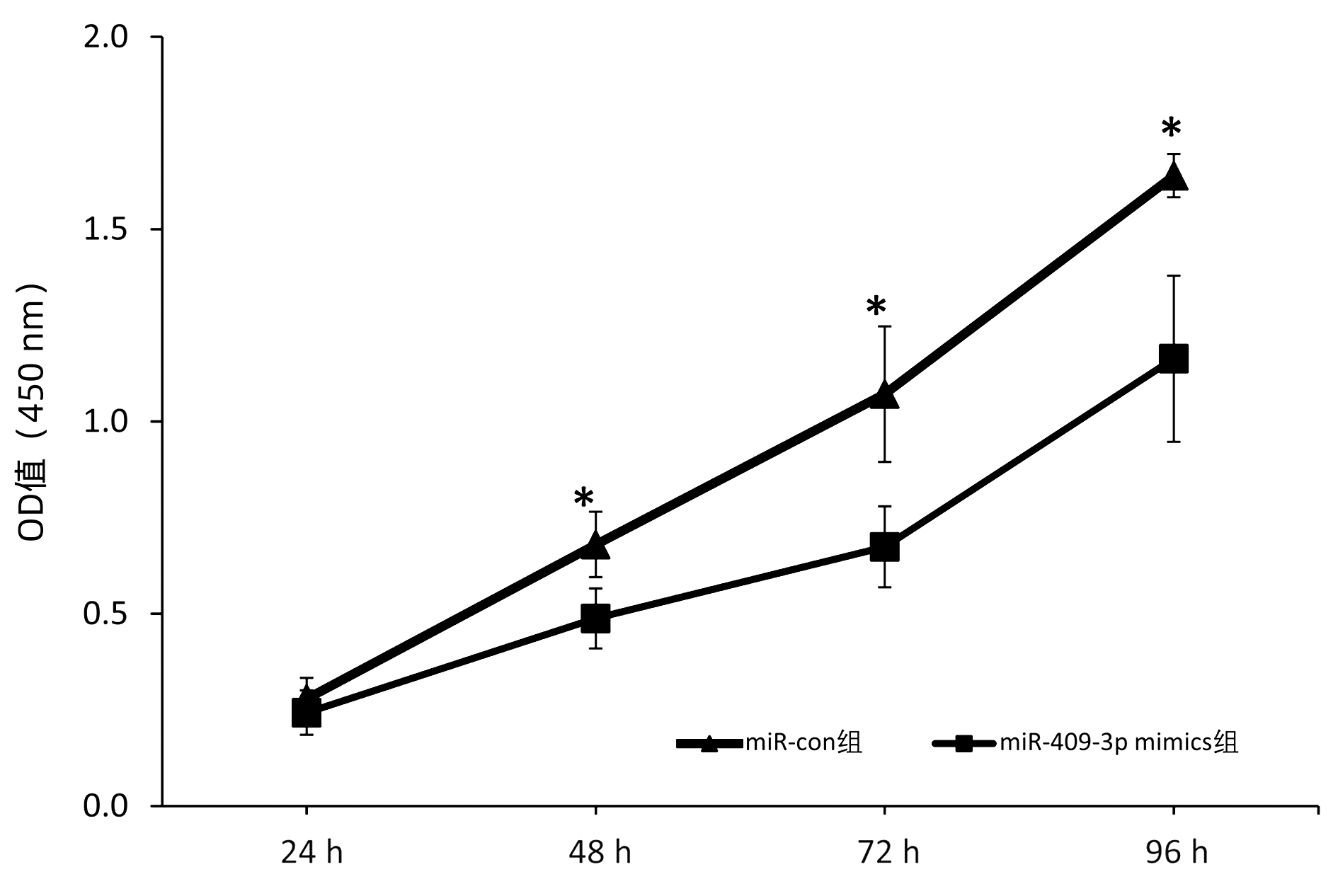
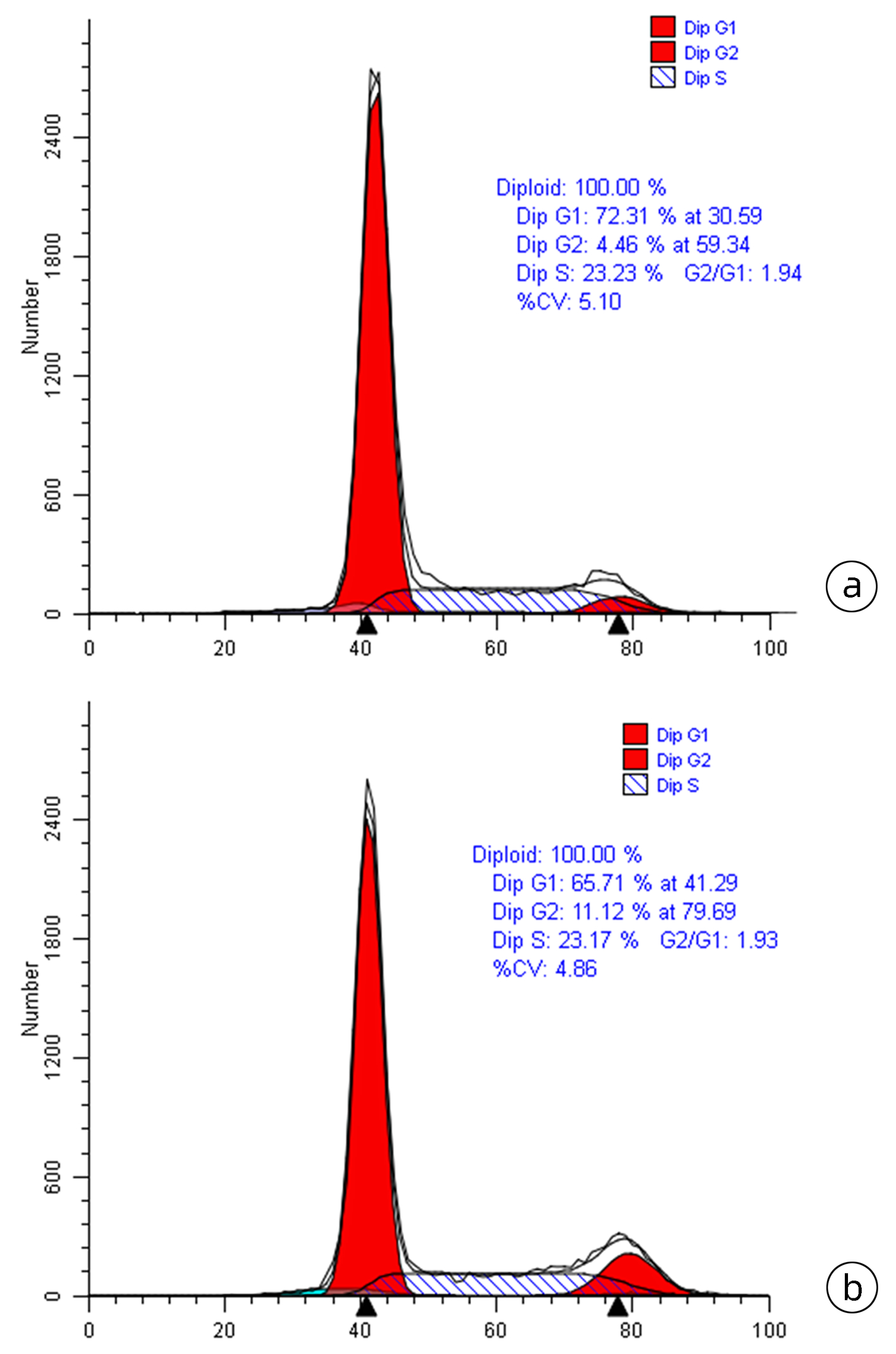
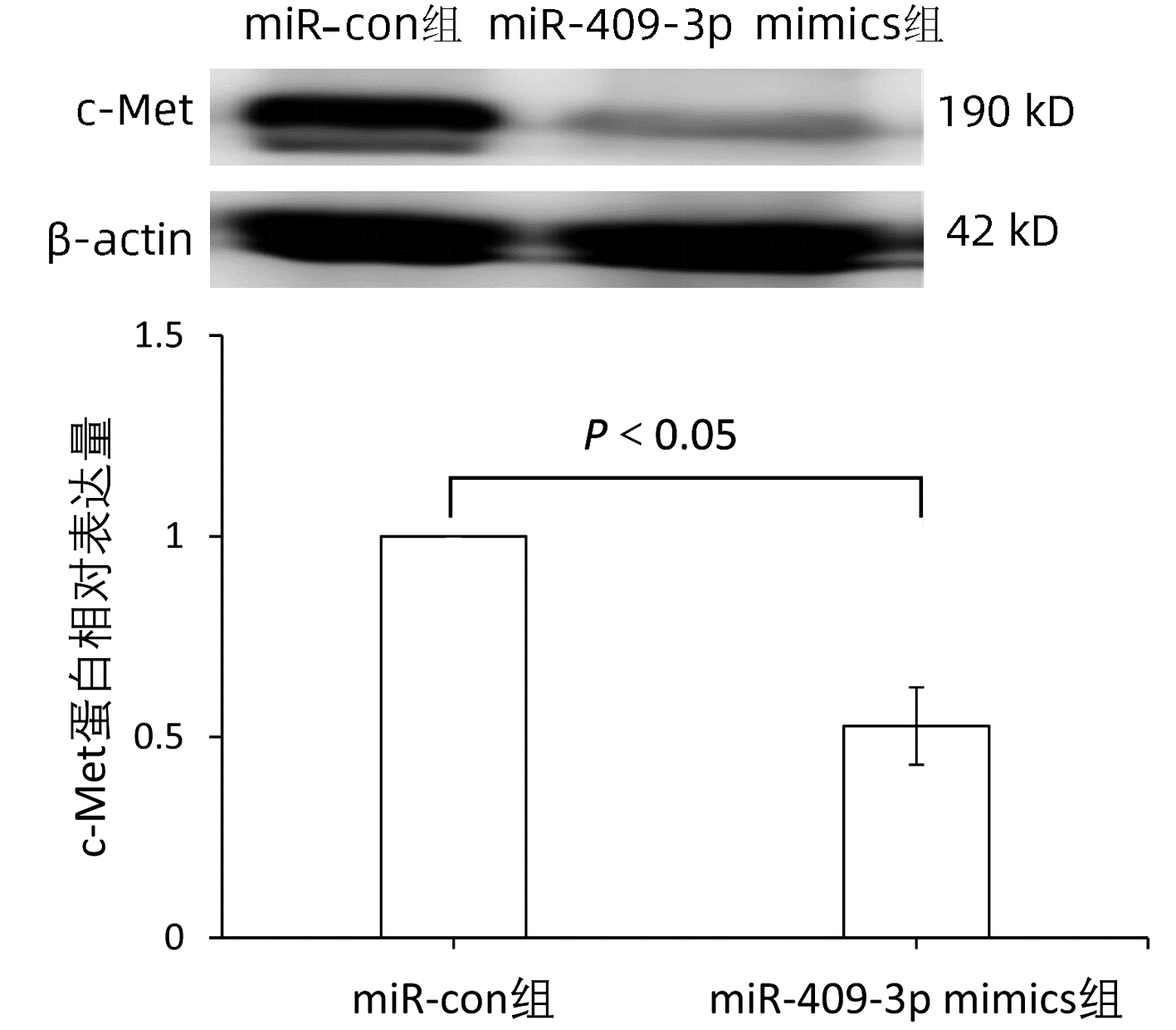
| [1] |
RUIZ-MANRIQUEZ LM, CARRASCO-MORALES O, SANCHEZ Z EA, et al. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of key signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma: A mechanistic insight[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 910733. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.910733. |
| [2] |
COOPER CS, PARK M, BLAIR DG, et al. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line[J]. Nature, 1984, 311(5981): 29-33. DOI: 10.1038/311029a0. |
| [3] |
FAIELLA A, RICCARDI F, CARTENÌ G, et al. The emerging role of c-Met in carcinogenesis and clinical implications as a possible therapeutic target[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 5179182. DOI: 10.1155/2022/5179182. |
| [4] |
CHEN L, SHI Y, ZHU X, et al. IL-10 secreted by cancer-associated macrophages regulates proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer cells via c-Met/STAT3 signaling[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 42(2): 595-604. DOI: 10.3892/or.2019.7206. |
| [5] |
MA Y, ZHANG M, WANG J, et al. High-affinity human anti-c-Met IgG conjugated to oxaliplatin as targeted chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 717. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00717. |
| [6] |
XU X, CHEN H, LIN Y, et al. MicroRNA-409-3p inhibits migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via targeting c-Met[J]. Mol Cells, 2013, 36(1): 62-68. DOI: 10.1007/s10059-013-0044-7. |
| [7] |
WAN L, ZHU L, XU J, et al. MicroRNA-409-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in human lung adenocarcinoma by targeting c-Met[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2014, 34(4): 1273-1290. DOI: 10.1159/000366337. |
| [8] |
General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(2): 288-303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. |
| [9] |
SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, GODING SAUER A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(3): 145-164. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21601. |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
RAY K. Liver cancer: The promise of new approaches in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma--adding to the toolbox?[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 10(4): 195. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.52. |
| [12] |
TRINCHET JC, CHAFFAUT C, BOURCIER V, et al. Ultrasonographic surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: a randomized trial comparing 3- and 6-month periodicities[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54(6): 1987-1997. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24545. |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
XIE HJ, RASHED N, NING Y, et al. Current status of research on circulating microRNAs as diagnostic markers for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(2): 448-451. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.042. |
| [15] |
HUSSEN BM, HIDAYAT HJ, SALIHI A, et al. MicroRNA: A signature for cancer progression[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 138: 111528. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111528. |
| [16] |
PIEROULI K, PAPAKONSTANTINOU E, PAPAGEORGIOU L, et al. Long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs as regulators of stress in cancer (Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2022, 26(6): 361. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12878. |
| [17] |
HUANG S, HE X. The role of microRNAs in liver cancer progression[J]. Br J Cancer, 2011, 104(2): 235-240. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6606010. |
| [18] |
LIU S, LI B, XU J, et al. SOD1 Promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer via an miR-409-3p/SOD1/SETDB1 epigenetic regulatory feedforward loop[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 213. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00213. |
| [19] |
WANG Y, ZHANG J, CHEN X, et al. Circ_0001023 promotes proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells thro ugh miR-409-3p/PHF10 axis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 4533-4544. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S244358. |
| [20] |
CUI X, CHEN J, ZHENG Y, et al. Circ_0000745 promotes the progression of cervical cancer by regulating miR-409-3p/ATF1 axis[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2022, 37(9): 766-778. DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3392. |
| [21] |
CHEN J, WANG R, LU E, et al. LINC00630 as a miR-409-3p sponge promotes apoptosis and glycolysis of colon carcinoma cells via regulating HK2[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2022, 14(2): 863-875.
|
| [22] |
YANG S, ZOU C, LI Y, et al. Knockdown circTRIM28 enhances tamoxifen sensitivity via the miR-409-3p/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2022, 20(1): 146. DOI: 10.1186/s12958-022-01011-3. |
| [23] |
KOTA J, CHIVUKULA RR, O'DONNELL KA, et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(6): 1005-1017. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.021. |
| [24] |
XU T, ZHU Y, XIONG Y, et al. MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50(1): 113-121. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22919. |
| [25] |
XIAO F, ZHANG W, CHEN L, et al. MicroRNA-503 inhibits the G1/S transition by downregulating cyclin D3 and E2F3 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Transl Med, 2013, 11: 195. DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-195. |
| [26] |
FORNARI F, GRAMANTIERI L, FERRACIN M, et al. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2008, 27(43): 5651-5661. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2008.178. |
| [27] |
LIU RF, XU X, HUANG J, et al. Down-regulation of miR-517a and miR-517c promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting Pyk2[J]. Cancer Lett, 2013, 329(2): 164-173. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.027. |
| [28] |
UEKI T, FUJIMOTO J, SUZUKI T, et al. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor, the c-met proto-oncogene, in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 1997, 25(3): 619-623. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510250321. |
| [29] |
GIORDANO S, COLUMBANO A. Met as a therapeutic target in HCC: facts and hopes[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60(2): 442-452. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.09.009. |
| [30] |
WANG Y, TAI Q, ZHANG J, et al. MiRNA-206 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration but promotes apoptosis by modulating cMET expression[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2019, 51(3): 243-253. DOI: 10.1093/abbs/gmy119. |
| [31] |
LIU Y, TAN J, OU S, et al. MicroRNA-101-3p suppresses proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the HGF/c-Met pathway[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2020, 38(1): 60-69. DOI: 10.1007/s10637-019-00766-8. |
| [32] |
XU X, JIANG W, HAN P, et al. MicroRNA-128-3p Mediates Lenvatinib Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Downregulating c-Met[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2022, 9: 113-126. DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S349369. |
| [33] |
HUYNH H, ONG R, SOO KC. Foretinib demonstrates anti-tumor activity and improves overall survival in preclinical models of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Angiogenesis, 2012, 15(1): 59-70. DOI: 10.1007/s10456-011-9243-z. |















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: