| [1] |
JIANG M, NI J, CUI W, et al. Emerging roles of lncRNA in cancer and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Cancers, 2019, 9(7): 1354-1366. DOI: 10.3390/cancers12123843. |
| [2] |
DALGLEISH AG, STEBBING J, ADAMSON DJ, et al. Randomised, open-label, phase Ⅱ study of gemcitabine with and without IMM-101 for advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2016, 115(7): 789-796. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2016.271. |
| [3] |
WAN J. Research progress of exosomes long chain non-coding RNA in pathogenesis and molecular diagnosis of pancreatic cancer[J]. China Med Pharm, 2021, 11(3): 42-45. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0616.2021.03.011. |
| [4] |
XIE Y, ZHANG Y, DU L, et al. Circulating long noncoding RNA act as potential novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Oncol, 2018, 12(5): 648-658. DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12188. |
| [5] |
LIU H, HAN L, LIU Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA MNX1-AS1 contributes to lung cancer progression through the miR-527/ BRF2 pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(8): 13843-13850. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28064. |
| [6] |
BANFAI B, JIA H, KHATUN J, et al. Long noncoding RNAs are rarely translated in two human cell lines[J]. Genome Res, 2012, 22(9): 1646-1657. DOI: 10.1101/gr.134767.111. |
| [7] |
TAHIRA AC, KUBRUSLY MS, FARIA MF, et al. Long noncoding intronic RNAs are differentially expressed in primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2011, 10: 141. DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-141. |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
YOSHIDA K, TODEN S, RAVINDRANATHAN P, et al. Curcumin sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine by attenuating PRC2 subunit EZH2, and the lncRNA PVT1 expression[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2017, 38(10): 1036-1046. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgx065. |
| [10] |
CAI H, YAO J, AN Y, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR acts a competing endogenous RNA to control the expression of notch3 via sponging miR-613 in pancreatic cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(20): 32905-32917. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16462. |
| [11] |
CHEN L, ZHANG J, CHEN Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA SOX2OT promotes the proliferation of pancreatic cancer by binding to FUS[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 147(1): 175-188. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.32827. |
| [12] |
AIELLO NM, BRABLETZ T, KANG Y, et al. Upholding a role for EMT in pancreatic cancer metastasis[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7661): E7-E8. DOI: 10.1038/nature22963. |
| [13] |
XING SN, CHEN W, YU HY. Research status of mesenchymal stem cells on tumorigenesis and development[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2020, 48(8): 980-982. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2020.08.45. |
| [14] |
XU J, LIU S, YANG X, et al. Paracrine HGF promotes EMT and mediates the effects of PSC on chemoresistance by activating c-Met/PI3K/Akt signaling in pancreatic cancer in vitro[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 263: 118523. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118523. |
| [15] |
TERASHIMA M, ISHIMURA A, WANNA-UDOM S, et al. MEG8 long noncoding RNA contributes to epigenetic progression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung and pancreatic cancer cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293(47): 18016-18030. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004006. |
| [16] |
WU L, ZHU L, LI Y, et al. Correction to: LncRNA MEG3 promotes melanoma growth, metastasis and formation through modulating miR-21/E-cadherin axis[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2020, 20: 158. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01239-2. |
| [17] |
CHEN CW, FU M, DU ZH, et al. Long noncoding RNA MRPL23-AS1 promotes adenoid cystic carcinoma lung metastasis[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(11): 2273-2285. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0819. |
| [18] |
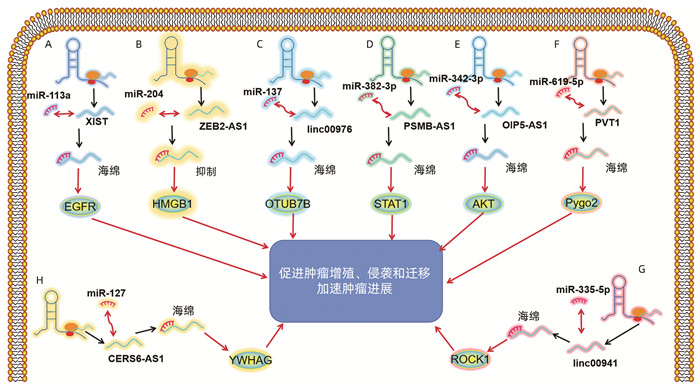
SHEN J, HONG L, YU D, et al. LncRNA XIST promotes pancreatic cancer migration, invasion and EMT by sponging miR-429 to modulate ZEB1 expression[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2019, 113: 17-26. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.05.021. |
| [19] |
GAO Y, ZHANG Z, LI K, et al. Linc-DYNC2H1-4 promotes EMT and CSC phenotypes by acting as a sponge of miR-145 in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(7): e2924. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.311. |
| [20] |
ZHENG S, CHEN H, WANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA LOC389641 promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and increases cell invasion by regulating E-cadherin in a TNFRSF10A-related manner[J]. Cancer Lett, 2016, 371(2): 354-365. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.010. |
| [21] |
WEI W, LIU Y, LU Y, et al. LncRNA XIST promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation through miR-133a/EGFR[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2017, 118(10): 3349-3358. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.25988. |
| [22] |
GAO H, GONG N, MA Z, et al. LncRNA ZEB2-AS1 promotes pancreatic cancer cell growth and invasion through regulating the miR-204/HMGB1 axis[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 116(545-551). DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.044. |
| [23] |
LEI S, HE ZW, CHEN TX, et al. Long noncoding RNA 00976 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through OTUD7B by sponging miR-137 involving EGFR/MAPK pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 470. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1388-4. |
| [24] |
ZHANG H, ZHU CH, HE ZW, et al. LncRNA PSMB8-AS1 contributes to pancreatic cancer progression via modulating miR-382-3p/STAT1/PD-L1 axis[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 39(1): 179. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-01687-8. |
| [25] |
ZHANG F, LI J, XIAO H, et al. AFAP1-AS1: A novel oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers[J]. Cell Prolif, 2018, 51(1): e12397. DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12397. |
| [26] |
WANG J, HE ZW, XU J, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00941 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by competitively binding miR-335-5p to regulate ROCK1-mediated LIMK1/Cofilin-1 signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(1): 36. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03316-w. |
| [27] |
XU J, WANG J, HE Z, et al. LncRNA CERS6-AS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis through the upregulation of YWHAG and activation of ERK signaling in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(7): 648. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03921-3. |
| [28] |
MENG XP, MA J, WANG BS, et al. Long non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 promotes pancreatic cancer cell growth through sponging miR-342-3p via AKT/ERK signaling pathway[J]. J Physiol Biochem, 2020, 76(2): 301-315. DOI: 10.1007/s13105-020-00734-4 |
| [29] |
GAI C, LIU C, WU X, et al. MT1DP loaded by folate-modified liposomes sensitizes erastin-induced ferroptosis via regulating miR-365a-3p/NRF2 axis in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(9): 751. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02939-3. |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
PAN L, ZHOU L, YIN W, et al. miR-125a induces apoptosis, metabolism disorder and migrationimpairment in pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Mfn2-related mitochondrial fission[J]. Int J Oncol, 2018, 53(1): 124-136. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4380. |
| [32] |
HAYANO M, YANG WS, CORN CK, et al. Loss of cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS) induces the transsulfuration pathway and inhibits ferroptosis induced by cystine deprivation[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2016, 23(2): 270-278. DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2015.93. |
| [33] |
ZHOU C, YI C, YI Y, et al. LncRNA PVT1 promotes gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic cancer via activating Wnt/β-catenin and autophagy pathway through modulating the miR-619-5p/Pygo2 and miR-619-5p/ATG14 axes[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 118. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01237-y. |
| [34] |
LI L, CHEN H, GAO Y, et al. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes aggressive pancreatic cancer proliferation and metastasis via the stimulation of autophagy[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2016, 15(9): 2232-2243. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0008. |
| [35] |
MAUSE SF, WEBER C. Microparticles: Protagonists of a novel communication network for intercellular information exchange[J]. Circ Res, 2010, 107(9): 1047-1057. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.226456. |
| [36] |
MAIA J, CAJA S, STRANO MORAES MC, et al. Exosome-based cell-cell communication in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2018, 6: 18. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00018. |
| [37] |
LI Z, JIANG P, LI J, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal lnc-Sox2ot promotes EMT and stemness by acting as a ceRNA in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2018, 37(28): 3822-3838. DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0237-9. |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
ZHANG H, SHI X, HUANG T, et al. Dynamic landscape and evolution of m6A methylation in human[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(11): 6251-6264. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa347. |
| [40] |
LIU Z, ZHANG JZ. Most m6A RNA modifications in protein-coding regions are evolutionarily unconserved and likely nonfunctional[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2018, 35(3): 666-675. DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msx320. |
| [41] |
KONG F, LIU X, ZHOU Y, et al. Downregulation of METTL14 increases apoptosis and autophagy induced by cisplatin in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2020, 122: 105731. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105731. |
| [42] |
ZHAO Y. Effect of m6A demethylation ALKBH5 on malignant biological behavior of pancreatic cancer and its mechanism[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018.
赵炎. m6A去甲基化酶ALKBH5对胰腺癌恶性生物学行为的影响及机制的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2018.
|
| [43] |
ZHANG C, ZHANG M, GE S, et al. Reduced m6A modification predicts malignant phenotypes and augmented Wnt/PI3K-Akt signaling in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2019, 8(10): 4766-4781. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2360. |
| [44] |
WU Y, YANG X, CHEN Z, et al. m6A-induced lncRNA RP11 triggers the dissemination of colorectal cancer cells via upregulation of Zeb1[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 87. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-019-1014-2. |













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: