CL. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy for cirrhosis and portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg, 2019, 22(12): 958-962. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2019.12.009. |
| [6] |
QI R, JIN X, SHI H, et al. Effect of laparoscopic splenectomy on portal vein thrombosis and serum YKL-40 in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2019, 18(6): 898-901. DOI: 10.1016/j.aohep.2019.06.009. |
| [7] |
LI DY. Comparison of different intra-splenectomy splenic pedicle vascular treatments for postoperative portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Guangxi Med J, 2019, 41(8): 985-988. DOI: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2019.08.14. |
| [8] |
ZHANG XY, LI C, PENG W, et al. Platelet count-spleen volume ratio prediction of both moderate and severe portal hypertention in patients with cirrhosis by platelet count-spleen volume ratio[J]. J Abdominal Surg, 2016, 29(3): 187-192. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5591.2016.03.009. |
| [9] |
XIONG ZJ, FAN HS, ZHU XN, et al. Application of FibroTouch combined with AST to platelet ratio index in diagnosis of portal hypertension in patients with hepatic cirrhosis[J/CD]. Chin J Hepat Surg(Electronic Edition), 2019, 8(4): 362-365. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2019.04.019. |
| [10] |
SONG LJ, YUAN Y, WANG W. Clinical value of quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of portal hypertension in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2020, 23(4): 568-571. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.04.029. |
| [11] |
GIOIA S, NARDELLI S, PASQUALE C, et al. Natural history of patients with non cirrhotic portal hypertension: Comparison with patients with compensated cirrhosis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2018, 50(8): 839-844. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.01.132. |
| [12] |
LYU SC, GU WQ. Research progress on prevention and treatment of portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy for patients with hepatic cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2015, 21(1): 59-63. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2015.01.019. |
| [13] |
YANG S, HE C, FAN X, et al. Early prophylactic anticoagulation via transjugular intrahepatic route for portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2015, 26(7): 1009-1017. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2015.03.008. |
| [14] |
FENG Q, XU C, SUN MH. miR-141 inhibits thrombosis in vascular pathways through the TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. Med J West China, 2021, 33(2): 186-190. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2021.02.006. |
| [15] |
GU YN, XIE CY. Advancing investigate of deep vein thrombosis for inflammation and signa-ling pathway[J]. Chin J Immunol, 2020, 36(1): 113-118. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.01.022. |
| [16] |
MALEMUD CJ. The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 2018, 10(5-6): 117-127. DOI: 10.1177/1759720X18776224. |
| [17] |
BANERJEE S, BIEHL A, GADINA M, et al. JAK-STAT signaling as a target for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: Current and future prospects[J]. Drugs, 2017, 77(5): 521-546. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-017-0701-9. |
| [18] |
LI Y, LI KH, WEN SH, et al. Role of JAK/STAT in intestinal injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats[J]. Chin J Pathophysioly, 2011, 27(12): 2338-2344. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2011.12.019. |










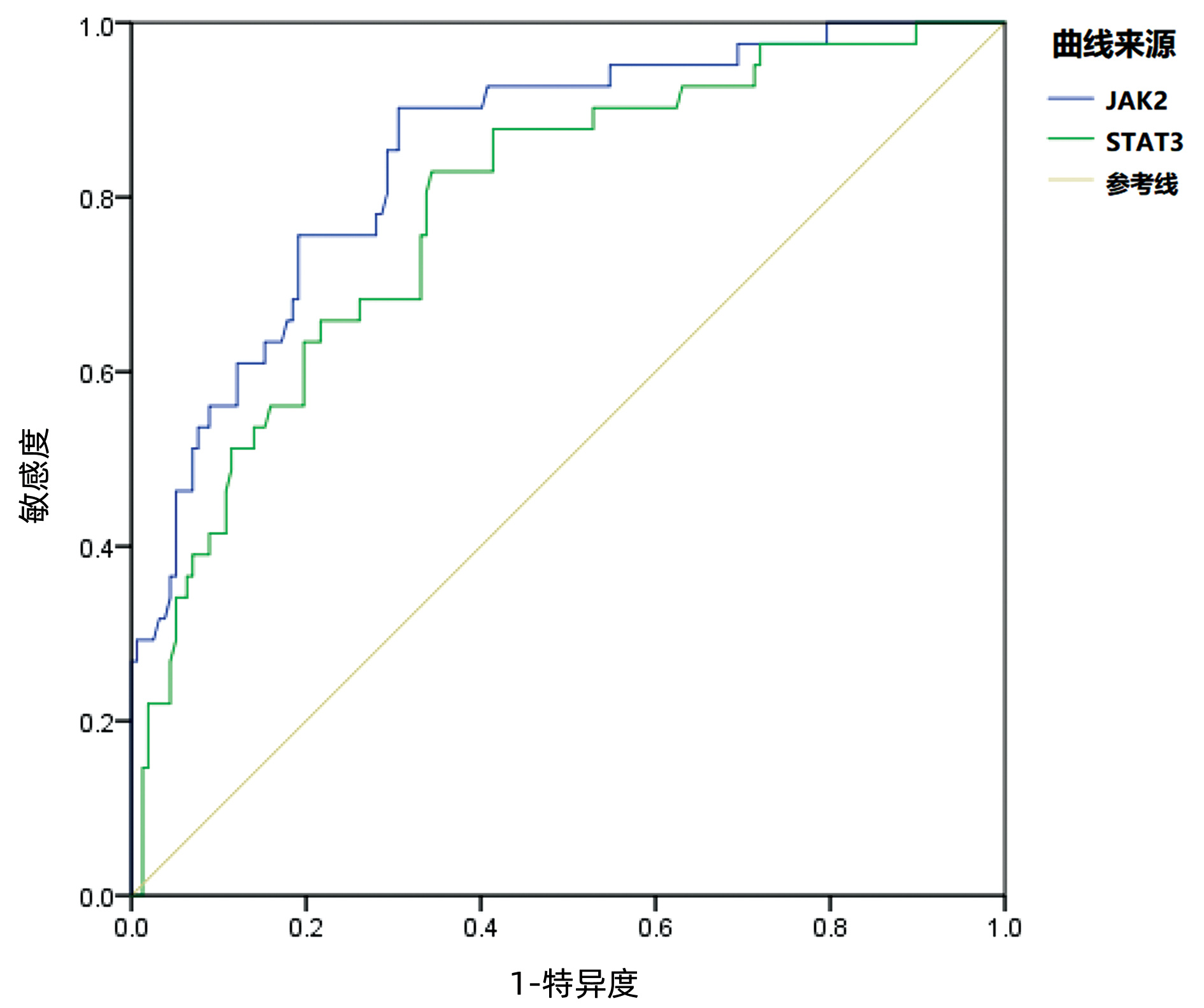




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: