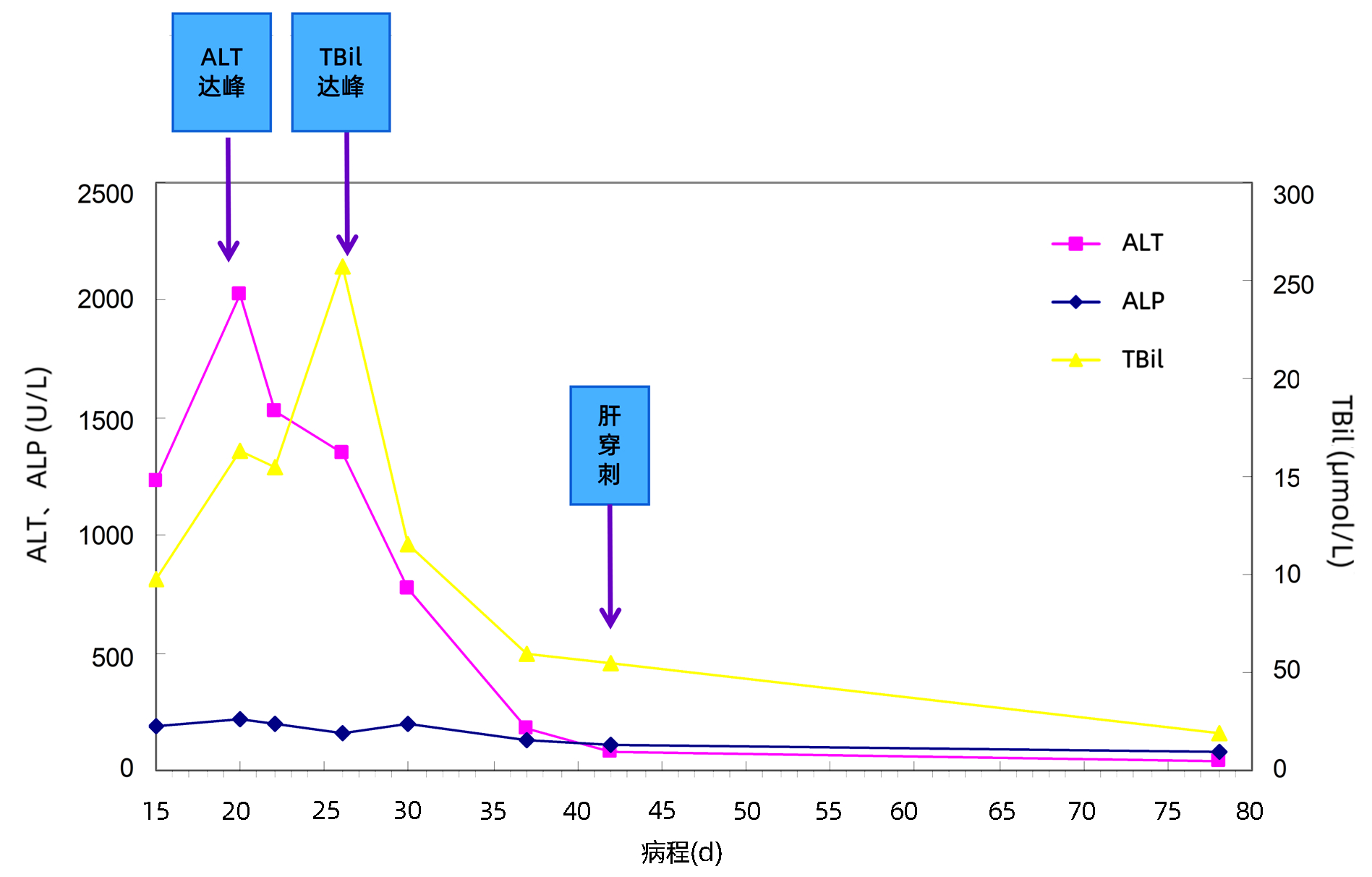
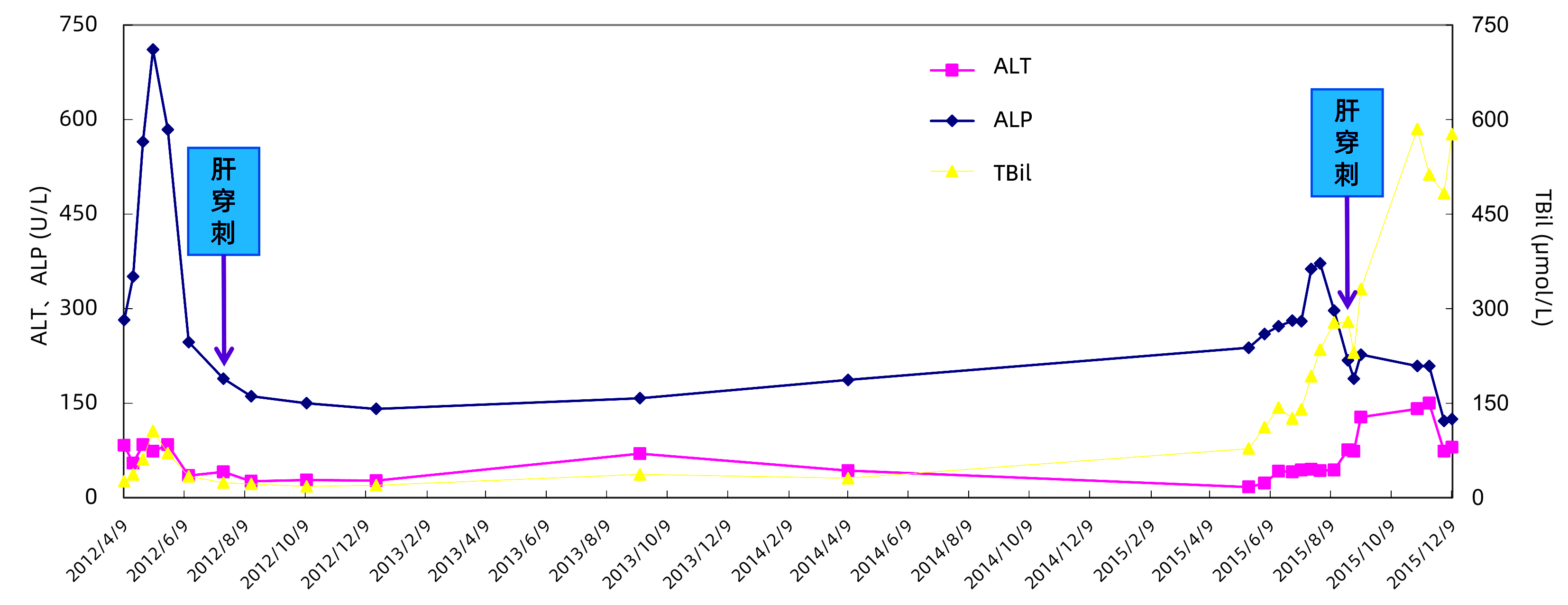
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
KLEINER DE, CHALASANI NP, LEE WM, et al. Hepatic histological findings in suspected drug-induced liver injury: Systematic evaluation and clinical associations[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59(2): 661-670. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26709. |
| [3] |
LEWIS JH, KLEINER DE. Hepatic injury due to drugs, herbal compounds, chemicals and toxins[M]// MacSween's Pathology of the Liver, 6th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2014: 654-655.
|
| [4] |
Drug-induced Liver Disease Study Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the management of drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(11): 1752-1769. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.11.002. |
| [5] |
Drug-induced Liver Disease Study Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Interpretation of CSH clinical guideline: The diagnosis and management of drug-induced liver injury[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2015.
中华医学会肝脏病学分会药物性肝病学组. 药物性肝损伤诊治指南解读[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2015.
|
| [6] |
VUPPALANCHI R, CHALASANI N, SAXENA R. Restoration of bile ducts in drug-induced vanishing bile duct syndrome due to zonisamide[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2006, 30(12): 1619-1623. DOI: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213342.78475.48. |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
WANG TL, ZHAO XY, SHAO C, et al. A proposed pathologic sub-classification of drug-induced liver injury[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13(3): 339-351. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09940-9. |
| [10] |
WASUWANICH P, CHOUDRY H, SO JM, et al. Vanishing bile duct syndrome after drug-induced liver injury[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2022, 46(9): 102015. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2022.102015. |
| [11] |
BELL LN, CHALASANI N. Epidemiology of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2009, 29(4): 337-347. DOI: 10.1055/s-0029-1240002. |
| [12] |
MEDINA-CALIZ I, ROBLES-DIAZ M, GARCIA-MUÑOZ B, et al. Definition and risk factors for chronicity following acute idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(3): 532-542. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.003. |
| [13] |
de VRIES E, BEUERS U. Management of cholestatic disease in 2017[J]. Liver Int, 2017, 37(Suppl 1): 123-129. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13306. |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
MANCO R, CLERBAUX LA, VERHULST S, et al. Reactive cholangiocytes differentiate into proliferative hepatocytes with efficient DNA repair in mice with chronic liver injury[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(6): 1180-1191. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.003. |
| [16] |
ZHU ZW, HUANG HL. Research progress on physiological characteristics of bile duct epithelial cells and their correlation with liver diseases[J]. J Hepatopancreatobiliary Surg, 2022, 34(3): 187-192. DOI: 10.11952/j.issn.1007-1954.2022.03.013. |
| [17] |
CHEUNG AC, LORENZO PISARELLO MJ, LARUSSO NF. Pathobiology of biliary epithelia[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864(4): 1220-1231. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.06.024. |
| [18] |
RAVEN A, LU WY, MAN TY, et al. Cholangiocytes act as facultative liver stem cells during impaired hepatocyte regeneration[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7663): 350-354. DOI: 10.1038/nature23015. |
| [19] |
CHALASANI NP, HAYASHI PH, BONKOVSKY HL, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: The diagnosis and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2014, 109(7): 950-966; quiz967. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2014.131. |



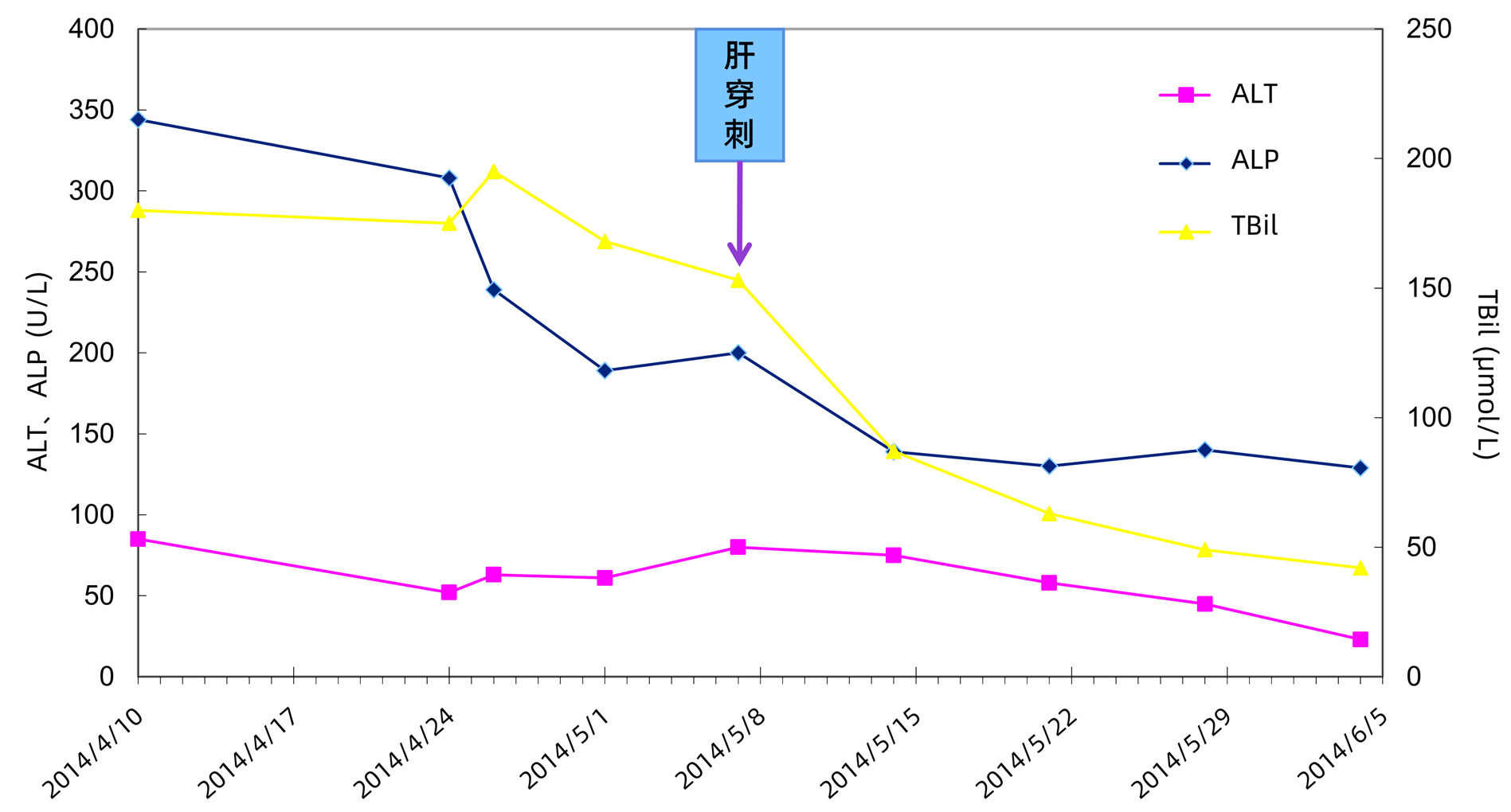




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: