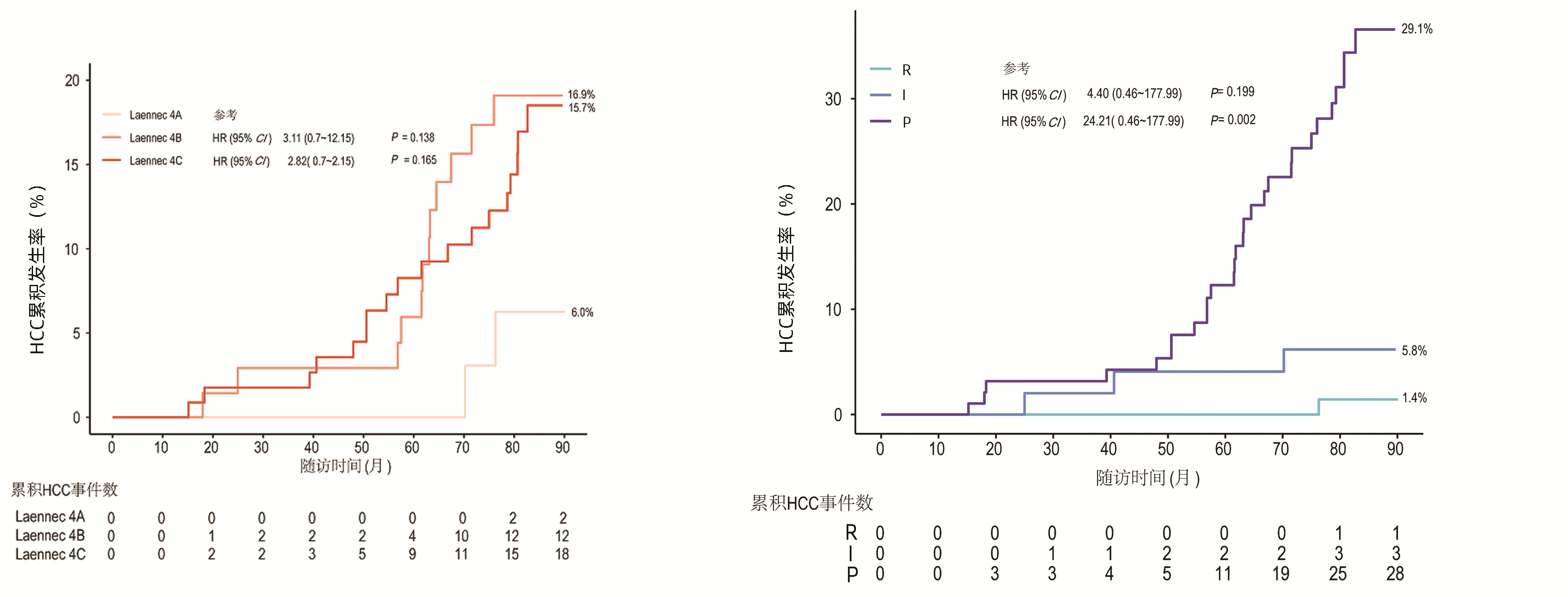
| [1] |
D'AMICO G, MORABITO A, D'AMICO M, et al. Clinical states of cirrhosis and competing risks[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(3): 563-576. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.10.020. |
| [2] |
HYTIROGLOU P, THEISE ND. Regression of human cirrhosis: an update, 18 years after the pioneering article by Wanless et al[J]. Virchows Arch, 2018, 473(1): 15-22. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-018-2340-2. |
| [3] |
CHANG TT, LIAW YF, WU SS, et al. Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 52(3): 886-893. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23785. |
| [4] |
SCHIFF ER, LEE SS, CHAO YC, et al. Long-term treatment with entecavir induces reversal of advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 9(3): 274-276. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.11.040. |
| [5] |
RAMACHANDRAN P, IREDALE JP, FALLOWFIELD JA. Resolution of liver fibrosis: basic mechanisms and clinical relevance[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2015, 35(2): 119-131. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1550057. |
| [6] |
SINGAL AG, LIM JK, KANWAL F. AGA clinical practice update on interaction between oral direct-acting antivirals for chronic hepatitis C infection and hepatocellular carcinoma: Expert review[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(8): 2149-2157. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.046. |
| [7] |
ROCKEY DC, CALDWELL SH, GOODMAN ZD, et al. Liver biopsy[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 49(3): 1017-1044. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22742. |
| [8] |
KNODELL RG, ISHAK KG, BLACK WC, et al. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 1981, 1(5): 431-435. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840010511. |
| [9] |
BATTS KP. Acute and chronic hepatic allograft rejection: pathology and classification[J]. Liver Transpl Surg, 1999, 5(4 Suppl 1): S21-S29. DOI: 10.1053/JTLS005s00021. |
| [10] |
SCHEUER PJ. Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: a need for reassessment[J]. J Hepatol, 1991, 13(3): 372-374. DOI: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90084-o. |
| [11] |
LUDWIG J. The nomenclature of chronic active hepatitis: an obituary[J]. Gastroenterology, 1993, 105(1): 274-278. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90037-d. |
| [12] |
WANG W, LI J, PAN R, et al. Association of the Laennec staging system with degree of cirrhosis, clinical stage and liver function[J]. Hepatol Int, 2015, 9(4): 621-626. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-015-9648-7. |
| [13] |
KIM MY, CHO MY, BAIK SK, et al. Histological subclassification of cirrhosis using the Laennec fibrosis scoring system correlates with clinical stage and grade of portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 55(5): 1004-1009. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.02.012. |
| [14] |
KIM SU, OH HJ, WANLESS IR, et al. The Laennec staging system for histological sub-classification of cirrhosis is useful for stratification of prognosis in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 57(3): 556-563. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.04.029. |
| [15] |
SUN Y, ZHOU J, WANG L, et al. New classification of liver biopsy assessment for fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients before and after treatment[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(5): 1438-1450. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29009. |
| [16] |
RONG G, CHEN Y, YU Z, et al. Synergistic effect of biejia-ruangan on fibrosis regression in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. J Infect Dis, 2022, 225(6): 1091-1099. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa266. |
| [17] |
JI D, CHEN Y, BI J, et al. Entecavir plus Biejia-Ruangan compound reduces the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77(6): 1515-1524. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.018. |
| [18] |
FATTOVICH G, STROFFOLINI T, ZAGNI I, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors[J]. Gastroenterology, 2004, 127(5 Suppl 1): S35-S50. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.09.014. |
| [19] |
NAGULA S, JAIN D, GROSZMANN RJ, et al. Histological-hemodynamic correlation in cirrhosis-a histological classification of the severity of cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2006, 44(1): 111-117. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.07.036. |
| [20] |
SETHASINE S, JAIN D, GROSZMANN RJ, et al. Quantitative histological-hemodynamic correlations in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55(4): 1146-1153. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24805. |
| [21] |
ZIPPRICH A, GARCIA-TSAO G, ROGOWSKI S, et al. Prognostic indicators of survival in patients with compensated and decompensated cirrhosis[J]. Liver Int, 2012, 32(9): 1407-1414. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02830.x. |
| [22] |
RIPOLL C, BAÑARES R, RINCÓN D, et al. Influence of hepatic venous pressure gradient on the prediction of survival of patients with cirrhosis in the MELD Era[J]. Hepatology, 2005, 42(4): 793-801. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20871. |
| [23] |
JAIN D, SREENIVASAN P, INAYAT I, et al. Thick fibrous septa on liver biopsy specimens predict the development of decompensation in patients with compensated cirrhosis[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2021, 156(5): 802-809. DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/aqab024. |
| [24] |
WANLESS IR, NAKASHIMA E, SHERMAN M. Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2000, 124(11): 1599-1607. DOI: 10.5858/2000-124-1599-ROHC. |
| [25] |
HE ZY, WANG BQ, YOU H. Clinical application of quantitative assessment of liver fibrosis based on pathology and imaging technology[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 35(1): 20-23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.01.003. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: