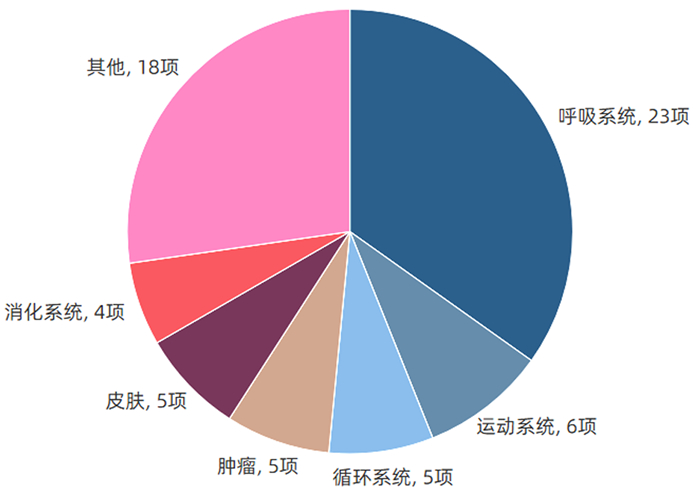
| [1] |
BARTUNEK J, BEHFAR A, DOLATABADI D, et al. Cardiopoietic stem cell therapy in heart failure: the C-CURE (Cardiopoietic stem Cell therapy in heart failURE) multicenter randomized trial with lineage-specified biologics[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013, 61(23): 2329-2338. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.02.071. |
| [2] |
SILVA JD, LOPES-PACHECO M, PAZ A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and lung tissue differentially mitigate lung and distal organ damage in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Crit Care Med, 2018, 46(2): e132-e140. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002833. |
| [3] |
SUK KT, YOON JH, KIM MY, et al. Transplantation with autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for alcoholic cirrhosis: Phase 2 trial[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(6): 2185-2197. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28693. |
| [4] |
JAIBAJI M, JAIBAJI R, VOLPIN A. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of cartilage defects of the knee: A systematic review of the clinical outcomes[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2021, 49(13): 3716-3727. DOI: 10.1177/0363546520986812. |
| [5] |
CHRIST B, BRVCKNER S, WINKLER S. The Therapeutic promise of mesenchymal stem cells for liver restoration[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2015, 21(11): 673-686. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2015.09.004. |
| [6] |
KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6478): eaau6977. DOI: 10.1126/science.aau6977. |
| [7] |
PAN BT, JOHNSTONE RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor[J]. Cell, 1983, 33(3): 967-978. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90040-5. |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
RANI S, RYAN AE, GRIFFIN MD, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Toward cell-free therapeutic applications[J]. Mol Ther, 2015, 23(5): 812-823. DOI: 10.1038/mt.2015.44. |
| [10] |
THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines[J]. J Extracell Vesicles, 2018, 7(1): 1535750. DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. |
| [11] |
MELDOLESI J. Exosomes and ectosomes in intercellular communication[J]. Curr Biol, 2018, 28(8): R435-R444. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.059. |
| [12] |
TSUCHIYA A, KOJIMA Y, IKARASHI S, et al. Clinical trials using mesenchymal stem cells in liver diseases and inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Inflamm Regen, 2017, 37: 16. DOI: 10.1186/s41232-017-0045-6. |
| [13] |
BORRELLI DA, YANKSON K, SHUKLA N, et al. Extracellular vesicle therapeutics for liver disease[J]. J Control Release, 2018, 273: 86-98. DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.01.022. |
| [14] |
RONG X, LIU J, YAO X, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10(1): 98. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1204-2. |
| [15] |
WATANABE T, TSUCHIYA A, TAKEUCHI S, et al. Development of a non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model with rapid accumulation of fibrosis, and its treatment using mesenchymal stem cells and their small extracellular vesicles[J]. Regen Ther, 2020, 14: 252-261. DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2020.03.012. |
| [16] |
TAKEUCHI S, TSUCHIYA A, IWASAWA T, et al. Small extracellular vesicles derived from interferon-γ pre-conditioned mesenchymal stromal cells effectively treat liver fibrosis[J]. NPJ Regen Med, 2021, 6(1): 19. DOI: 10.1038/s41536-021-00132-4. |
| [17] |
ZITO G, MICELI V, CARCIONE C, et al. Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells pre-conditioning inhibits inflammation and apoptosis of immune and parenchymal cells in an in vitro model of liver ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(4): 709. DOI: 10.3390/cells11040709. |
| [18] |
LIU Y, LOU G, LI A, et al. AMSC-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure by miR-17-mediated reduction of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 36: 140-150. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.08.054. |
| [19] |
SHAO M, XU Q, WU Z, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate IL-6-induced acute liver injury through miR-455-3p[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 37. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-1550-0. |
| [20] |
FAN Y, HERR F, VERNOCHET A, et al. Human fetal liver mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes impair natural killer cell function[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2019, 28(1): 44-55. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2018.0015. |
| [21] |
GUO L, LAI P, WANG Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells prevent skin fibrosis in the cGVHD mouse model by suppressing the activation of macrophages and B cells immune response[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 84: 106541. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106541. |
| [22] |
LEE SC, JEONG HJ, LEE SK, et al. Hypoxic conditioned medium from human adipose-derived stem cells promotes mouse liver regeneration through JAK/STAT3 signaling[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2016, 5(6): 816-825. DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0191. |
| [23] |
TAN CY, LAI RC, WONG W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote hepatic regeneration in drug-induced liver injury models[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2014, 5(3): 76. DOI: 10.1186/scrt465. |
| [24] |
YAN Y, JIANG W, TAN Y, et al. hucMSC exosome-derived GPX1 is required for the recovery of hepatic oxidant injury[J]. Mol Ther, 2017, 25(2): 465-479. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.019. |
| [25] |
TEMNOV A, ROGOV K, ZHALIMOV V, et al. The effect of a mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium fraction on morphological characteristics of hepatocytes in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: a preliminary study[J]. Hepat Med, 2019, 11: 89-96. DOI: 10.2147/HMER.S196354. |
| [26] |
HONG HE, KIM OH, KWAK BJ, et al. Antioxidant action of hypoxic conditioned media from adipose-derived stem cells in the hepatic injury of expressing higher reactive oxygen species[J]. Ann Surg Treat Res, 2019, 97(4): 159-167. DOI: 10.4174/astr.2019.97.4.159. |
| [27] |
SUN C, SHI C, DUAN X, et al. Exosomal microRNA-618 derived from mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the progression of hepatic fibrosis by targeting Smad4[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(3): 5915-5927. DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2023799. |
| [28] |
ÁLVAREZ-VIEJO M. Mesenchymal stem cells from different sources and their derived exosomes: A pre-clinical perspective[J]. World J Stem Cells, 2020, 12(2): 100-109. DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.100. |
| [29] |
LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2017, 49(6): e346. DOI: 10.1038/emm.2017.63. |
| [30] |
PIRES AO, MENDES-PINHEIRO B, TEIXEIRA FG, et al. Unveiling the differences of secretome of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, adipose tissue-derived stem cells, and human umbilical cord perivascular cells: a proteomic analysis[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2016, 25(14): 1073-1083. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2016.0048. |
| [31] |
WANG ZG, HE ZY, LIANG S, et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 511. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-02032-8. |
| [32] |
ZHAO S, LIU Y, PU Z. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate D-GaIN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by activating autophagy in vitro[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2019, 13: 2887-2897. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S220190. |
| [33] |
HAGA H, YAN IK, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Extracellular vesicles from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve survival from lethal hepatic failure in mice[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2017, 6(4): 1262-1272. DOI: 10.1002/sctm.16-0226. |
| [34] |
RONG X, LIU J, YAO X, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10(1): 98. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1204-2. |
| [35] |
LU FB, CHEN DZ, CHEN L, et al. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice with bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying MicroRNA-223-3p[J]. Mol Cells, 2019, 42(12): 906-918. DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2019.2283. |
| [36] |
LIU Y, LOU G, LI A, et al. AMSC-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure by miR-17-mediated reduction of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 36: 140-150. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.08.054. |
| [37] |
JIN Y, WANG J, LI H, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs) improve survival rate of rats with acute liver failure by releasing lncRNA H19[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 34: 231-242. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.015. |
| [38] |
WU HY, ZHANG XC, JIA BB, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure through activating ERK and IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 147(1): 143-155. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphs.2021.06.008. |
| [39] |
CHEN L, XIANG B, WANG X, et al. Exosomes derived from human menstrual blood-derived stem cells alleviate fulminant hepatic failure[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2017, 8(1): 9. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-016-0453-6. |
| [40] |
ZHANG S, JIANG L, HU H, et al. Pretreatment of exosomes derived from hUCMSCs with TNF-α ameliorates acute liver failure by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 in macrophage[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 246: 117401. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117401. |
| [41] |
CHEN L, ZHANG J, YANG L, et al. The effects of conditioned medium derived from mesenchymal stem cells cocultured with hepatocytes on damaged hepatocytes and acute liver failure in rats[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2018, 2018: 9156560. DOI: 10.1155/2018/9156560. |
| [42] |
JIAO Y, LU W, XU P, et al. Hepatocyte-derived exosome may be as a biomarker of liver regeneration and prognostic valuation in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Hepatol Int, 2021, 15(4): 957-969. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-021-10217-3. |
| [43] |
MA L, WEI J, ZENG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal circDIDO1 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT pathway in human liver fibrosis[J]. Drug Deliv, 2022, 29(1): 440-453. DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2030428. |
| [44] |
BANG OY, KIM EH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle therapy for stroke: challenges and progress[J]. Front Neurol, 2019, 10: 211. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00211. |
| [45] |
EGGENHOFER E, BENSELER V, KROEMER A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells are short-lived and do not migrate beyond the lungs after intravenous infusion[J]. Front Immunol, 2012, 3: 297. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00297. |
| [46] |
VOLAREVIC V, MARKOVIC BS, GAZDIC M, et al. Ethical and safety issues of stem cell-based therapy[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2018, 15(1): 36-45. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.21666. |
| [47] |
LÖRINCZ ÁM, TIMÁR CI, MAROSVÁRI KA, et al. Effect of storage on physical and functional properties of extracellular vesicles derived from neutrophilic granulocytes[J]. J Extracell Vesicles, 2014, 3: 25465. DOI: 10.3402/jev.v3.25465. |
| [48] |
SHOKRAVI S, BORISOV V, ZAMAN BA, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and their exosome in acute liver failure (ALF): a comprehensive review[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13(1): 192. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02825-z. |
| [49] |
CHENG Y, ZENG Q, HAN Q, et al. Effect of pH, temperature and freezing-thawing on quantity changes and cellular uptake of exosomes[J]. Protein Cell, 2019, 10(4): 295-299. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-018-0529-4. |
| [50] |
WIKLANDER OP, NORDIN JZ, O'LOUGHLIN A, et al. Extracellular vesicle in vivo biodistribution is determined by cell source, route of administration and targeting[J]. J Extracell Vesicles, 2015, 4: 26316. DOI: 10.3402/jev.v4.26316. |



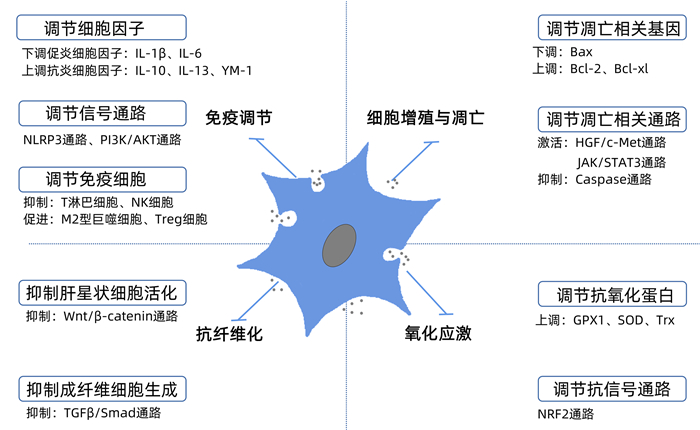




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: