| [1] |
WANG CE, XU WT, GONG J, et al. Research progress in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 9): 897- 899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06. |
| [2] |
SUN C, FAN JG. Characteristics and prevention strategies of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease combined with sarcopenia[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 29( 8): 841 -845. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2020.08.001.
|
| [3] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, KOENIG AB, ABDELATIF D, et al. Global epidemidogy of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64( 1): 73- 84. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28431. |
| [4] |
LI J, ZOU B, YEO YH, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4( 5): 389- 398. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30039-1. |
| [5] |
JOO SK, KIM W. Interaction between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2023, 29( Suppl): S68- S78. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0358. |
| [6] |
IANNUZZI-SUCICH M, PRESTWOOD KM, KENNY AM. Prevalence of sarcopenia and predictors of skeletal muscle mass in healthy, older men and women[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2002, 57( 12): M772- M777. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/57.12.m772. |
| [7] |
POUWELS S, SAKRAN N, GRAHAM Y, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD): a review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2022, 22( 1): 63. DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-00980-1. |
| [8] |
PÁR A, HEGYI JP, VÁNCSA S, et al. Sarcopenia-2021: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, therapy[J]. Orv Hetil, 2021, 162( 1): 3- 12. DOI: 10.1556/650.2021.32015. |
| [9] |
CHOE EK, KANG HY, PARK B, et al. The association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and CT-measured skeletal muscle mass[J]. J Clin Med, 2018, 7( 10): 310. DOI: 10.3390/jcm7100310. |
| [10] |
HONG HC, HWANG SY, CHOI HY, et al. Relationship between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59( 5): 1772- 1778. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26716. |
| [11] |
LEE YH, JUNG KS, KIM SU, et al. Sarcopaenia is associated with NAFLD independently of obesity and insulin resistance: Nationwide surveys(KNHANES 2008-2011)[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63( 2): 486- 493. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.051. |
| [12] |
LEE YH, KIM SU, SONG K, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with significant liver fibrosis independently of obesity and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Nationwide surveys(KNHANES 2008-2011)[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63( 3): 776- 786. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28376. |
| [13] |
KIM HY, KIM CW, PARK CH, et al. Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2016, 15( 1): 39- 47. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(15)60030-3. |
| [14] |
KOO BK, KIM D, JOO SK, et al. Sarcopenia is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and significant fibrosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66( 1): 123- 131. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.08.019. |
| [15] |
PETTA S, CIMINNISI S, DI MARCO V, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with severe liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 45( 4): 510- 518. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13889. |
| [16] |
WIJARNPREECHA K, KIM D, RAYMOND P, et al. Associations between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and advanced fibrosis in the USA[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31( 9): 1121- 1128. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001397. |
| [17] |
KIM G, LEE SE, LEE YB, et al. Relationship between relative skeletal muscle mass and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 7-year longitudinal study[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68( 5): 1755- 1768. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30049. |
| [18] |
HSIEH YC, JOO SK, KOO BK, et al. Myosteatosis, but not sarcopenia, predisposes NAFLD subjects to early steatohepatitis and fibrosis progression[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21( 2): 388- 397. e 10. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.020. |
| [19] |
ISSA D, ALKHOURI N, TSIEN C, et al. Presence of sarcopenia(muscle wasting) in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60( 1): 428- 429. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26908. |
| [20] |
SINN DH, KANG D, KANG M, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and accelerated loss of skeletal muscle mass: A longitudinal cohort study[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76( 6): 1746- 1754. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32578. |
| [21] |
ROH E, HWANG SY, YOO HJ, et al. Impact of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on the risk of sarcopenia: a nationwide multicenter prospective study[J]. Hepatol Int, 2022, 16( 3): 545- 554. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-021-10258-8. |
| [22] |
CANNATARO R, CARBONE L, PETRO JL, et al. Sarcopenia: etiology, nutritional approaches, and miRNAs[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 18): 9724. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22189724. |
| [23] |
NASSIR F. NAFLD: mechanisms, treatments, and biomarkers[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12( 6): 824. DOI: 10.3390/biom12060824. |
| [24] |
BREEN L, PHILLIPS SM. Skeletal muscle protein metabolism in the elderly: Interventions to counteract the‘anabolic resistance’ of ageing[J]. Nutr Metab(Lond), 2011, 8: 68. DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-8-68. |
| [25] |
KAMIMURA H, SATO T, NATSUI K, et al. Molecular mechanisms and treatment of sarcopenia in liver disease: a review of current knowledge[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 3): 1425. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22031425. |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
MASTROTOTARO L, RODEN M. Insulin resistance and insulin sensitizing agents[J]. Metabolism, 2021, 125: 154892. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154892. |
| [28] |
RINALDI L, PAFUNDI PC, GALIERO R, et al. Mechanisms of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the metabolic syndrome. a narrative review[J]. Antioxidants(Basel), 2021, 10( 2): 270. DOI: 10.3390/antiox10020270. |
| [29] |
LANG T, STREEPER T, CAWTHON P, et al. Sarcopenia: etiology, clinical consequences, intervention, and assessment[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2010, 21( 4): 543- 559. DOI: 10.1007/s00198-009-1059-y. |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
QIU J, THAPALIYA S, RUNKANA A, et al. Hyperammonemia in cirrhosis induces transcriptional regulation of myostatin by an NF-κB-mediated mechanism[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110( 45): 18162- 18167. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1317049110. |
| [32] |
OWEN OE, KALHAN SC, HANSON RW. The key role of anaplerosis and cataplerosis for citric acid cycle function[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277( 34): 30409- 30412. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R200006200. |
| [33] |
ROMBOUTS K, MARRA F. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Dig Dis, 2010, 28( 1): 229- 235. DOI: 10.1159/000282094. |
| [34] |
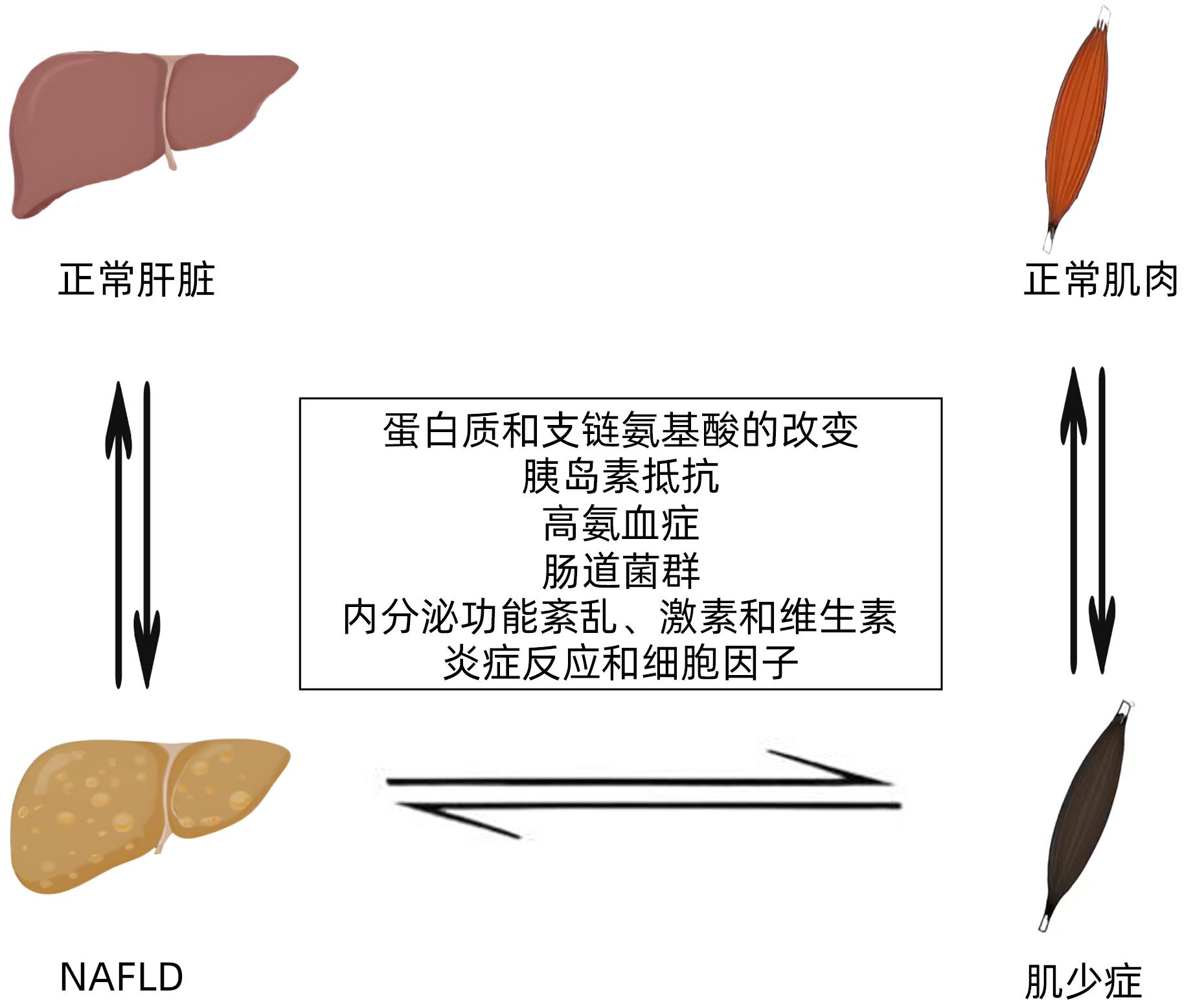
WANG ZX, FAN JG. Relationships and mechanisms of sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Dig Dis, 2021, 41( 2): 88- 91, 107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-534X.2021.02.004. |
| [35] |
MIELE L, VALENZA V, LA TORRE G, et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 49( 6): 1877- 1887. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22848. |
| [36] |
TRIPATHI A, DEBELIUS J, BRENNER DA, et al. The gut-liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15( 7): 397- 411. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0011-z. |
| [37] |
SARKAR M, YATES K, SUZUKI A, et al. Low testosterone is associated with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis severity in men[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 19( 2): 400- 402. e 2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.053. |
| [38] |
KUMAR R, PRAKASH SS, PRIYADARSHI RN, et al. Sarcopenia in chronic liver disease: a metabolic perspective[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2022, 10( 6): 1213- 1222. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00239. |
| [39] |
DASARATHY S. Is the adiponectin-AMPK-mitochondrial axis involved in progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60( 1): 22- 25. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27134. |
| [40] |
LI H, LIU DG, YAN SQ, et al. Improvement effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 combined with astragalus polysaccharide on insulin resistance of skeletal muscle cells in vitro and its mechanism[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2022, 48( 6): 1411- 1421. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220606. |
| [41] |
XIE Y, LIANG ZR, WANG J. Advances in research on the relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and vitamin D[J]. Transl Med J, 2021, 10( 5): 343- 346. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2021.05.015. |
| [42] |
HAMRICK MW. Role of the cytokine-like hormone leptin in muscle-bone crosstalk with aging[J]. J Bone Metab, 2017, 24( 1): 1- 8. DOI: 10.11005/jbm.2017.24.1.1. |
| [43] |
YI Y, WANG C, DING Y, et al. Diet was less significant than physical activity in the prognosis of people with sarcopenia and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver diseases: Analysis of the national health and nutrition examination survey III[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1101892. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1101892. |
| [44] |
PASCO JA, WILLIAMS LJ, JACKA FN, et al. Sarcopenia and the common mental disorders: a potential regulatory role of skeletal muscle on brain function?[J]. Curr Osteoporos Rep, 2015, 13( 5): 351- 357. DOI: 10.1007/s11914-015-0279-7. |
| [45] |
SUBRAMANIAN M, WOJTUSCISZYN A, FAVRE L, et al. Precision medicine in the era of artificial intelligence: implications in chronic disease management[J]. J Transl Med, 2020, 18( 1): 472. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-020-02658-5. |
| [46] |
FENG G, WANG XY, LI SS, et al. Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 10): 2352- 2356. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.029. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: