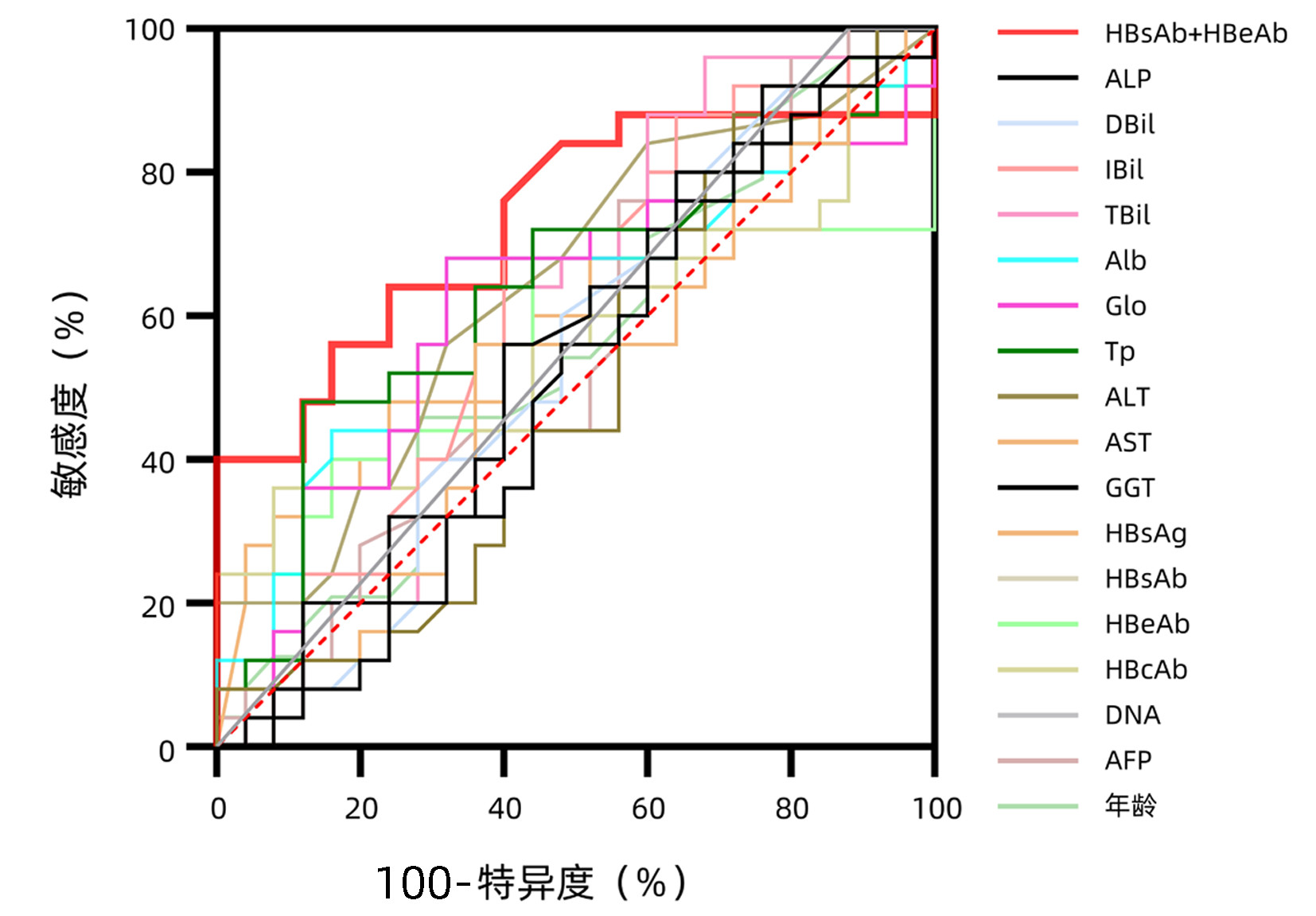
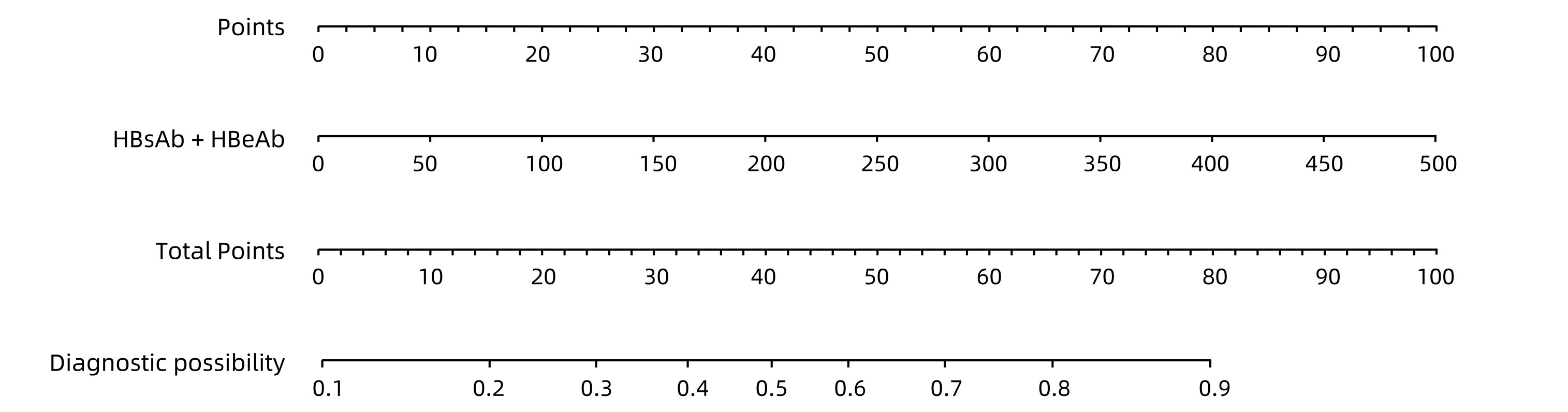
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [3] |
GU ZY, WANG AH, HE WC, et al. Influencing factors for HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(11): 2581-2585. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.029. |
| [4] |
YAO CC, LEE CM, HUNG CH, et al. Combining age and HBsAg level predicts post-treatment durability of nucleos(t)ide analogue-induced HBeAg seroconversion[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(5): 918-924. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12874. |
| [5] |
GISH RG, CHANG TT, LAI CL, et al. Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen analysis in hepatitis B e antigen-positive nucleoside-naive patients treated with entecavir[J]. Antivir Ther, 2013, 18(5): 691-698. DOI: 10.3851/IMP2559. |
| [6] |
ZOULIM F, CAROSI G, GREENBLOOM S, et al. Quantification of HBsAg in nucleos(t)ide-naïve patients treated for chronic hepatitis B with entecavir with or without tenofovir in the BE-LOW study[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62(1): 56-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.031. |
| [7] |
YANG SC, LU SN, LEE CM, et al. Combining the HBsAg decline and HBV DNA levels predicts clinical outcomes in patients with spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion[J]. Hepatol Int, 2013, 7(2): 489-499. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-012-9382-3. |
| [8] |
GENG MF, LI YX, GAO FY, et al. A scoring model predicts hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs: Real-world clinical practice[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2017, 62: 18-25. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2017.06.016. |
| [9] |
WANG Y, LIAO H, DENG Z, et al. Serum HBV RNA predicts HBeAg clearance and seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2022, 29(6): 420-431. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13671. |
| [10] |
WANG B, CAREY I, BRUCE M, et al. HBsAg and HBcrAg as predictors of HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2018, 25(8): 886-893. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12889. |
| [11] |
HUANG YJ, CHANG CS, PENG YC, et al. On-treatment HBV DNA level could predict HBeAg seroclearance in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B with entecavir therapy[J]. J Chin Med Assoc, 2017, 80(6): 341-346. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcma.2016.12.005. |
| [12] |
PENG CY, HSIEH TC, HSIEH TY, et al. HBV-DNA level at 6 months of entecavir treatment predicts HBeAg loss in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. J Formos Med Assoc, 2015, 114(4): 308-313. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfma.2013.10.023. |
| [13] |
JI X, XIA MY, ZHOU B, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA levels predict HBeAg seroconversion and virological response in chronic hepatitis B patients with high viral load treated with nucleos(t)ide analog[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2020, 13: 1881-1888. DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S252994. |
| [14] |
ZHANG M, LI GD, SHANG J, et al. Rapidly decreased HBV RNA predicts responses of pegylated interferons in HBeAg-positive patients: A longitudinal cohort study[J]. Hepatol Int, 2020, 14(2): 212-224. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-020-10015-3. |
| [15] |
WANG Y, LIAO H, DENG ZP, et al. Serum HBV RNA predicts HBeAg clearance and seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2022, 29(6): 420-431. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13671. |
| [16] |
LUO H, ZHANG XX, CAO LH, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is a predictor of HBeAg seroconversion and virological response with entecavir treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(6): 719-728. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i6.719. |
| [17] |
JIA W, ZHU MQ, QI X, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA levels as a predictor of HBeAg seroconversion during treatment with peginterferon alfa-2a[J]. Virol J, 2019, 16(1): 61. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-019-1152-6. |
| [18] |
ZHAO XG, WANG J, LIU JC, et al. Baseline serum hepatitis B core antibody level predicts HBeAg seroconversion in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B after antiviral treatment[J]. Antiviral Res, 2021, 193: 105146. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105146. |
| [19] |
WANG CT, ZHANG YF, SUN BH, et al. Models for predicting hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in response to interferon-α in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(18): 5668-5676. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5668. |
| [20] |
FAN R, SUN J, YUAN Q, et al. Baseline quantitative hepatitis B core antibody titre alone strongly predicts HBeAg seroconversion across chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon or nucleos(t)ide analogues[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(2): 313-320. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308546. |
| [21] |
CAI SH, LI ZD, YU T, et al. Serum hepatitis B core antibody levels predict HBeAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients with high viral load treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2018, 11: 469-477. DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S163038. |
| [22] |
FU XH, LOU HB, CHEN F, et al. Hepatitis B core antibody and liver stiffness measurements predict HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with minimally elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2020, 20(2): 241-248. DOI: 10.1007/s10238-019-00603-5. |
| [23] |
XU WZ, TONG YQ, LI Y. Comparison of Roche Elecsys and Sysmex HISCL immunoassays for the screening of common blood-borne pathogens[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2019, 7(14): 300. DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.05.83. |
| [24] |
WIJAYA RS, READ SA, TRUONG NR, et al. HBV vaccination and HBV infection induces HBV-specific natural killer cell memory[J]. Gut, 2021, 70(2): 357-369. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319252. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
KEENAN BP, FONG L, KELLEY RK. Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: The complex interface between inflammation, fibrosis, and the immune response[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2019, 7(1): 267. DOI: 10.1186/s40425-019-0749-z. |
| [27] |
CHEN T, ZHU L, SHI AC, et al. Functional restoration of CD56 bright NK cells facilitates immune control via IL-15 and NKG2D in patients under antiviral treatment for chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatol Int, 2017, 11(5): 419-428. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9803-4. |
| [28] |
HU X, MA S, HUANG X, et al. Interleukin-21 is upregulated in hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure and associated with severity of liver disease[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2011, 18(7): 458-467. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01475.x. |
| [29] |
YANG JZ, SHENG GP, XIAO DS, et al. The frequency and skewed T-cell receptor beta-chain variable patterns of peripheral CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T-cells are associated with hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion of chronic hepatitis B patients during antiviral treatment[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2016, 13(5): 678-687. DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2015.100. |
| [30] |
XIA J, HUANG R, CHEN YX, et al. Profiles of serum soluble programmed death-1 and programmed death-ligand 1 levels in chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients with different disease phases and after anti-viral treatment[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 51(11): 1180-1187. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15732. |
| [31] |
AN X, LIU SH, XIA LN, et al. Efficacy and clinical outcomes of different antiviral regimens in HBeAg/HBeAb double-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Army Med Univ, 2022, 44(2): 162-167. DOI: 10.16016/j.2097-0927.202107114. |
| [32] |
LUO L, ZHANG TC, LIU SG. Clinical characteristics of chronic hepatitis B patients with both HBeAg and HBeAb positive[J]. J Mol Diagn Ther, 2019, 11(5): 387-390, 433. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6929.2019.05.011. |
| [33] |
WANG H, WANG HP, QIAN LY, et al. Maternal breast feeding safety of hepatitis B virus carrying parturient women with hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen double positive[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2020, 38(1): 44-48. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2020.01.006. |
| [34] |
KAO JH, CHEN PJ, LAI MY, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotypes and spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in Taiwanese hepatitis B carriers[J]. J Med Virol, 2004, 72(3): 363-369. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.10534. |
| [35] |
SHIMAKAWA Y, LEMOINE M, NJAI HF, et al. Natural history of chronic HBV infection in West Africa: A longitudinal population-based study from The Gambia[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(12): 2007-2016. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309892. |
| [36] |
KRAMVIS A, KOSTAKI EG, HATZAKIS A, et al. Immunomodulatory function of HBeAg related to short-sighted evolution, transmissibility, and clinical manifestation of hepatitis B virus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9: 2521. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02521. |



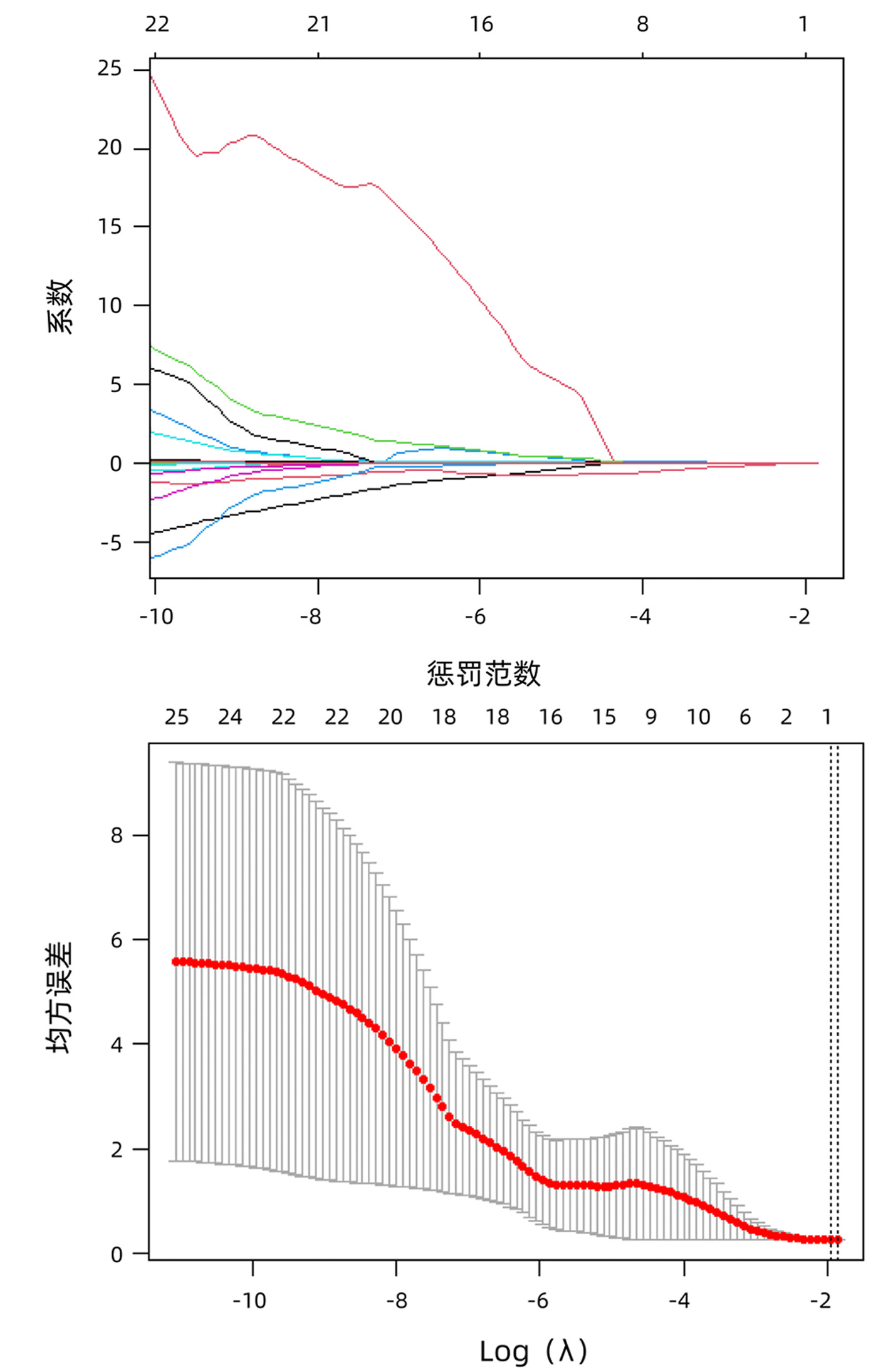




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: