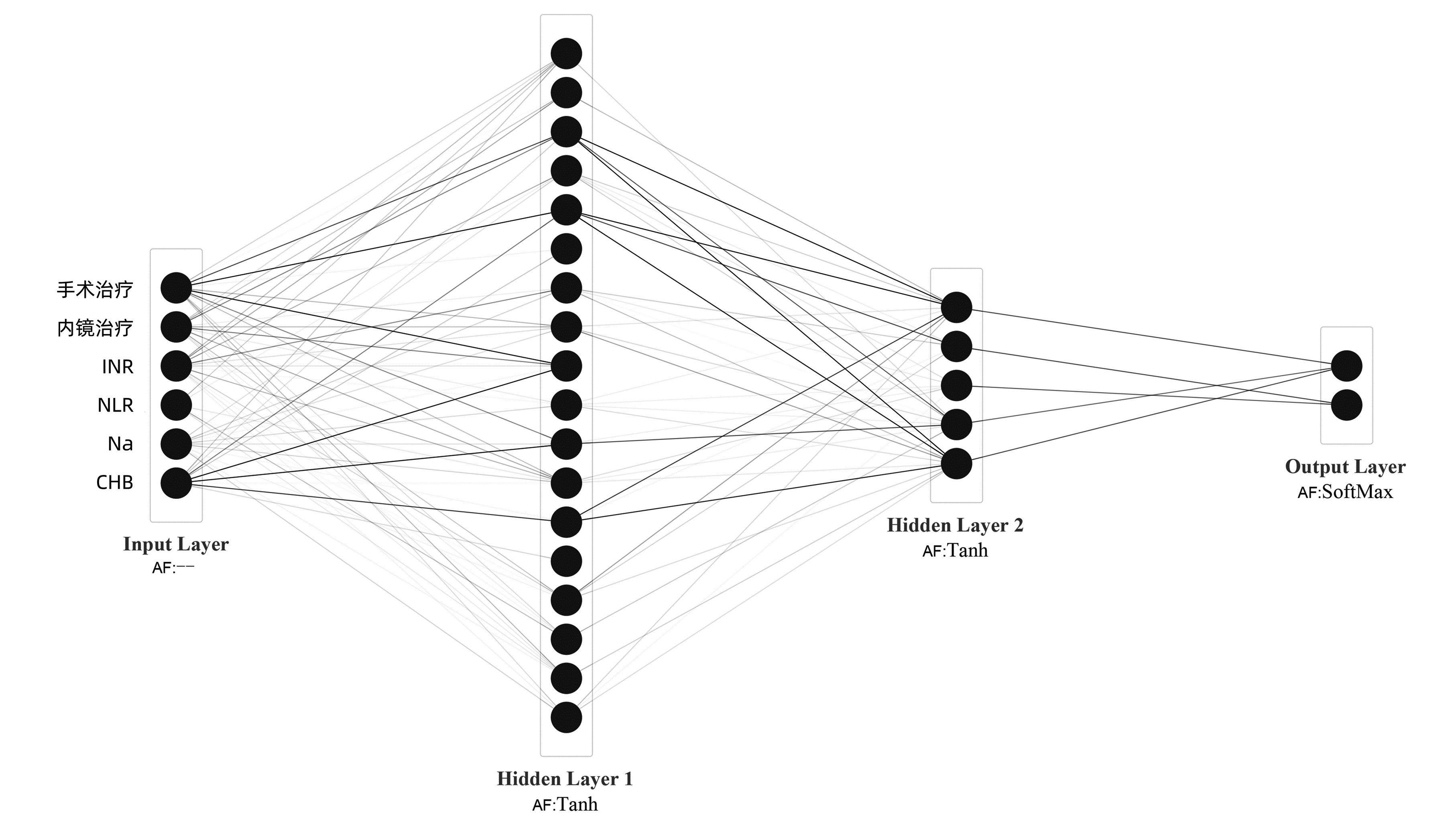
| [1] |
HOLSTER IL, TJWA ET, MOELKER A, et al. Covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic therapy+β-blocker for prevention of variceal rebleeding[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63(2): 581-589. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28318. |
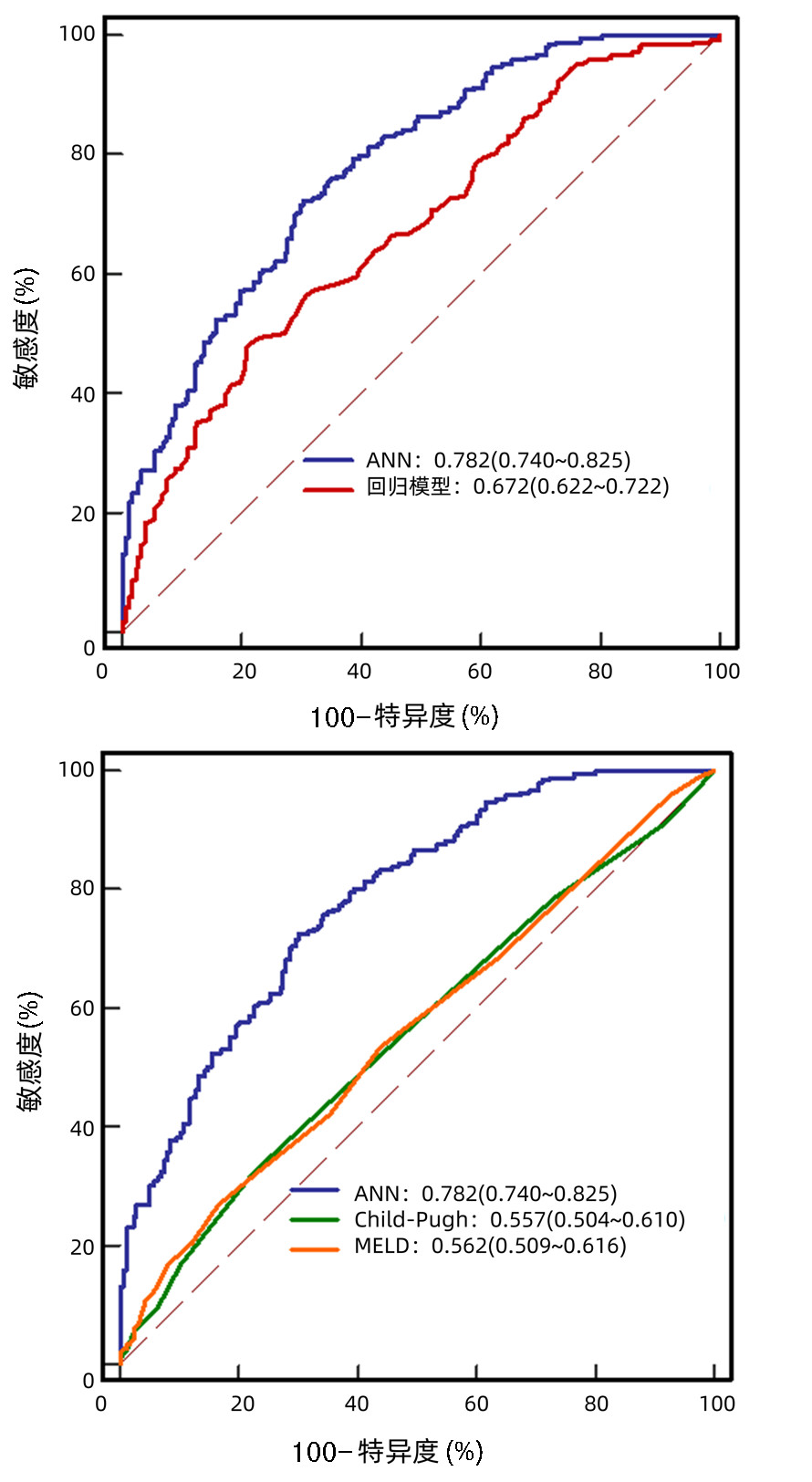
| [2] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Endoscopy, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002. |
| [3] |
VERDA D, PARODI S, FERRARI E, et al. Analyzing gene expression data for pediatric and adult cancer diagnosis using logic learning machine and standard supervised methods[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2019, 20(Suppl 9): 390. DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-2953-8. |
| [4] |
CHI S, TIAN Y, WANG F, et al. A novel lifelong machine learning-based method to eliminate calibration drift in clinical prediction models[J]. Artif Intell Med, 2022, 125: 102256. DOI: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102256. |
| [5] |
GARCIA-TSAO G, SANYAL AJ, GRACE ND, et al. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 46(3): 922-938. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21907. |
| [6] |
PUGH RN, MURRAY-LYON IM, DAWSON JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices[J]. Br J Surg, 1973, 60(8): 646-649. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. |
| [7] |
FONG TV, HUNG FC, CHIU KW, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score for predicting late esophageal varices rebleeding in cirrhotic patients[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2008, 55(84): 1055-1058.
|
| [8] |
DING RH, HU YM, LI XG, et al. Current status of prevention and treatment of esophagogastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension patients in Ningxia region: a multicenter study[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(10): 1078-1084. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210928-00464. |
| [9] |
DENG SM, ZHANG JX, QI Y, et al. Study on the application of endoscopic ligation in esophageal varices and the risk factors of postoperative rebleeding[J]. Chin J Med Offic, 2021, 49(6): 718-720. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2021.06.43. |
| [10] |
HAO Y, TAN P, ZHAO YG, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis in gastroesophageal variceal bleeding: A prospective study[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2012, 15(1): 29-31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2012.01.010. |
| [11] |
YANG H, LIU YX, LI P, et al. Analysis of risk factors for early rebleeding from esophageal and gastric varices in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2014, 30(6): 540-542. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2014.06.18. |
| [12] |
LIU X, HE L, HAN J, et al. Association of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and T lymphocytes with the pathogenesis and progression of HBV-associated primary liver cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0170605. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170605. |
| [13] |
PLEVRIS JN, DHARIWAL A, ELTON RA, et al. The platelet count as a predictor of variceal hemorrhage in primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1995, 90(6): 959-961.
|
| [14] |
CHEN LH, HU NZ, WANG YL. The value of MESO (MELD/Na index) scoring system in predicting prognosis of patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2011, 27(10): 1044-1046, 1054. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2011.10.008. 陈丽红, 胡乃中, 王亚雷. 终末期肝病模型与血清钠比值在肝硬化患者预后判断中的价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2011, 27(10): 1044-1046, 1054. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2011. 10.008.
|
| [15] |
HONG JB, LYU NH, WANG AJ, et al. Analysis of the risk factors for early rebleeding in oesophageal and gastric varices[J]. Chin J Dig, 2010, 30(11): 836-837. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2010.11.013. |
| [16] |
HUO TI, LIN HC, WU JC, et al. Proposal of a modified Child-Turcotte-Pugh scoring system and comparison with the model for end-stage liver disease for outcome prediction in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Liver Transpl, 2006, 12(1): 65-71. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20560. |
| [17] |
KAMATH PS, WIESNER RH, MALINCHOC M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 33(2): 464-470. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2001.22172. |
| [18] |
HEUMAN DM, ABOU-ASSI SG, HABIB A, et al. Persistent ascites and low serum sodium identify patients with cirrhosis and low MELD scores who are at high risk for early death[J]. Hepatology, 2004, 40(4): 802-810. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20405. |
| [19] |
ANGELI P, WONG F, WATSON H, et al. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Results of a patient population survey[J]. Hepatology, 2006, 44(6): 1535-1542. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21412. |









 本站查看
本站查看





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: