| [1] |
PAIK JM, GOLABI P, YOUNOSSI Y, et al. Changes in the global burden of chronic liver diseases from 2012 to 2017: The growing impact of NAFLD[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72( 5): 1605- 1616. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31173. |
| [2] |
IOANNOU GN. Epidemiology and risk-stratification of NAFLD-associated HCC[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 6): 1476- 1484. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.08.012. |
| [3] |
YAN SY, FAN JG. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 8): 1748- 1752. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.002. |
| [4] |
ZHOU F, ZHOU JH, WANG WX, et al. Unexpected rapid increase in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 4): 1119- 1133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30702. |
| [5] |
HOU D, SUN Y, ZHANG XR, et al. Analysis of disease spectrum of annual physical examination in Grade A tertiary hospital[J]. Trauma Crit Care Med, 2022, 10( 6): 435- 437. DOI: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2022.06.12. |
| [6] |
WANG CE, XU WT, GONG J, et al. Advances in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 9): 897- 899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06. |
| [7] |
LI TX, ZHU JZ, ZHANG Y, et al. Validation of the ZJU index for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in West China: A cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2016, 9( 9): 18395- 18399.
|
| [8] |
LI L, YOU W, REN W. The ZJU index is a powerful index for identifying NAFLD in the general Chinese population[J]. Acta Diabetol, 2017, 54( 10): 905- 911. DOI: 10.1007/s00592-017-1024-8. |
| [9] |
WANG JH, XU CF, XUN YH, et al. ZJU index: A novel model for predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Chinese population[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 16494. DOI: 10.1038/srep16494. |
| [10] |
FU CP, ALI H, RACHAKONDA VP, et al. The ZJU index is a powerful surrogate marker for NAFLD in severely obese North American women[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14( 11): e0224942. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224942. |
| [11] |
SONG JM, XIAN YJ, MOHEDESI SYT, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in community residents in Urumqi city[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2016, 24( 12): 1880- 1884.
宋江美, 咸亚静, 莫合德斯·斯依提, 等. 乌鲁木齐市社区居民非酒精性脂肪肝流行现状调查[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2016, 24( 12): 1880- 1884.
|
| [12] |
National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. |
| [13] |
FARRELL GC, CHITTURI S, LAU GKK, et al. Guidelines for the assessment and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region: Executive summary[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2007, 22( 6): 775- 777. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05002.x. |
| [14] |
Writing Group of 2018 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension, Chinese Hypertension League, Chinese Society of Cardiology, et al. 2018 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertensionWriting Group of 2018[J]. Chin J Cardiovasc Med, 2019, 24( 1): 24- 56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002. |
| [15] |
FENG BY, CHEN JC, LI Y, et al. Relationship between overweight/obesity and hypertension among adults in China: A prospective study[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2016, 37( 5): 606- 611.
冯宝玉, 陈纪春, 李莹, 等. 中国成年人超重和肥胖与高血压发病关系的随访研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2016, 37( 5): 606- 611.
|
| [16] |
SHENG GT, LU S, XIE QY, et al. The usefulness of obesity and lipid-related indices to predict the presence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2021, 20( 1): 134. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-021-01561-2. |
| [17] |
AMATO MC, GIORDANO C, GALIA M, et al. Visceral Adiposity Index: A reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk[J]. Diabetes Care, 2010, 33( 4): 920- 922. DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1825. |
| [18] |
GUERRERO-ROMERO F, SIMENTAL-MENDÍA LE, GONZÁLEZ-ORTIZ M, et al. The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2010, 95( 7): 3347- 3351. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2010-0288. |
| [19] |
LEE JH, KIM D, KIM HJ, et al. Hepatic steatosis index: A simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2010, 42( 7): 503- 508. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2009.08.002. |
| [20] |
LU ZY, SHAO Z, LI YL, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a Chinese population: An 8-year follow-up study[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22( 13): 3663- 3669. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3663. |
| [21] |
ZHOU YJ, LI YY, NIE YQ, et al. Natural course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Southern China: A prospective cohort study[J]. J Dig Dis, 2012, 13( 3): 153- 160. DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2011.00571.x. |
| [22] |
CAI W, YANG L, NIE YW, et al. Construction and analysis of NAFLD cohort risk assessment model for male and females in Urumqi City[J]. Chongqing Med, 2021, 50( 23): 4028- 4032. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2021.23.015. |
| [23] |
FANG JM. Study on the predictive value of the influencing factors and risk indexes of fatty liver[D]. Jinzhou: Jinzhou Medical University, 2021.
方建梅. 脂肪肝影响因素及风险指标对其预测价值研究[D]. 锦州: 锦州医科大学, 2021.
|
| [24] |
HU W, LIU ZY, HAO HR, et al. Correlation between income and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a Chinese population[J]. Ann Endocrinol, 2020, 81( 6): 561- 566. DOI: 10.1016/j.ando.2020.07.1109. |
| [25] |
XU CN, MA ZM, WANG YF, et al. Visceral adiposity index as a predictor of NAFLD: A prospective study with 4-year follow-up[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38( 12): 2294- 2300. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13941. |
| [26] |
LIU YX, LIU SY, HUANG JF, et al. Validation of five hepatic steatosis algorithms in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A population based study[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37( 5): 938- 945. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15799. |
| [27] |
OKADA A, YAMADA G, KIMURA T, et al. Diagnostic ability using fatty liver and metabolic markers for metabolic-associated fatty liver disease stratified by metabolic/glycemic abnormalities[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2023, 14( 3): 463- 478. DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13966. |
| [28] |
CAI JW, LIN CT, LAI SQ, et al. Waist-to-height ratio, an optimal anthropometric indicator for metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease in the Western Chinese male population[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2021, 20( 1): 145. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-021-01568-9. |
| [29] |
LEE SB, KIM MK, KANG S, et al. Triglyceride glucose index is superior to the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance for predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults[J]. Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 34( 2): 179- 186. DOI: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.179. |
| [30] |
JI BL, QU H, WANG H, et al. The ZJU index: A useful indicator for recognizing insulin resistance in the Chinese general population[J]. Acta Diabetol, 2016, 53( 5): 817- 823. DOI: 10.1007/s00592-016-0878-5. |
| [31] |
FOSCHI FG, CONTI F, DOMENICALI M, et al. External validation of surrogate indices of fatty liver in the general population: The bagnacavallo study[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10( 3): 520. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10030520. |
| [32] |
LI X, QIN P, CAO LM, et al. Dose-response association of the ZJU index and fatty liver disease risk: A large cohort in China[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 36( 5): 1326- 1333. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15286. |
| [33] |
GAGGINI M, MORELLI M, BUZZIGOLI E, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and its connection with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease[J]. Nutrients, 2013, 5( 5): 1544- 1560. DOI: 10.3390/nu5051544. |
| [34] |
PUTRI RR, CASSWALL T, HAGMAN E. Prevalence of increased transaminases and its association with sex, age, and metabolic parameters in children and adolescents with obesity-a nationwide cross-sectional cohort study[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2021, 21( 1): 271. DOI: 10.1186/s12887-021-02747-4. |
| [35] |
YANG MY, WU QZ, WANG SH, et al. Incidence of fatty liver and its effect on liver function and blood lipid in women of childbearing age[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 9): 985- 987. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.33. |
| [36] |
KWON YM, OH SW, HWANG SS, et al. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with components of metabolic syndrome according to body mass index in Korean adults[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2012, 107( 12): 1852- 1858. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2012.314. |
| [37] |
LIU M, WANG JH, ZENG J, et al. Association of NAFLD with diabetes and the impact of BMI changes: A 5-year cohort study based on 18, 507 elderly[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2017, 102( 4): 1309- 1316. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2016-3440. |
| [38] |
ZHANG LX, ZHANG MT, WANG M, et al. External validation and comparison of simple tools to screen for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese community population[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 34( 8): 865- 872. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002399. |










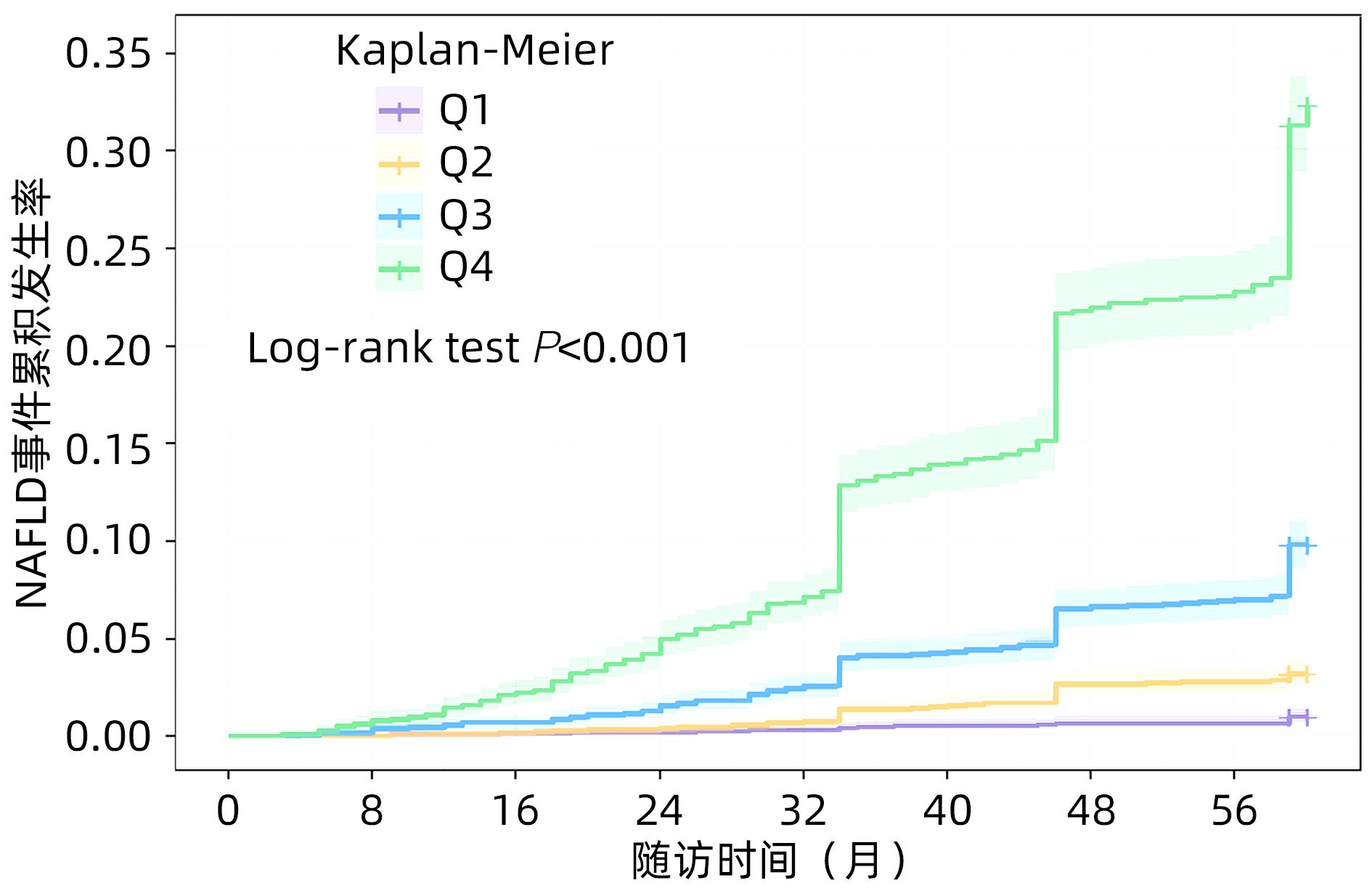




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: