|
[1]CHEON YK,LEHMAN GA.Identification of risk factors for stone recurrence after endoscopic treatment of bile duct stones[J].Eur JGastroenterol Hepatol,2006,18(18):461-464.
|
|
[2]SCHONFELS W,BUCH S,WOLK M,et al.Recurrence of gallstones after cholecystectomy is associated with ABCG5/8 genotype[J].J Gastroenterol,2013,48(3):391-396.
|
|
[3]KEIZMAN D,ISH-SHALOM M,KONIKOFF FM.The clinical significance of bile duct sludge:is it different from bile duct stones?[J].Surg Endosc,2007,21(5):769-773.
|
|
[4]SEO DB,BANG BW,JEONG S,et al.Does the bile duct angulation affect recurrence of choledocholithiasis?[J].World J Gastroenterol,2011,17(36):4118-4123.
|
|
[5]LI X,ZHU KX,ZHANG L,et al.Periampullary diverticulum may be an important factor for the occurrence and recurrence of bile duct stones[J].World J Surg,2012,36(11):2666-2669.
|
|
[6]YAMAMOTO R,TAZUMA S,KANNO K,et al.Ursodeoxycholic acid after bile duct stone removal and risk factors for recurrence:a randomized trial[J].J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci,2016,23(2):132-136.
|
|
[7]TAO YT,MENG XL,XU AM,et al.Study on the role of the activities ofβ-glucuronidase in the two type of primary cholelithiasis in the common bile duct[J].J Hepatobiliary Surg,2012,20(2):122-126.(in Chinese)陶应田,孟翔凌,徐阿曼,等.β-葡萄糖醛酸酶与两类原发性胆总管结石形成关系的研究[J].肝胆外科杂志,2012,20(2):122-126.
|
|
[8]TAKAHASHI Y,YAMAMICHI N,SHIMAMOTO T,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection is positively associated with gallstones:a large-scale cross-sectional study in Japan[J].J Gastroenterol,2014,49(5):882-889.
|
|
[9]YANG LC,HUANG BY,XUE GF,et al.Relationship between infection of clonorchis sinensis and hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases[J].Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg,2004,10(3):165-166.(in Chinese)杨六成,黄宝裕,薛桂芳,等.华支睾吸虫感染与肝胆胰外科疾病的关系[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2004,10(3):165-166.
|
|
[10]LIU XF,GUO RX,TIAN YL,et al.The relationship between HBV infection and the formation of biliary sludge and its significance[J].Chin J Gen Surg,1999,14(5):329-331.(in Chinese)刘小方,郭仁宣,田雨霖,等.乙肝病毒感染与胆泥形成的关系及其意义[J].中华普通外科杂志,1999,14(5):329-331.
|
|
[11]SONG ME,CHUNG MJ,LEE DJ,et al.Cholecystectomy for prevention of recurrence after endoscopic clearance of bile duct stones in Korea[J].Yonsei Med J,2016,57(1):132-137.
|
|
[12]JAKOBS R,HARTMANN D,KUDIS V,et al.Risk factors for symptomatic stone recurrence after transpapillary laser lithotripsy for difficult bile duct stones using a laser with a stone recognition system[J].Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2006,18(18):469-473.
|
|
[13]WU LY,WANG SH,JIA GF,et al.Risk factors for recurrent common bile duct stones after endoscopic sphincterotomy[J/CD].Chin J Digest Med Imageol:Electronic Edition,2015,5(1):5-9.(in Chinese)吴丽颖,王书海,贾国法,等.经十二指肠镜乳头括约肌切开取石术后胆总管结石复发危险因素分析[J/CD].中华消化病与影像杂志:电子版,2015,5(1):5-9.
|
|
[14]STRNAD P,FIGURA G,GRUSS R,et al.Oblique bile duct predisposes to the recurrence of bile duct stones[J].PLoS One,2013,8(1):e54601.
|
|
[15]KIM JH,KIM YS,KIM DK,et al.Short-term clinical outcomes based on risk factors of recurrence after removing common bile duct stones with endoscopic papillary large balloon dilatation[J].Clin Endosc,2011,44(2):123-128.
|
|
[16]HU B,TANG CB,SHI LH,et al.Study on relationship of cholelithiasis with Oddi sphincter peristalsis direction and physiological narrow distal segment length of choledochus[J].J North China Coal Medical College,2006,8(6):745-746.(in Chinese)胡兵,唐采白,石丽红,等.Oddi括约肌蠕动方向及胆总管远端生理狭窄段长度与胆石病成因的相关性研究[J].华北煤炭医学院学报,2006,8(6):745-746.
|
|
[17]PASPATIS GA,PARASKEVA K,VARDAS E,et al.Long-term recurrence of bile duct stones after endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation with sphincterotomy:4-year extended follow-up of a randomized trial[J].Surg Endosc,2016.[Epub ahead of print]
|
|
[18]MU HL,GAO JF,KONG QY,et al.Prognostic factors and postoperative recurrence of calculus following small-incision sphincterotomy with papillary balloon dilation for the treatment of intractable choledocholithiasis:a 72-month follow-up study[J].Dig Dis Sci,2015,60(7):2144-2149.
|
|
[19] ADMIRAND WH,SMALL DM.The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man[J].J Clin Invest,1968,47(47):1043-1052.
|
|
[20]XIE M,KOTECHA VR,ANDRADE JD,et al.Augmented cholesterol absorption and sarcolemmal sterol enrichment slow small intestinal transit in mice,contributing to cholesterol cholelithogenesis[J].J Physiol,2012,590(8):1811-1824.
|
|
[21]YANG Y,QU Q,LIU W,et al.Increased bile cholesterol content inhibits gallbladder contraction by affecting the re-distribution of CCK-1R[J].Basic Clin Med,2014,34(7):984-989.(in Chinese)杨阳,曲强,刘卫,等.胆汁中胆固醇升高通过影响CCK-1R再分布抑制胆囊收缩[J].基础医学与临床,2014,34(7):984-989.
|
|
[22]WANG HH,PORTINCASA P,WANG DQ.Molecular pathophysiology and physical chemistry of cholesterol gallstones[J].Front Biosci,2008,13(2):401-423.
|
|
[23]LI L,LI B,DING HG.Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on bile secretion after endoscopic nanobiliary drainage in patients with cholestatic liver disease of various causes[J].J Clin Hepatol,2016,32(3):522-525.(in Chinese)李磊,李冰,丁惠国.熊去氧胆酸对不同原因胆汁淤积性肝病患者鼻胆管引流术后胆汁排泌的影响[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2016,32(3):522-525.
|
|
[24]SUN Z,BO WH,JIANG P,et al.Different types of periampullary duodenal diverticula are associated with occurrence and recurrence of bile duct stones:a case-control study from a Chinese center[J].Gastroenterol Res Pract,2016,2016:9381759.
|
|
[25]KIM CW,CHANG JH,KIM JH,et al.Size and type of periampullary duodenal diverticula are associated with bile duct diameter and recurrence of bile duct stones[J].J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2013,28(5):893-898.
|
|
[26]LAU JY,LEOW CK,FUNG TM,et al.Cholecystectomy or gallbladder in situ after endoscopic sphincterotomy and bile duct stone removal in chinese patients[J].Gastroenterology,2006,130(1):96-103.
|
|
[27]LI JS,ZHANG GN,ZHONG Y.Clinical efficacy of laparoscope combined with choledochoscope in treatment of choledocholithiasis after cholesystectomy[J].Chin J Dig Surg,2015,14(2):155-156.(in Chinese)李建水,张光年,钟扬.腹腔镜联合胆道镜治疗胆囊切除术后胆总管结石的临床疗效[J].中华消化外科杂志,2015,14(2):155-156.
|
|
[28]CHEN Z,ZHANG HY,XU XB,et al.Recurrence after gallbladder-preserving cholecystolithotomy for sand-like and non-sandlike gallstones:a comparative analysis[J].J Clin Hepatol,2016,32(7):1351-1353.(in Chinese)陈智,张洪义,徐新保,等.胆囊泥沙样与非泥沙样结石保胆取石术后复发情况的比较[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2016,32(7):1351-1353.
|
|
[29]YOON H,KWON C,JEONG S,et al.Clinical significance of biliary dilatation and cholelithiasis after subtotal gastrectomy[J].Korean J Gastroenterol,2015,66(1):33-40.
|
|
[30]LIU YG.Study on risk factors for the recurrence of cholecystolithiasis after surger[J].Hainan Med J,2012,23(8):57-58.(in Chinese)刘永国.胆总管结石术后复发的相关因素分析[J].海南医学,2012,23(8):57-58.
|
|
[31]HARADA R,MAGUCHI H,TAKAHASHI K,et al.Large balloon dilation for the treatment of recurrent bile duct stones prevents short-term recurrence in patients with previous endoscopic sphincterotomy[J].J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci,2013,20(5):498-503.
|
|
[32]TAZUMA S.Epidemiology,pathogenesis,and classification of biliary stones(common bile duct and intrahepatic)[J].Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol,2006,20(6):1075-1083.
|
|
[33]TSAI TJ,LAI KH,LIN CK,et al.The relationship between gallbladder status and recurrent biliary complications in patients with choledocholithiasis following endoscopic treatment[J].J Chin Med Assoc,2012,75(11):560-566.
|
|
[34]ZHANG Z,TIAN J,LIAO Q,et al.The analysis of expression of CCK and IP3 receptors in gallstones patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Hepatogastroenterology,2014,61(136):2173-2176.
|
|
[35]KEIZMAN D,SHALOM MI,KONIKOFF FM.Recurrent symptomatic common bile duct stones after endoscopic stone extraction in elderly patients[J].Gastrointest Endosc,2006,64(1):60-65.
|
|
[36]FAN Y,WU SD,FU BB,et al.Decreased number of interstitial cells of Cajal play an important role in the declined intestinal transit during cholesterol gallstone formation in guinea pigs fed on high cholesterol diet[J].Int J Clin Exp Med,2014,7(5):1262-1268.
|
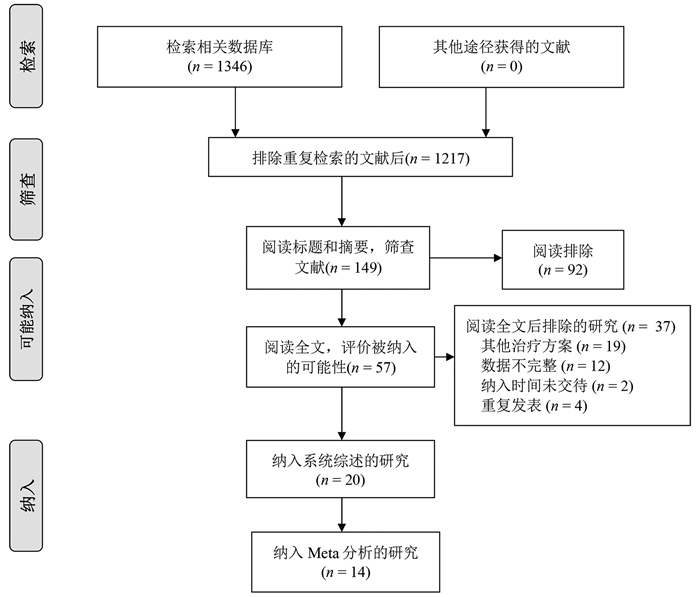








 下载:
下载:
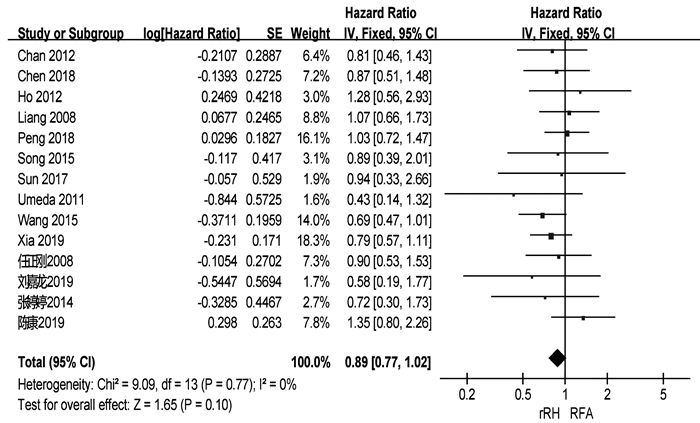
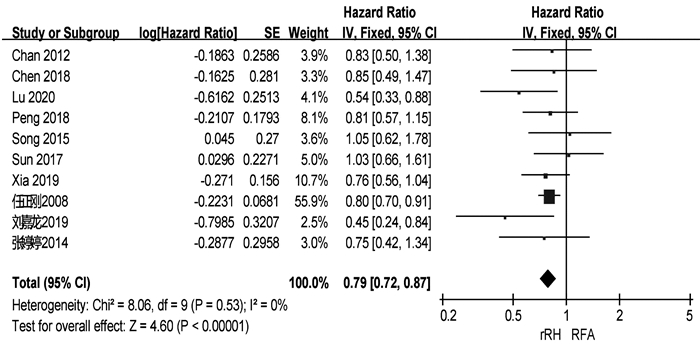
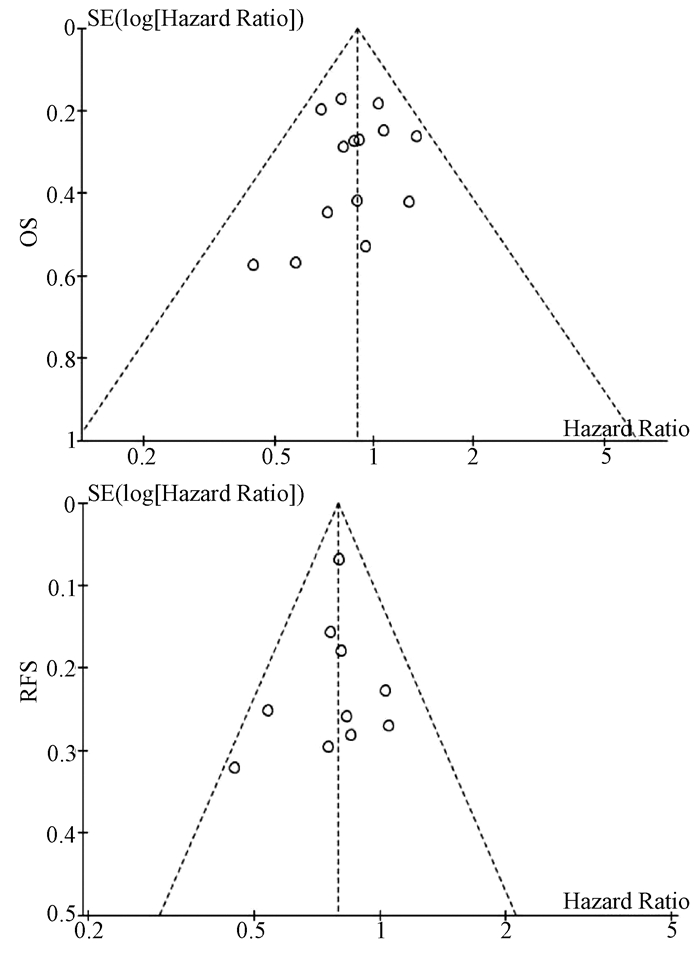

 本站查看
本站查看




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: