| [1] |
ESLAM M, SANYAL AJ, GEORGE J. MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158( 7): 1999- 2014. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312. |
| [2] |
COBBINA E, AKHLAGHI F. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)-pathogenesis, classification, and effect on drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters[J]. Drug Metab Rev, 2017, 49( 2): 197- 211. DOI: 10.1080/03602532.2017.1293683. |
| [3] |
DEPRINCE A, HAAS JT, STAELS B. Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease[J]. Mol Metab, 2020, 42: 101092. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101092. |
| [4] |
ALVES-BEZERRA M, COHEN DE. Triglyceride metabolism in the liver[J]. Compr Physiol, 2017, 8( 1): 1- 8. DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c170012. |
| [5] |
CHÁVEZ-TALAVERA O, TAILLEUX A, LEFEBVRE P, et al. Bile acid control of metabolism and inflammation in obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152( 7): 1679- 1694. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.055. |
| [6] |
WANG XW, SEED B. A PCR primer bank for quantitative gene expression analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2003, 31( 24): e154. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gng154. |
| [7] |
O'LEARY NA, WRIGHT MW, BRISTER JR, et al. Reference sequence(RefSeq) database at NCBI: Current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44( D1): D733- D745. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1189. |
| [8] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, RINELLA ME, SANYAL AJ, et al. From NAFLD to MAFLD: Implications of a premature change in terminology[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 3): 1194- 1198. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31420. |
| [9] |
Italian Association for the Study of the Liver(AISF). AISF position paper on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD): Updates and future directions[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2017, 49( 5): 471- 483. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.01.147. |
| [10] |
JIANG TT, SUN FF, ZENG Z, et al. Progress on metabolic associated fatty liver disease related liver cancer[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2022, 14( 3): 14- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2022.03.004. |
| [11] |
RIZZOLO D, BUCKLEY K, KONG B, et al. Bile acid homeostasis in a cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase and sterol 27-hydroxylase double knockout mouse model[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 1): 389- 402. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30612. |
| [12] |
WATANABE S, FUJITA K. Dietary hyodeoxycholic acid exerts hypolipidemic effects by reducing farnesoid X receptor antagonist bile acids in mouse enterohepatic tissues[J]. Lipids, 2014, 49( 10): 963- 973. DOI: 10.1007/s11745-014-3947-y. |
| [13] |
SONG M, MA XY, ZHANG FL, et al. Effects of hyodeoxycholic acid on growth performance, energy metabolism and fat digestion and absorption of mice[J]. Chin J Anim Nutr, 2022, 34( 6): 3983- 3990. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.06.057. |
| [14] |
SEHAYEK E, ONO JG, DUNCAN EM, et al. Hyodeoxycholic acid efficiently suppresses atherosclerosis formation and plasma cholesterol levels in mice[J]. J Lipid Res, 2001, 42( 8): 1250- 1256.
|
| [15] |
SHIH DM, SHAPOSHNIK Z, MENG YH, et al. Hyodeoxycholic acid improves HDL function and inhibits atherosclerotic lesion formation in LDLR-knockout mice[J]. FASEB J, 2013, 27( 9): 3805- 3817. DOI: 10.1096/fj.12-223008. |
| [16] |
FORMAN BM, GOODE E, CHEN J, et al. Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by farnesol metabolites[J]. Cell, 1995, 81( 5): 687- 693. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90530-8. |
| [17] |
PELLICCIARI R, COSTANTINO G, FIORUCCI S. Farnesoid X receptor: From structure to potential clinical applications[J]. J Med Chem, 2005, 48( 17): 5383- 5403. DOI: 10.1021/jm0582221. |
| [18] |
PARKS DJ, BLANCHARD SG, BLEDSOE RK, et al. Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor[J]. Science, 1999, 284( 5418): 1365- 1368. DOI: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1365. |
| [19] |
DOWNES M, VERDECIA MA, ROECKER AJ, et al. A chemical, genetic, and structural analysis of the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR[J]. Mol Cell, 2003, 11( 4): 1079- 1092. DOI: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00104-7. |
| [20] |
PELLICCIARI R, FIORUCCI S, CAMAIONI E, et al. 6alpha-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid(6-ECDCA), a potent and selective FXR agonist endowed with anticholestatic activity[J]. J Med Chem, 2002, 45( 17): 3569- 3572. DOI: 10.1021/jm025529g. |
| [21] |
SAYIN S, WAHLSTRÖM A, FELIN J, et al. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist[J]. Cell Metab, 2013, 17( 2): 225- 235. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.01.003. |
| [22] |
SUN LL, XIE C, WANG G, et al. Gut microbiota and intestinal FXR mediate the clinical benefits of metformin[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24( 12): 1919- 1929. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0222-4. |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
MUELLER M, THORELL A, CLAUDEL T, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid exerts farnesoid X receptor-antagonistic effects on bile acid and lipid metabolism in morbid obesity[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62( 6): 1398- 1404. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.034. |
| [25] |
HARRISON SA, BASHIR MR, LEE KJ, et al. A structurally optimized FXR agonist, MET409, reduced liver fat content over 12 weeks in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 1): 25- 33. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.01.047. |
| [26] |
HAN CY, RHO HS, KIM A, et al. FXR inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatocytes and ameliorates liver injury[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 24( 11): 2985- 2999. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.068. |
| [27] |
JUNG K, KIM M, SO J, et al. Farnesoid X receptor activation impairs liver progenitor cell-mediated liver regeneration via the PTEN-PI3K-AKT-mTOR axis in zebrafish[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74( 1): 397- 410. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31679. |
| [28] |
FRIEDMAN ES, LI Y, SHEN TC D, et al. FXR-dependent modulation of the human small intestinal microbiome by the bile acid derivative obeticholic acid[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155( 6): 1741- 1752. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.022. |
| [29] |
MAKRI E, CHOLONGITAS E, TZIOMALOS K. Emerging role of obeticholic acid in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22( 41): 9039- 9043. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9039. |
| [30] |
XU J, YAO X, LI X, et al. Farnesoid X receptor regulates PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, lipid metabolism, and immune response in hybrid grouper[J]. Fish Physiol Biochem, 2022, 48( 6): 1521- 1538. DOI: 10.1007/s10695-022-01130-z. |



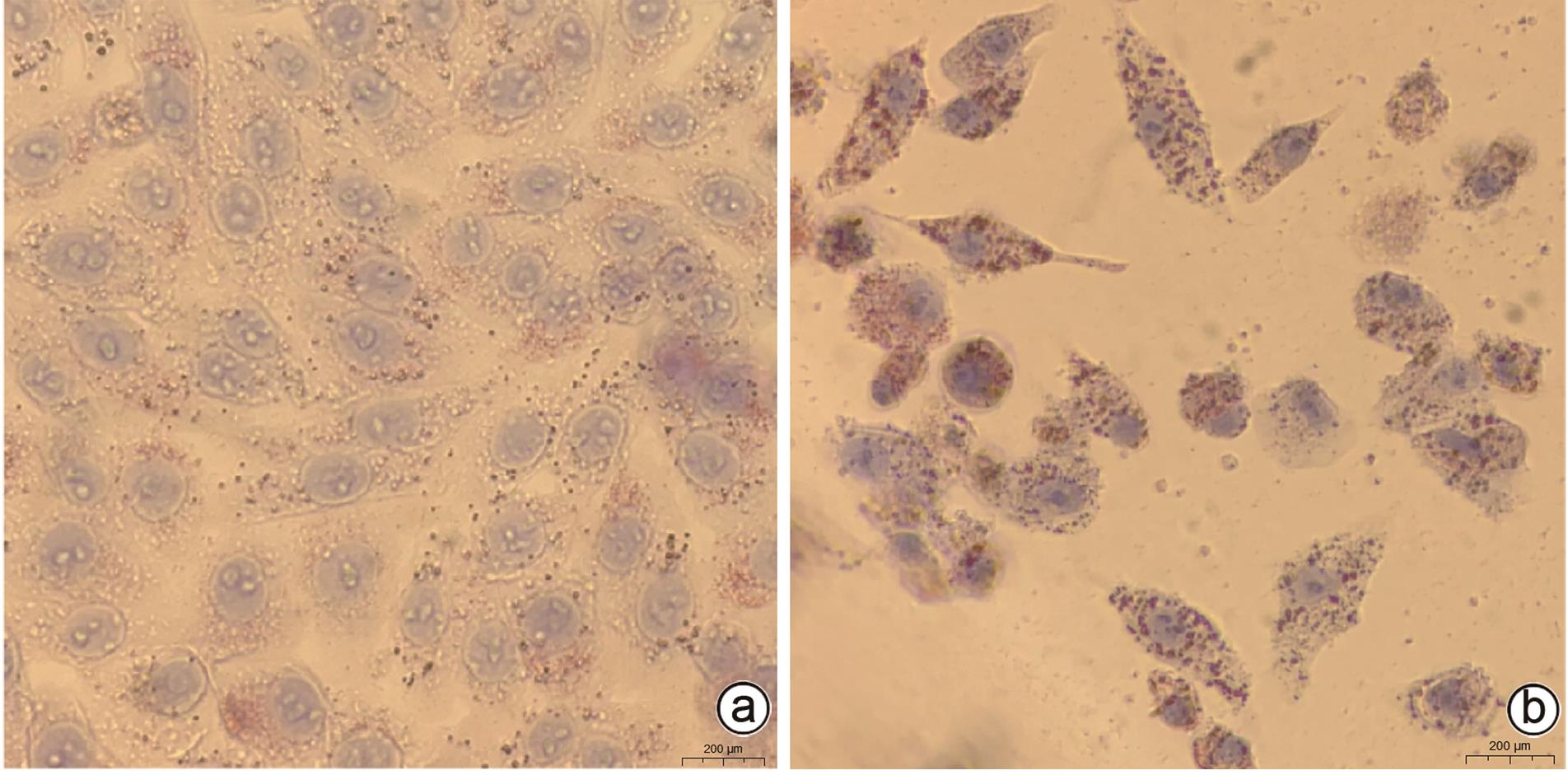




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: