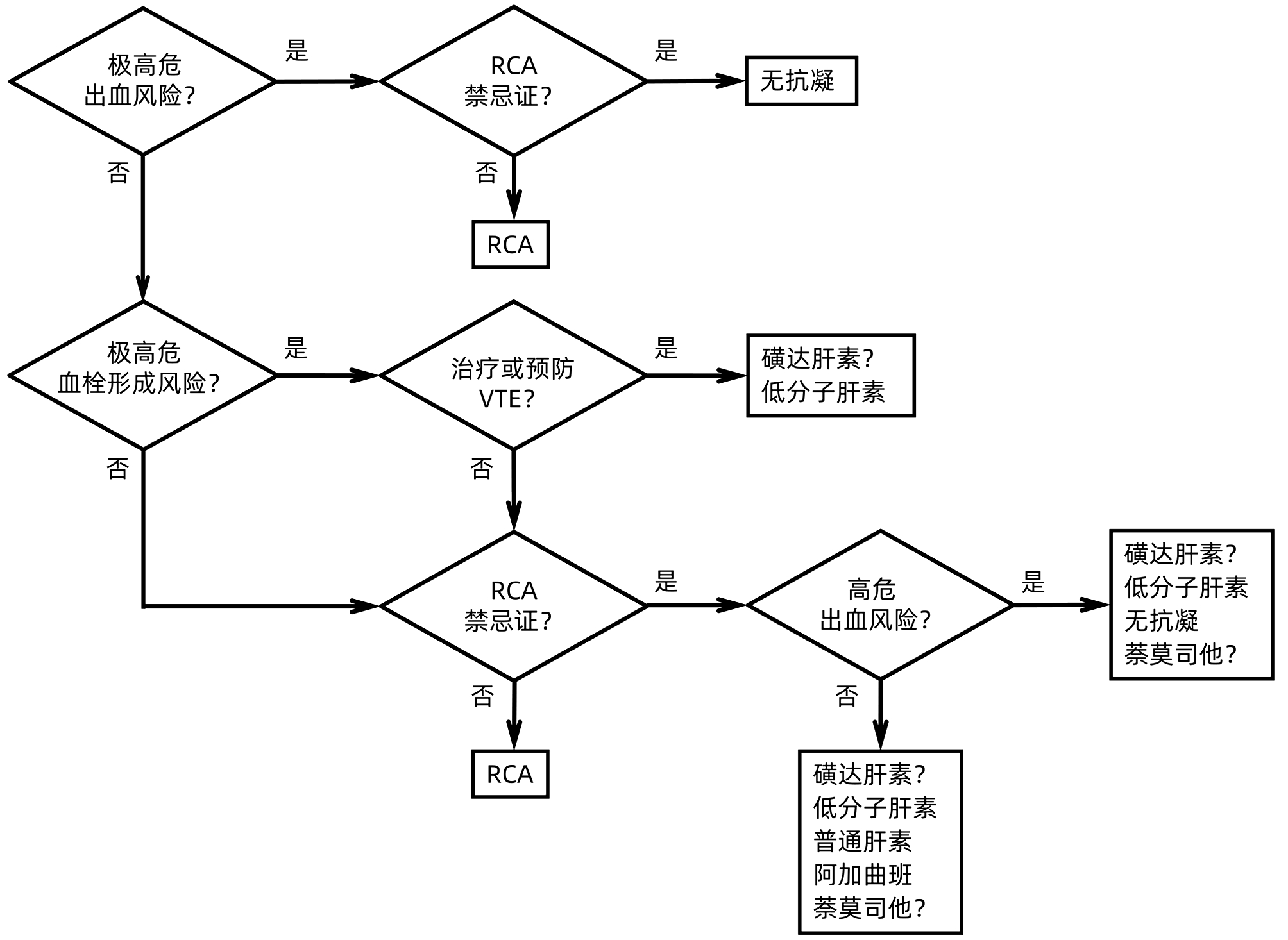
| [1] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [2] |
LAN XQ, JI YL, CHEN JJ, et al. Effect of artificial liver support therapy on the short-term prognosis of patients with liver failure in the plateau stage: A stratified analysis based on Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(9): 2005-2009. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.09.019. |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
MA YJ, BAI L, TANG H. Research progress of the application of regional citrate anticoagulation in artificial liver to treat liver failure[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2020, 28(6): 532-535. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200509-00238. |
| [5] |
MA Y, CHEN F, XU Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of regional citrate anticoagulation during plasma adsorption plus plasma exchange therapy for patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: a pilot study[J]. Blood Purif, 2019, 48(3): 223-232. DOI: 10.1159/000500408. |
| [6] |
ZOU PF, TU MM, DAI XH, et al. Comparison of anticoagulation efficacy and safety between small dose argatroban and low molecular weight heparin applied in Li's artificial liver support system[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2019, 12(3): 201-205. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2019.03.008. |
| [7] |
YUAN S, QIAN Y, TAN D, et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange: A prospective randomized trial to evaluate 2 strategies in patients with liver failure[J]. Transfus Apher Sci, 2018, 57(2): 253-258. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2018.02.001. |
| [8] |
KONG M, LI S, GENG H, et al. Influencing factors of heparin anticoagulant effect in the treatment of double plasma molecular adsorption system[J]. J Capit Med Univ, 2021, 42(4): 647-652. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2021.04.022. |
| [9] |
NIU RZ, XIANG DD, WANG YM, et al. Effects of different anticoagulants on blood coagulation during treatment of severe hepatitis with artificial liver[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2003, 23(10): 593-595. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2194.2003.10.009. |
| [10] |
PANG YL, LI LS, ZHANG ZP, et al. The clinical application of plasma exchange in the treatment with low molecular weight heparins of hepatitis gravis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2006, 22(5): 330-332. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2006.05.003. |
| [11] |
NILIUS H, KAUFMANN J, CUKER A, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of anticoagulants for the treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia[J]. Am J Hematol, 2021, 96(7): 805-815. DOI: 10.1002/ajh.26194. |
| [12] |
KELLUM JLAMEIRE NASPELIN P, et al. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury[J]. Kidney Int Suppl, 2012, 2(1): 1-138. DOI: 10.1038/kisup.2012.1 |
| [13] |
YE T, ZHAO WQ, ZHOU L, et al. Efficacy and safety of in vitro sodium citrate anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2020, 48(4): 415-416, 419. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2020.04.19. |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
SCHNEIDER AG, JOURNOIS D, RIMMELÉ T. Complications of regional citrate anticoagulation: accumulation or overload?[J]. Crit Care, 2017, 21(1): 281. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1880-1. |
| [16] |
KLINGELE M, STADLER T, FLISER D, et al. Long-term continuous renal replacement therapy and anticoagulation with citrate in critically ill patients with severe liver dysfunction[J]. Crit Care, 2017, 21(1): 294. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1870-3. |
| [17] |
ZHANG W, BAI M, YU Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy in liver failure patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Crit Care, 2019, 23(1): 22. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-019-2317-9. |
| [18] |
FAYBIK P, HETZ H, MITTERER G, et al. Regional citrate anticoagulation in patients with liver failure supported by a molecular adsorbent recirculating system[J]. Crit Care Med, 2011, 39(2): 273-279. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181fee8a4. |
| [19] |
MEIJERS B, LALEMAN W, VERMEERSCH P, et al. A prospective randomized open-label crossover trial of regional citrate anticoagulation vs. anticoagulation free liver dialysis by the Molecular Adsorbents Recirculating System[J]. Crit Care, 2012, 16(1): R20. DOI: 10.1186/cc11180. |
| [20] |
SENTVRK E, ESEN F, OZCAN PE, et al. The treatment of acute liver failure with fractionated plasma separation and adsorption system: Experience in 85 applications[J]. J Clin Apher, 2010, 25(4): 195-201. DOI: 10.1002/jca.20238.PMID:20818714. |
| [21] |
WANG M, MA Y, DU L, et al. Association between longer duration of citrate accumulation and 90-day mortality of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Crit Care, 2021, 25(1): 387. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03819-8. |
| [22] |
SCHNEIDER AG, JOANNES-BOYAU O. Regional citrate anticoagulation for CRRT: Still hesitating?[J]. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med, 2021, 40(2): 100855. DOI: 10.1016/j.accpm.2021.100855. |
| [23] |
JOANNES-BOYAU O, VELLY L, ICHAI C. Optimizing continuous renal replacement therapy in the ICU: a team strategy[J]. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2018, 24(6): 476-482. DOI: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000564. |
| [24] |
van COTT EM, ROBERTS AJ, DAGER WE. Laboratory monitoring of parenteral direct thrombin inhibitors[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2017, 43(3): 270-276. DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1597297. |
| [25] |
YARBROUGH PM, VAREDI A, WALKER A, et al. Argatroban dose reductions for suspected heparin-induced thrombocytopenia complicated by child-pugh class C liver disease[J]. Ann Pharmacother, 2012, 46(11): e30. DOI: 10.1345/aph.1R226. |
| [26] |
KITAMURA N, ZHANG L. Nafamostat mesilate in anticoagulation of continuous renal replacement therapy[J]. West China Med J, 2018, 33(7): 801-805. DOI: 10.7507/1002-0179.201806036. |
| [27] |
MAKINO S, EGI M, KITA H, et al. Comparison of nafamostat mesilate and unfractionated heparin as anticoagulants during continuous renal replacement therapy[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2016, 39(1): 16-21. DOI: 10.5301/ijao.5000465. |
| [28] |
SWARTZ RD, PORT FK. Preventing hemorrhage in high-risk hemodialysis: regional versus low-dose heparin[J]. Kidney Int, 1979, 16(4): 513-518. DOI: 10.1038/ki.1979.157. |
| [29] |
BAHL V, HU HM, HENKE PK, et al. A validation study of a retrospective venous thromboembolism risk scoring method[J]. Ann Surg, 2010, 251(2): 344-350. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b7fca6. |
| [30] |
TRITSCHLER T, KRAAIJPOEL N, LE GAL G, et al. Venous thromboembolism: Advances in diagnosis and treatment[J]. JAMA, 2018, 320(15): 1583-1594. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.14346. |
| [31] |
GOLEMI I, SALAZAR ADUM JP, TAFUR A, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis using the Caprini score[J]. Dis Mon, 2019, 65(8): 249-298. DOI: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2018.12.005. |
| [32] |
ALBERTSEN IE, GOLDHABER SZ, PIAZZA G, et al. Predictors of not initiating anticoagulation after incident venous thromboembolism: A Danish nationwide cohort study[J]. Am J Med, 2020, 133(4): 463-472. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.08.051. |
| [33] |
LYU BY, LI Q. Strategies in the evaluation of coagulation status in patients with liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(4): 928-931. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.049. |
| [34] |
Expert Consensus Group on Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Hemorrhagic Coagulation Disorders. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of acute hemorrhagic coagulation disorders[J]. Chin J Emerg Med, 2020, 29(6): 780-787. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2020.06.007. |
| [35] |
LISMAN T, HERNANDEZ-GEA V, MAGNUSSON M, et al. The concept of rebalanced hemostasis in patients with liver disease: Communication from the ISTH SSC working group on hemostatic management of patients with liver disease[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2021, 19(4): 1116-1122. DOI: 10.1111/jth.15239. |
| [36] |
STRAVITZ RT. Algorithms for managing coagulation disorders in liver disease[J]. Hepatol Int, 2018, 12(5): 390-401. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-018-9886-6. |
| [37] |
SCHARF RE. Thrombocytopenia and hemostatic changes in acute and chronic liver disease: pathophysiology, clinical and laboratory features, and management[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(7): 1530. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10071530. |
| [38] |
TAPPER EB, ROBSON SC, MALIK R. Coagulopathy in cirrhosis-the role of the platelet in hemostasis[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59(4): 889-890. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.040. |
| [39] |
LI XR, MA YJ, BAI L, et al. Recent advances in simple plasma exchange therapy with regional citrate anticoagulation[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 14(6): 475-480. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2021.06.013. |
| [40] |
XU Y, CHEN F, WANG Y, et al. Nursing care of patients with liver failure undergoing plasma adsorption plus sequential plasma exchange artificial liver model therapy combined with regional citrate anticoagulation[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Intensive Crit Care, 2019, 26(6): 685-687. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2019.06.012. |
| [41] |
|








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: