| [1] |
SAMUEL D, COILLY A. Management of patients with liver diseases on the waiting list for transplantation: A major impact to the success of liver transplantation[J]. BMC Med, 2018, 16(1): 113. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-018-1110-y. |
| [2] |
BERTACCO A, BARBIERI S, GUASTALLA G, et al. Risk factors for mortality in liver transplant patients[J]. Transplant Proc, 2019, 51 (1): 179-183. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.06.025 |
| [3] |
AKAMATSU N, SUGAWARA Y, HASHIMOTO D. Biliary reconstruction, its complications and management of biliary complications after adult liver transplantation: A systematic review of the incidence, risk factors and outcome[J]. Transpl Int, 2011, 24(4): 379-392. DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2010.01202.x. |
| [4] |
FORDE JJ, BHAMIDIMARRI KR. Management of biliary complications in liver transplant recipients[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2022, 26(1): 81-99. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2021.08.008. |
| [5] |
HU XW, LI T. Diagnosis and treatment of common biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation in adults[J]. Organ Transplant, 2022, 13(5): 569-576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.05.004. |
| [6] |
KOCHHAR G, PARUNGAO JM, HANOUNEH IA, et al. Biliary complications following liver transplantation[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(19): 2841-2846. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2841. |
| [7] |
TRAN LT, CARULLO PC, BANH DPT, et al. Pediatric liver transplantation: Then and now[J]. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth, 2020, 34(8): 2028-2035. DOI: 10.1053/j.jvca.2020.02.019. |
| [8] |
GREIF F, BRONSTHER OL, VAN THIEL DH, et al. The incidence, timing, and management of biliary tract complications after orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. Ann Surg, 1994, 219(1): 40-45. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199401000-00007. |
| [9] |
TAI Q, HE XS, YANG JA, et al. The diagnosis and treatment of biliary complications in liver transplant patients[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2010, 25(12): 969-972. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2010.12.010. |
| [10] |
FANG C, YAN S, ZHENG SS. Influencing factors, diagnosis and treatment of biliary complications after liver transplantation[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2014, 29(6): 486-488. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2014.06.028. |
| [11] |
KALTENBORN A, GUTCKE A, GWIASDA J, et al. Biliary complications following liver transplantation: Single-center experience over three decades and recent risk factors[J]. World J Hepatol, 2017, 9(3): 147-154. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i3.147. |
| [12] |
SARHAN MD, OSMAN AMA, MOHAMED MA, et al. Biliary complications in recipients of living-donor liver transplant: A single-center review of 120 patients[J]. Exp Clin Transplant, 2017, 15(6): 648-657. DOI: 10.6002/ect.2016.0210. |
| [13] |
WIEDERKEHR JC, IGREJA MR, NOGARA MS, et al. Analysis of survival after primary liver transplantation: Multivariate analysis of 155 cases in a single center[J]. Transplant Proc, 2010, 42(2): 511-512. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.01.014. |
| [14] |
GIRARD E, RISSE O, ABBA J, et al. Internal biliary stenting in liver transplantation[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2018, 403(4): 487-494. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-018-1669-y. |
| [15] |
YOON JU, BYEON GJ, PARK JY, et al. Bloodless living donor liver transplantation: Risk factors, outcomes, and diagnostic predictors[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97(50): e13581. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013581. |
| [16] |
JACOB M, COPLEY LP, LEWSEY JD, et al. Pretransplant MELD score and post liver transplantation survival in the UK and Ireland[J]. Liver Transpl, 2004, 10(7): 903-907. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20169. |
| [17] |
ODEN-BRUNSON H, MCDONALD MF, GODFREY E, et al. Is liver transplant justified at any MELD score?[J]. Transplantation, 2023, 107(3): 680-692. DOI: 10.1097/tp.0000000000004345. |
| [18] |
LIU CC. Real-world study on SⅡ/ALB ratio to predict the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of malignant tumors[D]. Dalian: Dalian Medical University, 2021.
刘成成. SⅡ/ALB比值预测免疫检查点抑制剂治疗恶性肿瘤疗效真实世界研究[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2021.
|
| [19] |
LI HW, WANG GC, ZHANG HH, et al. Prognostic role of the systemic immune-inflammation index in brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with different EGFR mutations[J]. Genes Immun, 2019, 20(6): 455-461. DOI: 10.1038/s41435-018-0050-z. |
| [20] |
AN R, QIN C, WU Q, et al. Predictive value of systemic immune inflammation index (SⅡ)in the short-term prognosis of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50(11): 1129-1133. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.11.07. |
| [21] |
REN A, LI ZQ, CHENG PR, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index is a prognostic predictor in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma undergoing liver transplantation[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2021, 2021: 6656996. DOI: 10.1155/2021/6656996. |
| [22] |
FU HY, ZHENG J, CAI JY, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SⅡ) is useful to predict survival outcomes in patients after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma within Hangzhou criteria[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 47(1): 293-301. DOI: 10.1159/000489807. |
| [23] |
LICHTENEGGER P, SCHIEFER J, GRAF A, et al. The association of pre-operative anaemia with survival after orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. Anaesthesia, 2020, 75(4): 472-478. DOI: 10.1111/anae.14918. |
| [24] |
JÓŹWIK A, KARPETA E, NITA M, et al. Impact of blood loss and intraoperative blood transfusion during liver transplantation on the incidence of early biliary complications and mortality[J]. Transplant Proc, 2020, 52(8): 2477-2479. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.03.052. |
| [25] |
CHU HH, KIM JH, SHIM JH, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a biomarker predicting overall survival after chemoembolization for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(11): 2830. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112830. |
| [26] |
NYLEC M, DERBISZ K, CHRZ SZCZ P, et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent predictor of 1-year graft loss and mortality after orthotopic LiverTransplantation[J]. Transplant Proc, 2020, 52(8): 2472-2476. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.03.036. |
| [27] |
KWON HM, MOON YJ, JUNG KW, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a predictor of early graft dysfunction following living donor liver transplantation[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(8): 1545-1556. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14103. |
| [28] |
LUÉ A, SOLANAS E, BAPTISTA P, et al. How important is donor age in liver transplantation?[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(21): 4966-4976. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.4966. |
| [29] |
ZHANG QB, SHEN CH, TAO YF, et al. Risk factor analysis and classified therapeutic strategies for biliary complications after liver transplantation from organ donation by citizens after death: A report of 48 cases at a single center[J]. Chin J Organ Transplant, 2020, 41(10): 623-628. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn421203-20191115-00415. |



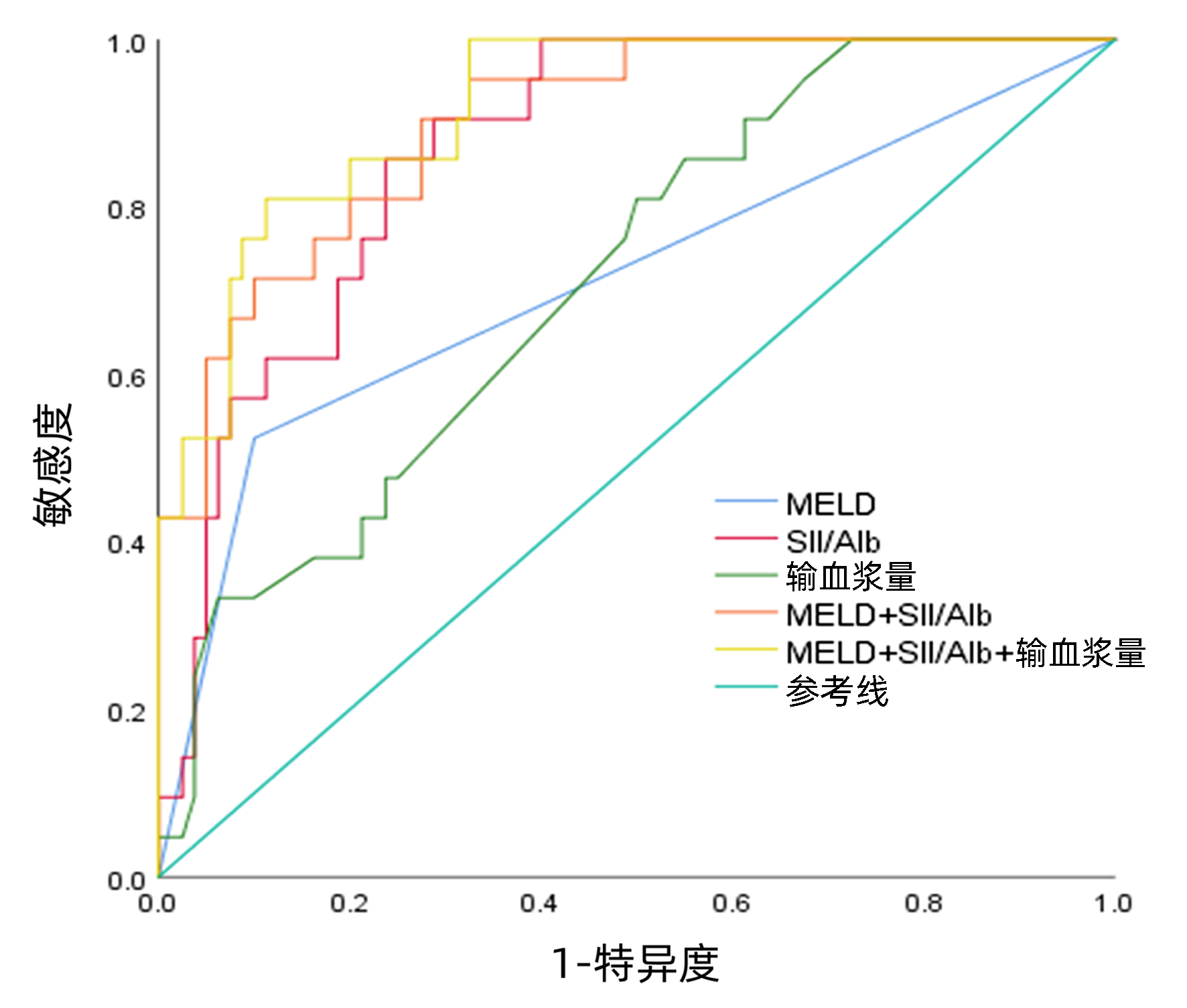




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: