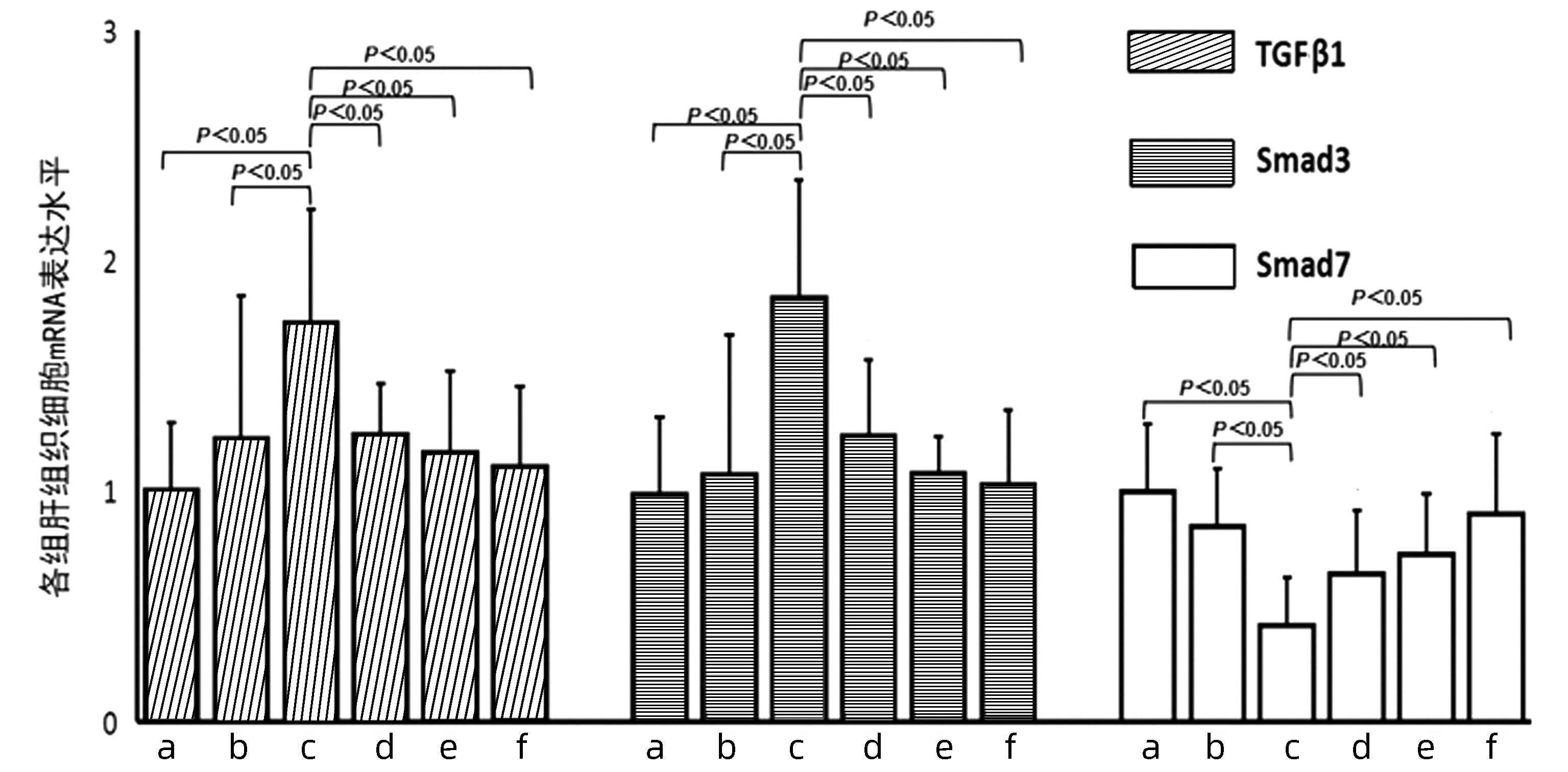
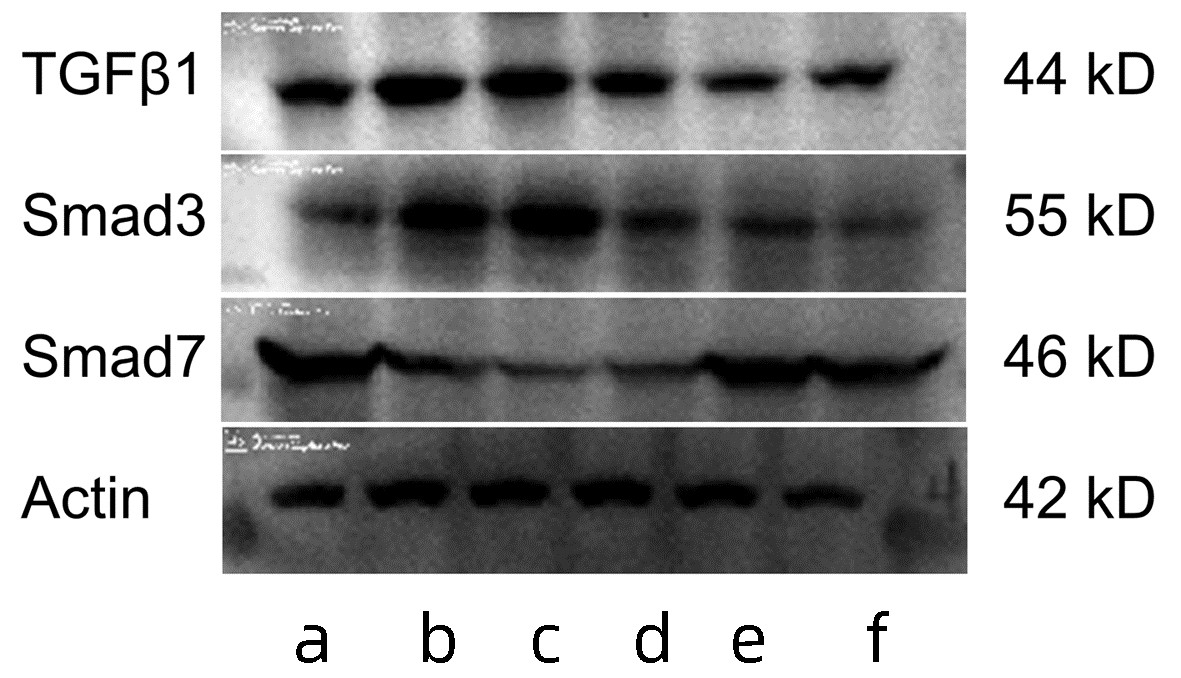
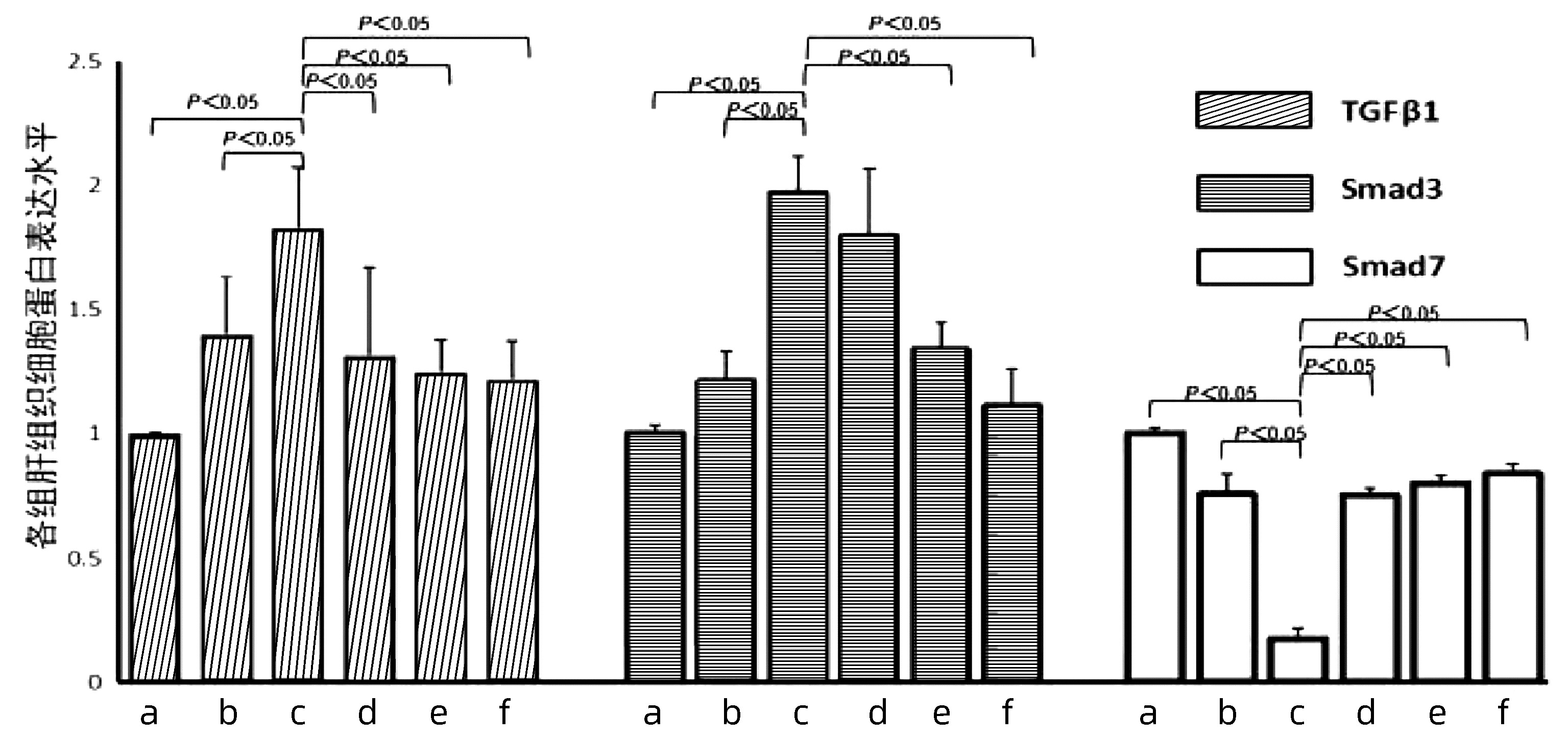
| [1] |
DONGIOVANNI P, ROMEO S, VALENTI L. Hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver: role of environmental and genetic factors[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(36): 12945-12955. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12945. |
| [2] |
LEE JH, JANG EJ, SEO HL, et al. Sauchinone attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2014, 224: 58-67. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.10.005. |
| [3] |
HAMZAVI J, EHNERT S, GODOY P, et al. Disruption of the Smad7 gene enhances CCI 4-dependent liver damage and fibrogenesis in mice[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2008, 12(5B): 2130-2144. DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00262.x. |
| [4] |
ATTA HM. Reversibility and heritability of liver fibrosis: Implications for research and therapy[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(17): 5138-5148. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5138. |
| [5] |
ELPEK GÖ. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: An update[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(23): 7260-7276. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260. |
| [6] |
OAKLEY F, MESO M, IREDALE JP, et al. Inhibition of inhibitor of kappaB kinases stimulates hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and accelerated recovery from rat liver fibrosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2005, 128(1): 108-120. DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00541-10. |
| [7] |
DOOLEY S, TEN DIJKE P. TGF-β in progression of liver disease[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2012, 347(1): 245-256. DOI: 10.1007/s00441-011-1246-y. |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
CUI W, JIN HB, LI ZW. Mechanism of the transforming growth factor-beta induction of fibronectin expression in hepatic stem-like cells[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2010, 43(1): 36-42. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23354. |
| [10] |
LATELLA G, VETUSCHI A, SFERRA R, et al. Targeted disruption of Smad3 confers resistance to the development of dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice[J]. Liver Int, 2009, 29(7): 997-1009. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02011.x. |
| [11] |
YANG XY, YANG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Effect of exogenous Smad7 gene transfected hepatic stellate cells on mRNA expression of transforming growth factor beta 1, collagen Ⅰ and collagen Ⅲ [J]. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res, 2009, 13(50): 9887-9891. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2009.50.018. |








 本站查看
本站查看






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: