Influence of long-term entecavir treatment on renal function in patients with chronic hepatitis B
-
摘要: 目的探讨长期应用ETV抗病毒治疗对慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者肾功能的影响。方法回顾性分析2015年1月-2019年6月在淮安市第四人民医院接受ETV抗病毒治疗半年以上的CHB患者232例。按不同性别、年龄(<或≥65岁)、有无肝硬化和肾小球滤过率(e GFR)(<或≥90 ml·min-1·1.73 m-2)分组,探讨各个亚组的ETV治疗前后的肾功能指标[血尿素氮(BUN)、血肌酐(Scr)和e GFR]变化情况。并比较ETV抗病毒方案在抗病毒前后总体ALT、AST、Alb、HBs Ag、HBV DNA和肾功能指标(BUN、Scr和e GFR)变化。采用全自动生化分析仪检测血生化指标,包括ALT、AST、Alb、BUN、Scr和e GFR,采用实时荧光定量PCR法检测HBV DNA,采用罗氏电化学发光法检测血清HBs Ag定量。正态分布的计量资料组间比较采用配对t检验,非正态分布的计量资料组间比较采用Wilcoxon秩和检验,采用二分类logistic回归分析筛选ETV抗病毒治疗后e GFR <90 ml·min-1·1. ...Abstract: Objective To investigate the influence of long-term entecavir( ETV) antiviral therapy on renal function in patients with chronic hepatitis B( CHB). Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 232 CHB patients who received ETV antiviral therapy for more than half a year in Huai'an Fourth People's Hospital from January 2015 to June 2019. The patients were divided into groups according to sex,age( < 65 years or ≥65 years),presence or absence of liver cirrhosis,and estimated glomerular filtration rate( eGFR)( < 90 ml/min/1. 73 m2 or ≥90 ml/min/1. 73 m2),and the changes in renal function markers[blood urea nitrogen( BUN),serum creatinine( SCr),and eGFR] after treatment were observed for each group. The changes in alanine aminotransferase( ALT),aspartate aminotransferase( AST),albumin( Alb),HBsAg,HBV DNA,and renal function markers( BUN,SCr,and eGFR) after ETV antiviral therapy were also observed. An automatic biochemical analyzer was used to measure biochemical parameters including ALT,AST,Alb,BUN,SCr,and eGFR; RT-qPCR was used to measure HBV DNA; Roche electrochemical luminescence was used to measure serum HBsAg quantification. The paired t-test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between groups,and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between groups; a binary logistic regression analysis was used to identify the risk factors for eGFR < 90 ml/min/1. 73 m2 after ETV antiviral therapy. Results After ETV antiviral therapy for more than half a year,there were significant reductions in ALT,AST,HBs Ag,and HBV DNA( Z =-9. 496 and-9. 577,t = 5. 013 and20. 777,all P < 0. 05) and a significant increase in Alb( t =-10. 832,P < 0. 05); compared with baseline,there were significant increases in BUN and SCr( t =-2. 685 and-2. 376,both P < 0. 05) and a significant reduction in e GFR( t = 3. 207,P < 0. 05). Further analysis of each subgroup showed that the e GFR ≥90 ml/min/1. 73 m2 group,the non-elderly group,the liver cirrhosis group,and the male group had significant increases in BUN( t =-3. 403,-3. 187,-2. 267,and-2. 187,all P < 0. 05) and SCr( t =-3. 716,-3. 614,-2. 291,and-2. 115,all P < 0. 05) and a significant reduction in e GFR( t = 4. 846,4. 152,2. 458,and 2. 946,all P < 0. 05),and the non-liver cirrhosis group had a significant reduction in e GFR( t = 2. 163,P < 0. 05) and had no significant changes in BUN and SCr( P >0. 05). The binary logistic regression analysis showed that with the increase in glucose level( odds ratio [OR]= 1. 296,95% confidence interval [Cl]: 1. 052-1. 597,P = 0. 015) and the reduction in total cholesterol( TC)( OR = 0. 436,95% Cl: 0. 286-0. 664,P <0. 001),the risk of e GFR < 90 ml/min/1. 73 m2 increased after ETV therapy. Conclusion ETV antiviral therapy can effectively reduce ALT,AST,HBs Ag,and HBV DNA and increase Alb,but it can cause the increases in BUN and SCr and the reduction in e GFR in patients with e GFR > 90 ml/min/1. 73 m2,non-elderly patients,and patients with liver cirrhosis. Blood glucose and TC are influencing factors for eGFR < 90 ml/min/1. 73 m2 after ETV therapy.
-
Key words:
- hepatitis B,Chronic /
- therapeutics /
- entecavir /
- renal insufficiency
-
肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC)是全球第六大常见肿瘤和我国第二大癌症死亡原因,早期发现、及时采取有效的治疗是改善患者生存预后的重要手段[1-2]。射频消融术(radiofrequency ablation,RFA)在早期肝癌特别是直径≤2 cm的患者中的疗效与手术切除相当,是不能切除的早期肝癌患者的首选治疗方法[3-6]。许多临床和实验研究[7-8]表明,全身炎症反应在肿瘤的进展中发挥重要作用。近年来,多项研究[9-11]证实了全身炎症标志物包括中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值(neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, NLR)、红细胞分布宽度/淋巴细胞比值(red blood cell distribution width-to-lymphocyte ratio, RLR)、淋巴细胞/单核细胞比值(lymphocyte-to- monocyte ratio, LMR)等在包括HCC在内的恶性肿瘤和肝衰竭预后中的作用。本研究旨在探讨术前全身炎症标志物NLR、RLR及LMR在早期小肝癌RFA后预后中的价值。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2011年9月—2020年12月在天津市第二人民医院行RFA的132例初诊HCC患者。HCC的诊断及分期符合《原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)》[2],基于动态增强MRI/CT、超声造影等2种或以上影像学支持,具体表现为动脉期病灶明显强化,门静脉期和/或平衡期病灶强化低于肝实质即“快进快出”的肝癌典型特征,伴或不伴AFP水平升高。纳入标准:(1)单个病灶直径≤3 cm;(2)巴塞罗那临床(BCLC)分期为0/A期;(3)不适合手术切除或者患者拒绝手术切除治疗;(4)接受RFA作为首次治疗。排除标准:(1)Child-Pugh分级为C级;(2)合并其他恶性肿瘤或严重心脑血管病等;(3)2周内服用过抗炎药物;(4)随访资料不全或围术期死亡;(5)随访时间<3个月。
1.2 研究方法
收集RFA前1周内的数据。一般资料:性别、年龄、BMI;病因学资料:HBV、HCV、代谢相关脂肪性肝病(MAFLD)和乙醇摄入等;实验室指标:血常规、肝功能、肾功能、AFP等;影像学资料:CT、磁共振成像(MRI)、腹部彩超、超声造影等。
1.3 RFA方案
在超声引导下经皮射频消融。严格按照《2011 CSLC/CSCO/CMA肝癌射频消融治疗规范的专家共识》流程进行。患者在穿刺部位接受2%盐酸利多卡因治疗,并静脉滴注50 mg盐酸哌替啶与50 mL 5%葡萄糖水混合。手术过程中持续监测心血管和呼吸系统。对于所有肿瘤,消融边缘至少应达到肿瘤边缘以外5 mm。完全消融定义为肝脏动态增强MRI/CT或超声造影提示肿瘤所在区域为低密度(超声表现为高回声),动脉期无强化。术后28 d复查动态增强MRI/CT及动脉造影评估肿瘤是否完全消融。对于未完全消融者再次消融,直至肿瘤完全反应。
1.4 患者随访
本研究的目标事件为无复发生存(recurrence free survival, RFS)和总生存(overall survival,OS)。RFS时间定义为从RFA术后到首次复发或死亡之间的时间。OS定义为从RFA术后到患者死亡或随访截止日期之间的时间。完全消融后,患者前2年内,每3个月复查1次AFP及动态增强MRI/CT、超声造影等,之后每半年监测1次上述指标,如动态增强MRI/CT和/或超声造影提示原病灶周围或者肝内远处出现动脉期异常强化影,门脉期及平衡期密度降低,伴或不伴AFP升高,考虑肿瘤复发,记录复发肿瘤的位置、数目、大小、有无血管侵犯等。通过多学科会诊综合评估患者情况,给予针对肝癌复发的相关治疗。治疗后继续随访,直至患者死亡或研究截止日期2021年6月30日。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0软件及R语言4.0.3进行统计分析。计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验。运用X-tile工具以5年生存率及RFS率为结局事件,采用“枚举法”确定NLR、RLR和LMR的最佳截断值[12]。使用Kaplan-Meier方法绘制生存曲线,并采用log-rank检验比较复发及生存的组间差异。单因素分析采用log-rank检验,将log-rank检验分析中具有统计学意义的因素纳入多因素Cox回归分析以确定RFS率与OS率的危险因素,计算风险比(HR)及其95%CI。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
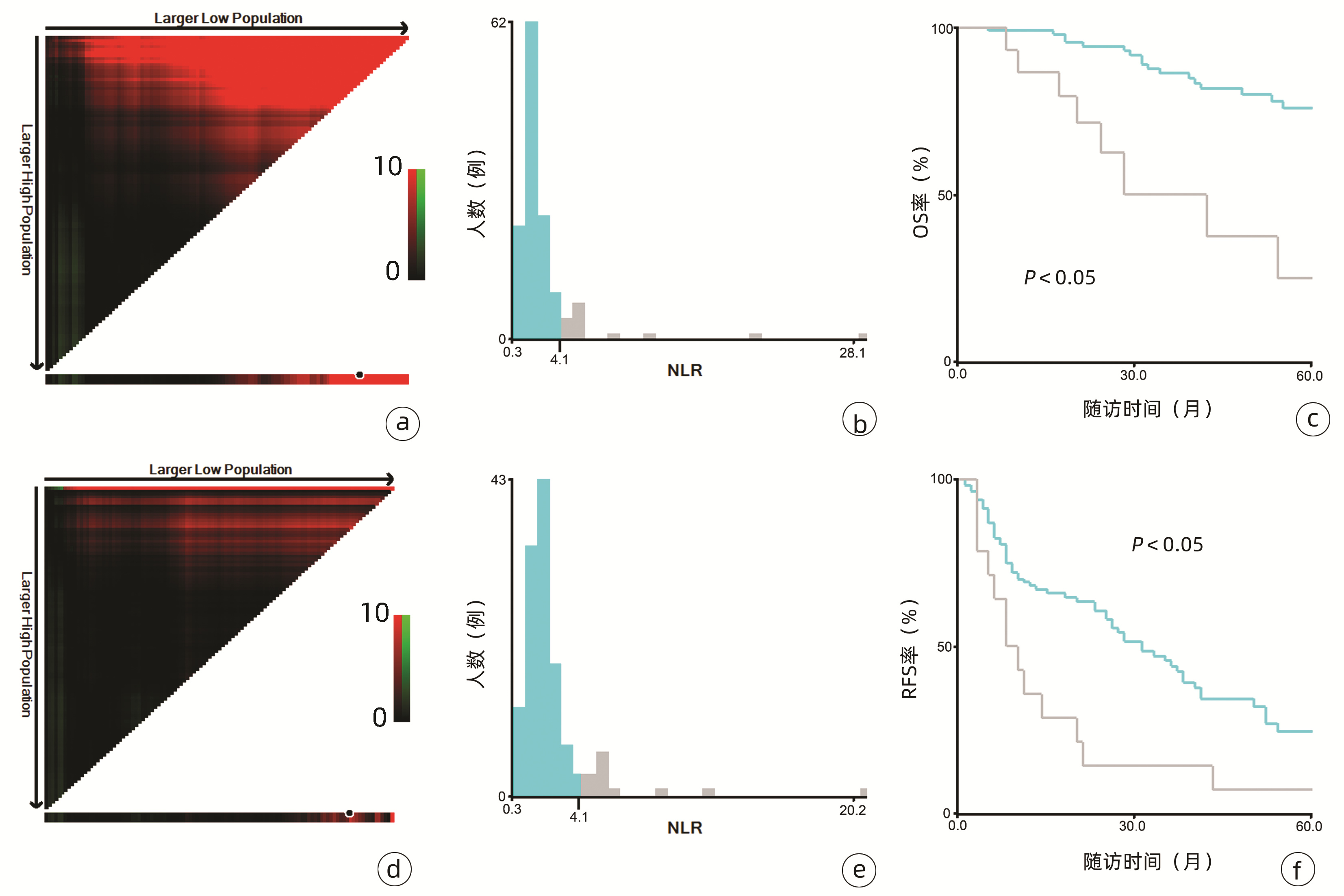
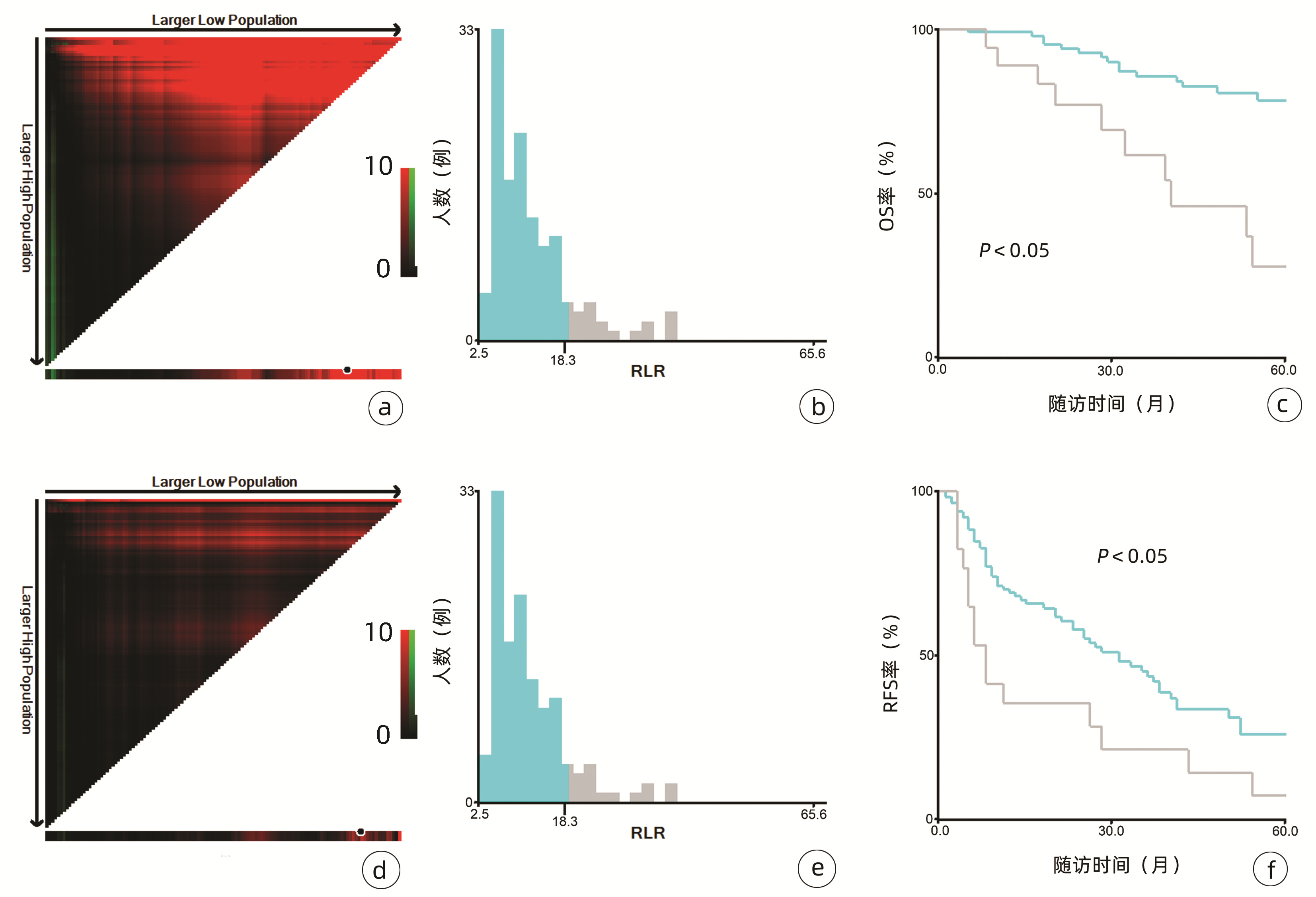
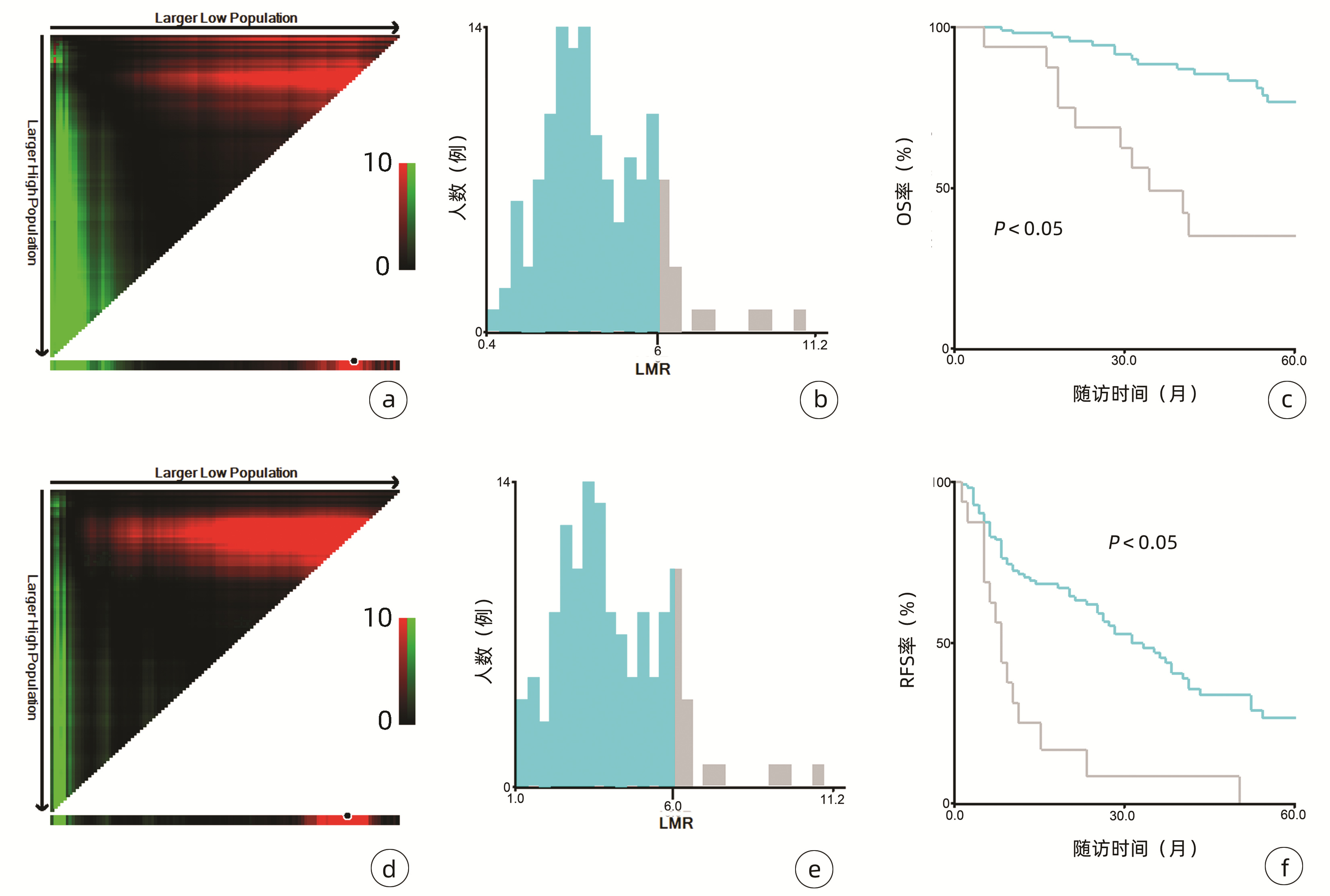
132例患者中男性96例,平均年龄(58.50±9.66)岁。利用患者数据对5年OS和RFS进行X-tile分析,确定NLR、RLR和LMR的最佳截断值分别为4.1、18.3和6(图 1~3)。根据NLR、RLR、LMR分组与OS及RFS的相关性,将NLR、RLR及LMR按积分计算(表 1),根据N-R-L评分的得分情况将患者分为3组:N-R-L 0分组,N-R-L 1分组和N-R-L 2分组,并将其作为OS和RFS的预后指标。3组患者Child-Pugh分级、Alb比较差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)(表 2)。
表 1 N-R-L评分的计分及分组方式Table 1. Scoring and grouping of N-R-L score变量 得分 NLR <4.1 0 ≥4.1 1 RLR <18.3 0 ≥18.3 1 LMR <6 0 ≥6 1 N-R-L NLR+RLR+LMR=0 0 NLR+RLR+LMR=1 1 NLR+RLR+LMR=2 2 注:N-R-L,NLR、RLR和LMR三项评分之和。 表 2 术前N-R-L分组患者的临床特征Table 2. Clinical characteristics of patients in preoperative N-R-L group临床特征 N-R-L 0分组(n=92) N-R-L 1分组(n=29) N-R-L 2分组(n=11) χ2值 P值 性别[例(%)] 0.545 0.762 男 66(71.7) 21(72.4) 9(81.8) 女 26(28.3) 8(27.6) 2(18.2) 年龄[例(%)] 0.371 0.831 <60岁 48(52.2) 17(58.6) 6(54.5) ≥ 60岁 44(47.8) 12(41.4) 5(45.5) BMI[例(%)] 2.024 0.363 <24 kg/m2 42(45.7) 9(31.0) 5(45.5) ≥24 kg/m2 50(54.3) 20(69.0) 6(54.5) Child-Pugh分级[例(%)] 10.992 0.001 A级 81(88.0) 26(89.7) 4(36.4) B级 11(12.0) 3(10.3) 7(63.6) BCLC分期[例(%)] 3.640 0.056 0期 18(19.6) 3(10.3) 0 A期 74(80.4) 26(89.7) 11(100) 肿瘤直径[例(%)] 3.876 0.144 <2 cm 53(57.6) 17(58.6) 3(27.3) ≥2 cm 39(42.4) 12(41.4) 8(72.7) HBV感染[例(%)] 1.601 0.449 否 22(23.9) 5(17.2) 4(36.4) 是 70(76.1) 24(82.8) 7(63.6) HCV感染[例(%)] 1.029 0.598 否 76(82.6) 22(75.9) 8(71.7) 是 16(17.4) 7(24.1) 3(27.3) MAFLD[例(%)] 0.367 0.832 否 56(60.9) 16(55.2) 7(63.6) 是 36(39.1) 13(44.8) 4(36.4) AFP[例(%)] 1.266 0.531 <15 ng/mL 59(64.1) 21(72.4) 6(54.5) ≥15 ng/mL 33(35.9) 8(27.6) 5(45.5) ALBI分级[例(%)] 2.845 0.092 1级 54(58.7) 16(55.2) 5(45.4) 2级 36(39.1) 13(44.8) 3(27.3) 3级 2(2.2) 0 3(27.3) TBil[例(%)] 0.904 0.636 ≤20 μmol/L 55(59.8) 16(55.2) 5(45.5) >20 μmol/L 37(40.2) 13(44.8) 6(54.5) Alb[例(%)] 5.699 0.017 ≥35 g/L 82(89.1) 23(79.3) 7(63.6) <35 g/L 10(10.9) 6(20.7) 4(36.4) ALT[例(%)] 0.109 0.741 ≤50 U/L 76(82.6) 28(96.6) 7(63.6) >50 U/L 16(17.4) 1(3.4) 4(36.4) AST[例(%)] 1.572 0.456 ≤40 U/L 71(77.2) 24(82.8) 7(63.6) >40 U/L 21(22.8) 5(17.2) 4(36.4) MELD评分[例(%)] 3.022 0.221 <9分 65(70.7) 18(62.1) 5(45.5) ≥9分 27(29.3) 11(37.9) 6(54.5) 注:ALBI分级,白蛋白-胆红素分级。 2.2 RFA术后的复发和生存
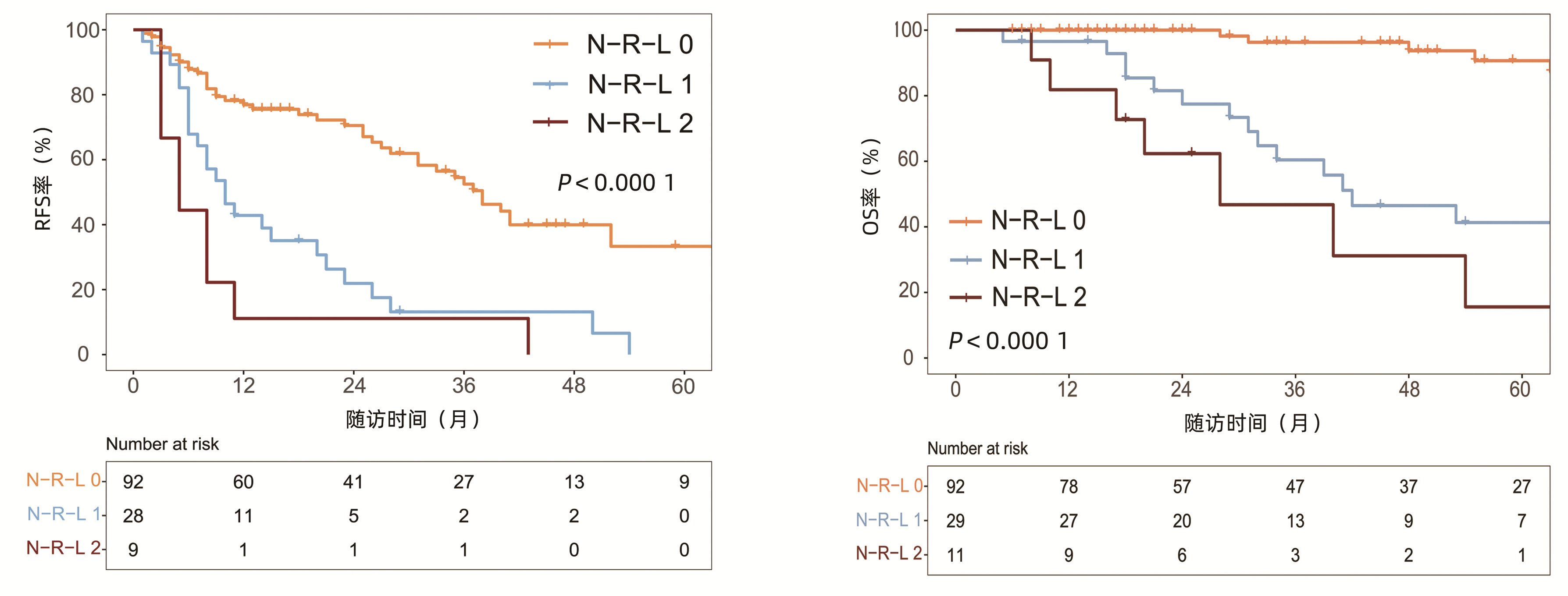
中位随访时间为34个月(5~111个月)。所有患者的1、3和5年RFS率分别为64.3%、40.0%和21.5%,中位RFS为26个月;1、3和5年OS率分别为97.6%、82.1%和69.8%。N-R-L 0分组、N-R-L 1分组和N-R-L 2分组的1、3和5年RFS率分别为76.9%、52.5%、33.3%,42.9%、13.1%、0和11.1%、0、0(χ2=35.345,P<0.000 1)(图 4);3组的1、3和5年OS率分别为100%、96.3%、90.7%,96.6%、60.4%、41.3%和81.8%、46.8%、15.6%(χ2=38.460,P<0.000 1)(图 4)。N-R-L 0分组、N-R-L 1分组和N-R-L 2分组的中位RFS分别为38个月、10个月和5个月,组间差异有统计学意义(χ2=35.345,P<0.000 1)。
2.3 RFS率的预测因素
对患者RFA术前相关指标进行单因素及多因素分析,以确定RFS率的预测因素(表 3)。log-rank检验结果显示,男性、Child-Pugh B级、肿瘤直径≥2 cm、TBil>20 μmol/L、Alb>35 g/L、ALBI分级2/3级以及N-R-L评分1/2分与RFS率显著相关(P值均<0.05)。进一步行多因素Cox回归分析结果表明,肿瘤直径≥2 cm(HR=2.10, 95%CI: 1.28~3.43,P=0.003)、N-R-L评分1分(HR= 3.14, 95%CI: 1.81~5.46,P<0.000 1)以及N-R-L评分2分(HR=2.61, 95%CI: 1.06~6.42,P=0.037)是RFS率的独立预测因素(P值均<0.05)。
表 3 Cox回归分析RFS率的影响因素Table 3. Results of RFS by Cox regression analysis变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P值 HR(95%CI) P值 性别(男/女) 1.97(1.14~3.40) 0.015 1.55(0.87~2.76) 0.136 BMI(≥24 kg/m2/<24 kg/m2) 1.22(0.77~1.92) 0.402 MAFLD(是/否) 1.03(0.65~1.61) 0.916 Child-Pugh分级(B级/A级) 2.58(1.50~4.45) 0.001 1.28(0.56~2.91) 0.564 肿瘤直径(≥2 cm/<2 cm) 2.28(1.43~3.62) 0.001 2.10(1.28~3.43) 0.003 BCLC分期(A期/0期) 2.06(0.89~4.75) 0.090 ALT(>50 U/L/≤50 U/L) 1.41(0.78~2.57) 0.260 AST(>40 U/L/≤40 U/L) 1.63(0.98~2.70) 0.058 TBil(≤20 μmol/L/>20 μmol/L) 1.69(1.07~2.65) 0.024 1.60(0.96~2.67) 0.074 Alb(<35 g/L/≥35 g/L) 2.45(1.45~4.12) 0.001 1.01(0.44~2.32) 0.974 AFP(>400 ng/mL/≤400 ng/mL) 0.81(0.33~2.01) 0.650 ALBI分级(ref: 1级) 2级 1.25(0.79~2.00) 0.341 0.92(0.49~1.70) 0.781 3级 4.15(1.61~10.70) 0.003 1.91(0.48~7.59) 0.356 MELD评分(>9分/≤9分) 1.44(0.91~2.28) 0.124 N-R-L得分(ref: 0分) 1分 3.13(1.89~5.20) <0.000 1 3.14(1.81~5.46) <0.000 1 2分 4.99(2.40~10.37) <0.000 1 2.61(1.06~6.42) 0.037 2.4 OS率的预测因素
表 4总结了RFA术后OS率的预测因素。log-rank检验结果提示Child-Pugh B级、肿瘤直径≥2 cm、TBil>20 μmol/L、Alb>35 g/L、ALBI分级2/3级以及N-R-L评分1/2分与OS显著相关。多因素Cox回归结果表明,肿瘤直径≥2 cm(HR=3.67, 95%CI: 1.58 ~ 8.52,P=0.002)、N-R-L评分1分(HR=8.27, 95%CI: 3.15 ~ 21.71,P<0.000 1)以及N-R-L评分2分(HR=14.59, 95%CI: 3.96 ~ 53.78,P<0.000 1)是OS率的独立预测因素。
表 4 Cox回归分析OS率的影响因素Table 4. Results of OS by Cox regression analysis变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P值 HR(95%CI) P值 性别(男/女) 2.17(0.88~5.33) 0.093 BMI(≥24 kg/m2/<24 kg/m2) 1.64(0.78~3.44) 0.191 MAFLD(是/否) 1.20(0.58~2.51) 0.620 Child-Pugh分级(B级/A级) 3.54(1.52~8.25) 0.003 0.99(0.28~3.52) 0.987 肿瘤直径(≥2 cm/<2 cm) 2.89(1.36~6.14) 0.006 3.67(1.58~8.52) 0.002 BCLC分期(A期/0期) 1.10(0.33~3.63) 0.880 ALT(>50 U/L/≤50 U/L) 1.21(0.46~3.17) 0.705 AST(>40 U/L/≤40 U/L) 1.30(0.58~2.94) 0.530 TBil(≤20 μmol/L/>20 μmol/L) 2.27(1.08~4.76) 0.030 1.97(0.82~4.77) 0.132 Alb(<35 g/L/≥35 g/L) 3.49(1.58~7.74) 0.002 1.36(0.36~5.09) 0.649 AFP(>400 ng/mL/≤400 ng/mL) 1.35(0.41~4.50) 0.621 ALBI分级(ref: 1级) 2级 1.67(0.78~3.56) 0.184 0.97(0.35~2.65) 0.950 3级 12.94(2.55~65.68) 0.002 2.11(0.25~17.94) 0.495 MELD评分(>9分/≤9分) 1.59(0.75~3.33) 0.224 N-R-L得分(ref: 0分) 1分 6.92(2.82~17.00) <0.000 1 8.27(3.15~21.71) <0.000 1 2分 13.50(4.68~38.91) <0.000 1 14.59(3.96~53.78) <0.000 1 3. 讨论
多项研究表明,对于不可切除的早期小肝癌,RFA能提供良好的治疗效果。本研究选取了单发直径≤3 cm的早期/极早期HCC患者,将RFA作为首次治疗方法。在整个随访期内,共有77例(58.3%)复发,29例(22%)死亡,与先前研究[4, 13-14]结果类似。所有患者接受RFA治疗后,仅3例患者出现轻微并发症,经治疗后均好转,没有患者出现严重并发症,表明RFA安全性较高,更具成本效益。
评估了RFA率与OS率的危险因素,发现肿瘤直径≥2 cm、N-R-L评分1分及2分与患者不良预后独立相关。HCC的复发及预后的差异与初始肿瘤大小相关已经在先前的研究[15-16]中被证实。在HCC的发生发展中,随着病灶直径的增加,微浸润的发生率明显增加,这可能是HCC治疗后复发的重要原因。研究[4]表明,对于直径≤3 cm的HCC患者,HCC≥2 cm的微转移和微血管浸润更明显。另外,肿瘤直径增大可能造成消融不彻底,残存的微病灶直接导致复发,这些结果均会影响患者的生存预后。
炎症在肿瘤发生发展的各个阶段均发挥重要作用,可驱动肿瘤的发生、生长、进展和转移等重要过程[17-18]。除了局部肿瘤微环境外,全身性炎症反应通过干扰组织内环境稳态从而影响肿瘤的发展,特别是肿瘤的转移[19]。血常规作为反映全身炎症反应最普遍的工具,在临床广泛应用且易于获取。单独的血细胞计数可能与整体预后没有显著关系,但由这些细胞计数组合产生的全身炎症标志物如NLR、RLR和LMR等被认为是各类癌症的独立预测因素。
淋巴细胞是机体免疫监视和免疫应答的重要组成成分,参与肿瘤的免疫反应,特别是在抗肿瘤增殖和转移的过程[20]。淋巴细胞浸润增加与癌症患者预后良好相关[21],而淋巴细胞数量减少和功能抑制可能会削弱肿瘤特异性免疫,造成利于肿瘤侵袭和转移的环境,进而影响患者预后[22-23]。中性粒细胞可直接释放炎症因子,促进肿瘤血管生成,加速肿瘤的生长和转移[24]。NLR是反映中性粒细胞促肿瘤特性与淋巴细胞抗肿瘤宿主免疫反应之间平衡的一个因素,但在炎症环境下,随着中性粒细胞增加和淋巴细胞减少,这一平衡被打破,直接导致机体抗肿瘤能力下降。这提示机体处于抗肿瘤免疫抑制状态,炎症反应将向促肿瘤进展方向发展,最终导致患者预后不良。另外,炎症可以刺激单核细胞到外周血,进而被招募到肿瘤组织并分化为肿瘤相关巨噬细胞,进一步与肿瘤细胞相互作用促进肿瘤进展[25-26]。红细胞分布宽度(red blood cell distribution width, RDW)反映了红细胞在循环中体积分布的变化。有研究[27]表明RDW升高与HCC患者无病生存率较低和OS率较差相关。而作为RDW与淋巴细胞比值, RLR升高已被证明能够预测肝功能衰竭和结肠癌的不良预后,并与肝硬化的严重程度相关[9-10, 28]。
与先前结果一致,本研究亦明确了NLR、RLR和LMR在早期小肝癌RFA后的预后价值。由于先前研究对于上述炎症标志物的分组尚无统一标准,本研究采用X-tile工具基于患者5年OS及RFS计算出3个指标的最佳截断值分别为4.1、18.3和6,据此分组后三者在患者RFS及OS方面均表现出优异的预后价值,特别是将三者结合后得到的N-R-L评分,在N-R-L评分≥1与早期HCC首次RFA后的早期复发和预后不良显著相关,因此可作为早期HCC患者RFA治疗预后不良的独立预后生物标志物。
另外,本研究的大多数患者为HBV或HCV相关HCC,机体本身存在慢性持续性炎症。肿瘤相关炎症反应刺激炎症介质的释放,加之血细胞计数异常所致的抗肿瘤免疫功能下降,为肿瘤的侵袭和转移提供有利条件。提示炎症反应越明显,N-R-L评分越高,患者预后也越差。
总之,全身炎症反应标志物N-R-L评分作为一种简单、易于获取且成本极低的指标,有望成为有用的无创生物标志物,用以预测早期HCC患者RFA术后的复发和生存。
-
[1]IDILMAN R.Management of special patient groups with hepatitis Bvirus infection:The EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines[J].Turk J Gastroenterol,2017,28(6):518-521. [2]Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases,Chinese Medical Association.The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B:A 2015 update[J].J CIin Hepatol,2015,32(12):1941-1960.(in Chinese)中华医学会肝病学分会,中华医学会感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年更新版)[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2015,32(12):1941-1960. [3]OU H,CAI S,LIU Y,et al.A noninvasive diagnostic model to assess nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Therap Adv Gastroenterol,2017,10(2):207-217. [4]CAI SH,LU SX,LIU LL,et al.Increased expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha transcribed by promoter 2 indicates a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Therap Adv Gastroenterol,2017,10(10):761-771. [5]YANG YM,CHOI EJ.Renal safety of tenofovir and/or entecavir in patients with chronic HBV monoinfection[J].Ther Clin Risk Manag,2017,13:1273-1285. [6]LIM L,THOMPSON A,PATTERSON S,et al.Five-year efficacy and safety of tenofovir-based salvage therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B who previously failed LAM/ADV therapy[J].Liver Int,2017,37(6):827-835. [7]YANG X,MA Z,ZHOU S,et al.Multiple drug transporters are involved in renal secretion of entecavir[J].Antimicrob Agents Chemother,2016,60(10):6260-6270. [8]CIHLAR T,HO ES,LIN DC,et al.Human renal organic anion transporter 1(h OAT1)and its role in the nephrotoxicity of antiviral nucleotide analogs[J].Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids,2001,20(4-7):641-648. [9]MANDKOVJ,VOLKOVM,PVEK P,et al.Entecavir interacts with influx transporters h OAT1,h CNT2,h CNT3,but Not with h OCT2:The potential for renal transporter-mediated cytotoxicity and drug-drug interactions[J].Front Pharmacol,2015,6:304. [10]FUJII T,KAWASOE K,OHTA A,et al.A case of entecavir-induced Fanconi syndrome[J].CEN Case Rep,2019,8(4):256-260. [11]WU IT,HU TH,HUNG CH,et al.Comparison of the efficacy and safety of entecavir and tenofovir in nucleos(t)ide analogue-naive chronic hepatitis B patients with high viraemia:A retrospective cohort study[J].Clin Microbiol Infect,2017,23(7):464-469. [12]WU X,CAI S,LI Z,et al.Potential effects of telbivudine and entecavir on renal function:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Virol J,2016,13:64. [13]LIN YS,SHIH SC,WANG HY,et al.Comparison of telbivudine and entecavir on the change of off-treatment e GFR after 3 years of treatment in non-cirrhotic chronic hepatitis B patients[J].BMC Gastroenterol,2017,17(1):22. [14]HE P,ZHANG D,LI H,et al.Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates apoptosis in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J].Int J Mol Med,2013,31(5):1017-1029. [15]ZHANG JB,GUO HH.Research advances in hepatitis B cirrhosis with renal injury and the application of antiviral drugs[J].J CIin Hepatol,2019,35(1):191-196.(in Chinese)张洁冰,郭宏华.乙型肝炎肝硬化合并肾损伤及抗病毒药物的应用[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2019,35(1):191-196. [16]ZHENG S,LIU L,LU J,et al.Efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection:A 2-year prospective study[J].Medicine(Baltimore),2019,98(42):e17590. [17]NEUGARTEN J,ACHARYA A,SILBIGER SR.Effect of gender on the progression of nondiabetic renal disease:A meta-analysis[J].JAm Soc Nephrol,2000,11(2):319-329. [18]BRAR A,MARKELL M.Impact of gender and gender disparities in patients with kidney disease[J].Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens,2019,28(2):178-182. [19]LIMA-POSADA I,PORTAS-CORTS C,PREZ-VILLALVAR,et al.Gender differences in the acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition[J].Sci Rep,2017,7(1):12270. [20]KRAUTBAUER S,WIEST R,LIEBISCH G,et al.Associations of systemic sphingolipids with measures of hepatic function in liver cirrhosis are related to cholesterol[J].Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat,2017,131:25-32. [21]YAN LT,WANG LL,YAO J,et al.Total bile acid-to-cholesterol ratio as a novel noninvasive marker for significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with non-cholestatic chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J].Medicine(Baltimore),2020,99(8):e19248. [22]LIU Y,FAN R,CHEN J,et al.Assessment of renal function and risk factors for renal impairment in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis[J].J South Med Univ,2014,34(4):472-476.(in Chinese)刘颖,樊蓉,陈简,等.慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染相关肝硬化患者的肾功能及危险因素分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2014,34(4):472-476. [23]CHEN YC,SU YC,LI CY,et al.13-year nationwide cohort study of chronic kidney disease risk among treatment-na6ve patients with chronic hepatitis B in Taiwan[J].BMC Nephrol,2015,16:110. 期刊类型引用(9)
1. 陈玉凤,明文,陈镜晶,王茜,李溢馨. FAR、RLR水平对乙型肝炎肝硬化并发食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血患者治疗后再出血风险的评估价值. 现代生物医学进展. 2025(01): 72-79 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 赵孟杰,邢恩涛,董源,金鹏飞,孙景武. 不可逆电穿孔和射频消融治疗原发性肝癌效果比较. 青岛大学学报(医学版). 2024(01): 110-114 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 谢亚明,梁磊,肖遵强,刘军伟,张成武,黄东胜. Naples预后评分对肝细胞癌患者肝切除术后预后的影响. 中华肝胆外科杂志. 2024(05): 341-346 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 叶建刚,彭俊文,李莉. 乳腺X线和MRI参数联合外周血RLR水平预测乳腺癌改良根治术后复发转移的价值. 中华内分泌外科杂志. 2024(03): 404-408 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 张玉霞,谢钦,魏思瑞,姜龙琳,谢丽,韩泳涛,缪艳. 炎症及营养指标对老年食管鳞癌患者术后生存的预测价值. 中华消化外科杂志. 2024(09): 1200-1208 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 张兰,李胜棉. 《肝癌新辅助治疗中国专家共识(2023版)》专家解读. 疑难病杂志. 2024(11): 1281-1286 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 潘伟华,黄腾钦,曾耿华. 经皮微波消融术和腹腔镜肝癌切除术治疗小肝癌的临床效果. 中国医学创新. 2023(17): 17-20 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 张旭,哈福双,李凤惠,高艳颖,梁静. 肝纤维化-4指数(FIB-4)联合预后营养指数(PNI)对早期肝癌射频消融术后复发及生存期的预测价值. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2023(11): 2614-2622 .  本站查看
本站查看9. 陈雪岩,乔建梁,李军,牛剑祥,赵建国,韩赛,孟兴凯. 小野寺预后营养指数对消化系统恶性肿瘤预后预测价值的研究进展. 中华消化外科杂志. 2022(10): 1390-1394 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1943 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1943 KB)


 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: