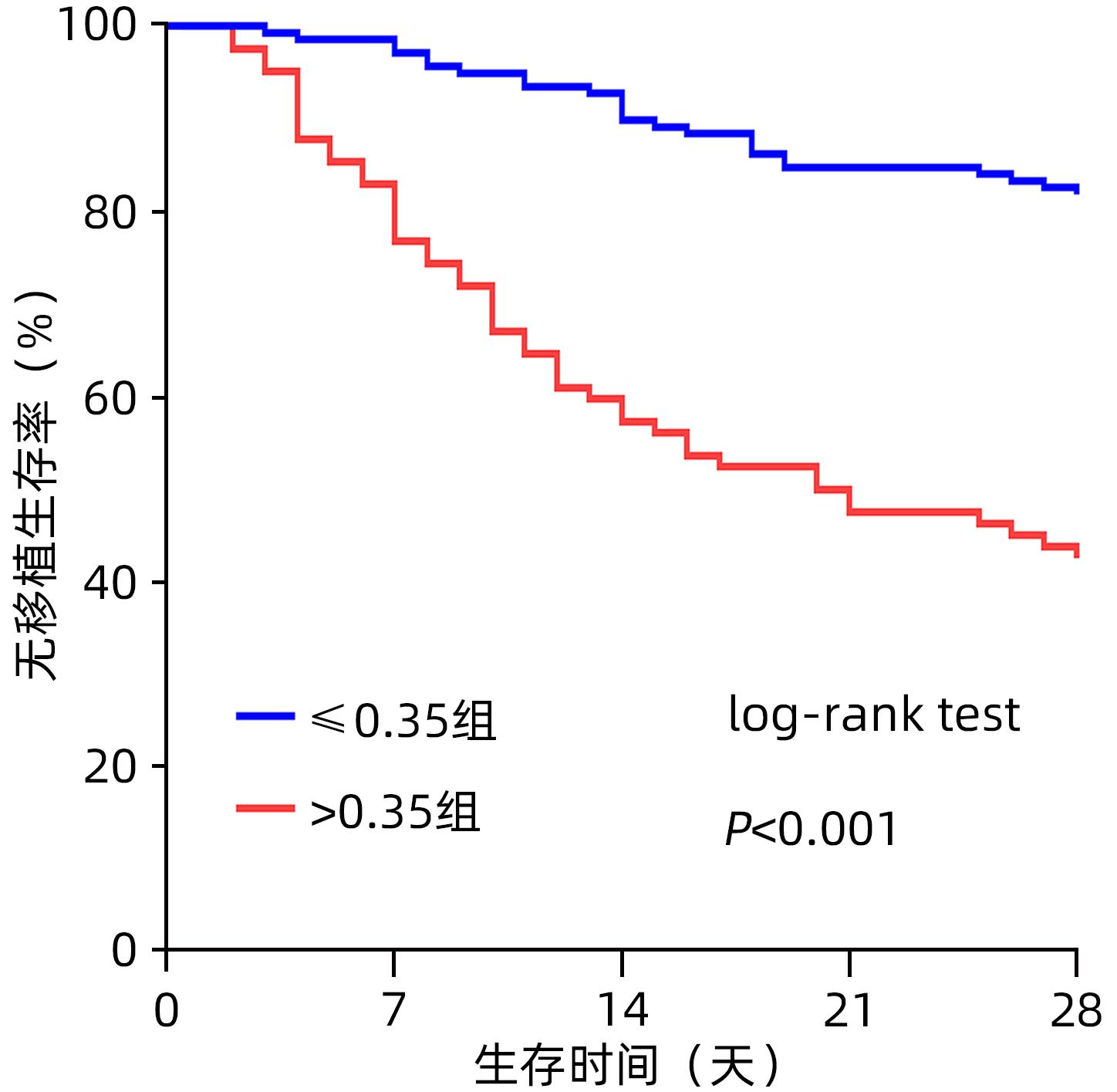
| [1] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [2] |
ARROYO V, ANGELI P, MOREAU R, et al. The systemic inflammation hypothesis: Towards a new paradigm of acute decompensation and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74( 3): 670- 685. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.048. |
| [3] |
LI J, LIANG X, JIANG J, et al. PBMC transcriptomics identifies immune-metabolism disorder during the development of HBV-ACLF[J]. Gut, 2022, 71( 1): 163- 175. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323395. |
| [4] |
WIESNER R, EDWARDS E, FREEMAN R, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease(MELD) and allocation of donor livers[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 124( 1): 91- 96. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2003.50016. |
| [5] |
LI JQ, LIANG X, YOU SL, et al. Development and validation of a new prognostic score for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 5): 1104- 1115. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.026. |
| [6] |
CAI JJ, WANG K, HAN T, et al. Evaluation of prognostic values of inflammation-based makers in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97( 46): e13324. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013324. |
| [7] |
GAO FY, SUN L, YE XQ, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic model for acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 29( 6): 669- 678. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000854. |
| [8] |
LEI Q, AO KJ, ZHANG YH, et al. Prognostic factors of the short-term outcomes of patients with hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Clinics, 2017, 72( 11): 686- 692. DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2017(11)07. |
| [9] |
GAO X, ZHAO CJ, HU SH. Short-term prognostic value of age-bilirubin-international normalized ratio-creatinine score in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis(Electronic Edition), 2022, 16( 2): 108- 114. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2022.02.005. |
| [10] |
TRIANTAFYLLOU E, WOOLLARD KJ, MCPHAIL MJW, et al. The role of monocytes and macrophages in acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2948. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02948. |
| [11] |
ZHANG DJ, ZHOU B, HOU JL. Research progress in prognostic models of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 6): 1351- 1356. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.06.047. |
| [12] |
CHEN W, YOU J, CHEN J, et al. Modified model for end-stage liver disease improves short-term prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23( 40): 7303- 7309. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7303. |
| [13] |
MONSANTO P, ALMEIDA N, LRIAS C, et al. Evaluation of MELD score and Maddrey discriminant function for mortality prediction in patients with alcoholic hepatitis[J]. Hepato-gastroenterology, 2013, 60( 125): 1089- 1094. DOI: 10.5754/hge11969. |
| [14] |
DURAND F, VALLA D. Assessment of the prognosis of cirrhosis: Child-Pugh versus MELD[J]. J Hepatol, 2005, 42 Suppl(1): S100-S 107. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.11.015. |
| [15] |
ARABI YM, DARA SI, MEMISH Z, et al. Antimicrobial therapeutic determinants of outcomes from septic shock among patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 56( 6): 2305- 2315. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25931. |
| [16] |
RUBIN JB, HAMEED B, GOTTFRIED M, et al. Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure is more common and more severe in women[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 16( 6): 936- 946. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.11.042. |
| [17] |
NEPHEW LD, ZIA Z, GHABRIL M, et al. Sex disparities in waitlisting and liver transplant for acute liver failure[J]. JHEP Rep, 2020, 3( 1): 100200. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100200. |
| [18] |
WLODZIMIROW KA, ESLAMI S, ABU-HANNA A, et al. A systematic review on prognostic indicators of acute on chronic liver failure and their predictive value for mortality[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33( 1): 40- 52. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02790.x. |
| [19] |
HAN CJ, JIN X, WU ZX, et al. Predicting the prognosis of patients with HBV-related acute liver failure by combining the ratio of neutrophils to lymphocytes and the ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin[J]. Chin J Clin Lab Sci, 2022, 40( 4): 281- 285. DOI: 10.13602/j.cnki.jcls.2022.04.10. |
| [20] |
QIANG L, QIN J, SUN CF, et al. Prognostic evaluation of a prediction model based on neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and red blood cell distribution width of inflammatory factors on hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2021, 46( 3): 317- 324. DOI: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.002486. |
| [21] |
CHEN LL, LI Q. Short-term prognostic value of peripheral blood NLR, PCT and MELD score in patients with acute-on-chronic(subacute) liver failure[J]. J Tianjin Med Univ, 2017, 23( 2): 151- 154.
陈岭岭, 李谦. 外周血NLR、PCT及MELD评分对慢加急(亚急)性肝衰竭近期预后的预测价值[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2017, 23( 2): 151- 154.
|
| [22] |
LEITHEAD JA, RAJORIYA N, GUNSON BK, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts mortality in patients listed for liver transplantation[J]. Liver Int, 2015, 35( 2): 502- 509. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12688. |



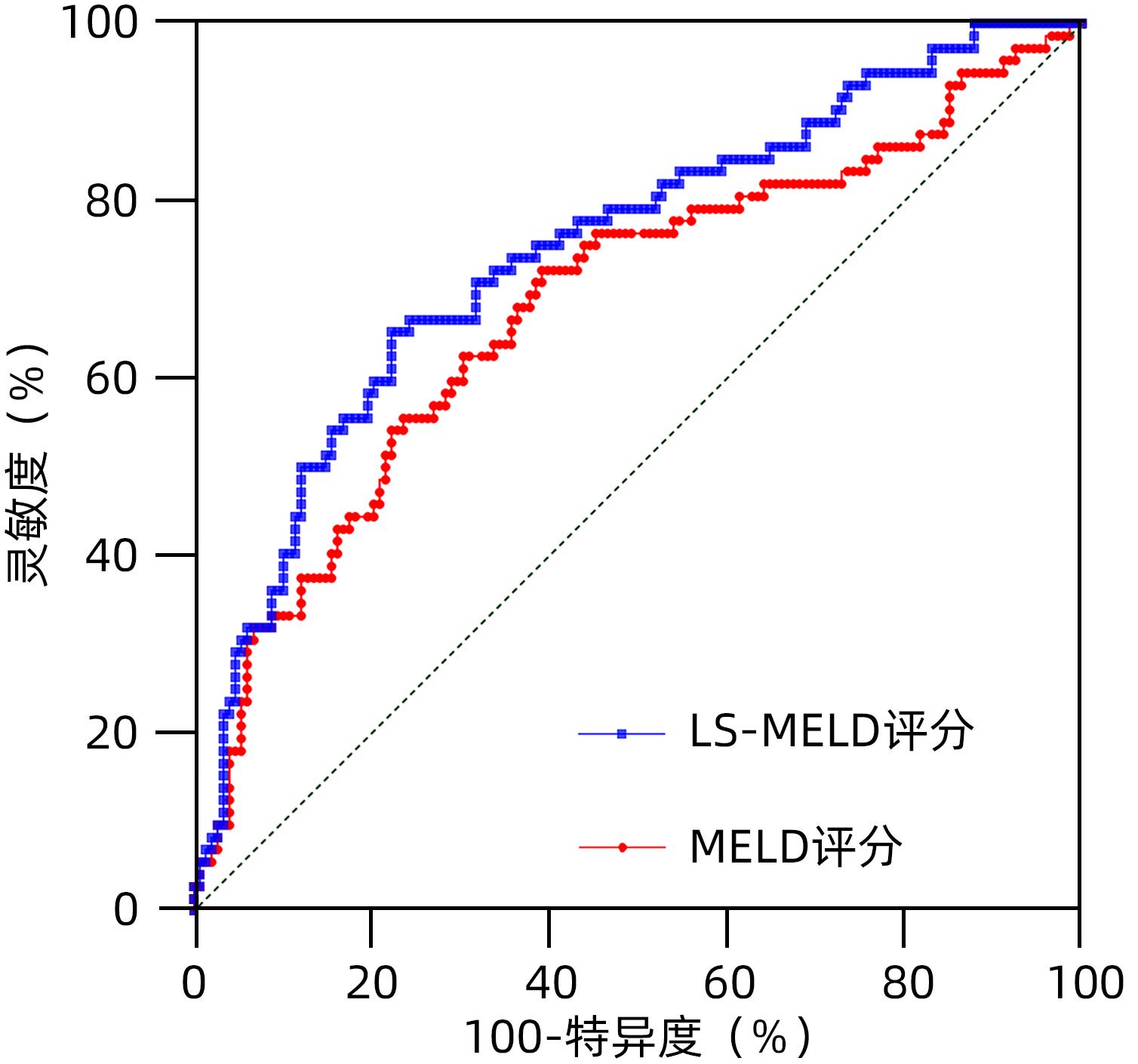




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: