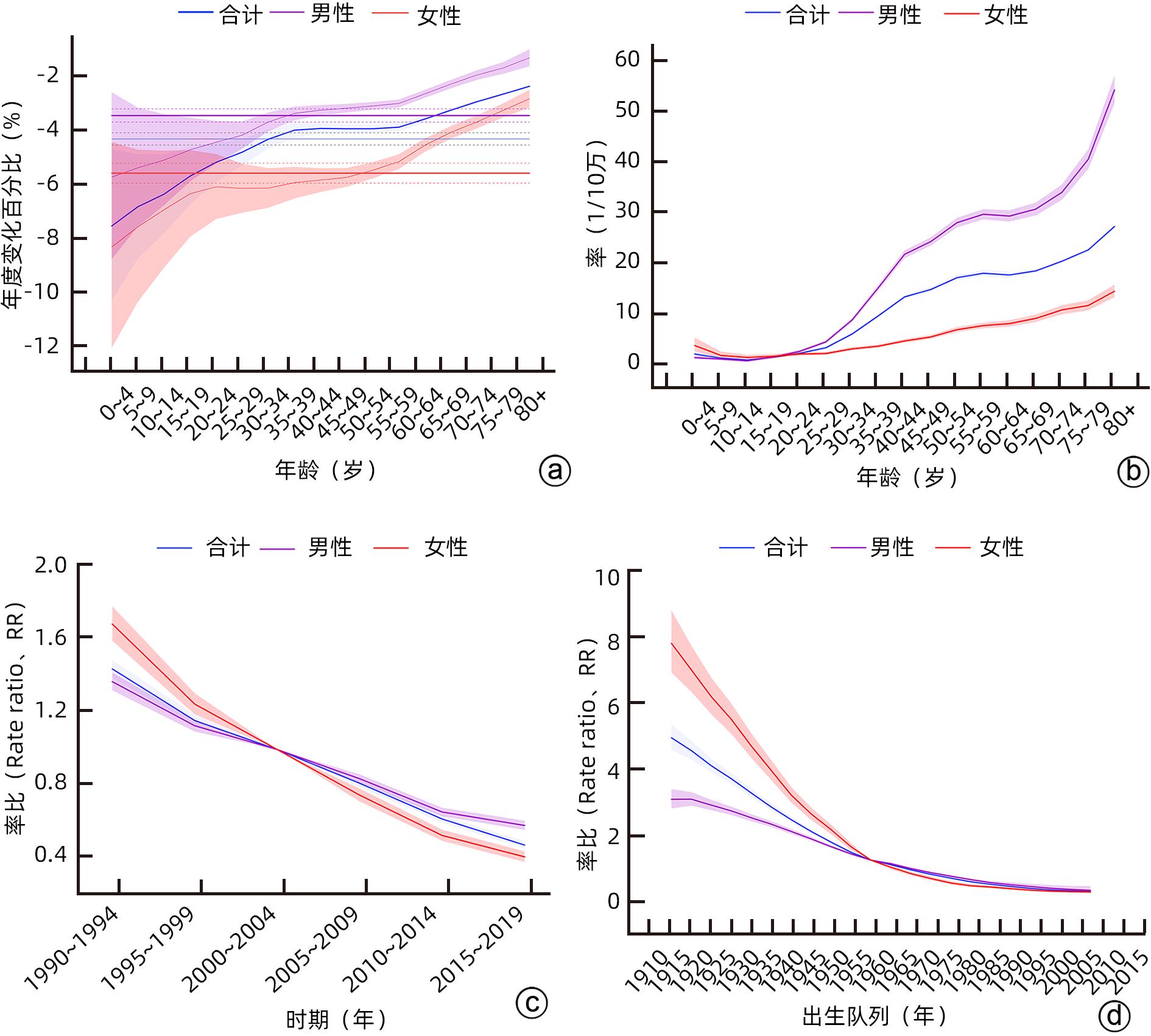
| [1] |
PAROLA M, PINZANI M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019, 65: 37- 55. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.09.002. |
| [2] |
DEVARBHAVI H, ASRANI SK, ARAB JP, et al. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 2): 516- 537. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017. |
| [3] |
XU XY, DING HG, LI WG, et al. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis(abbreviated version)[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26( 45): 7088- 7103. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7088. |
| [4] |
HUANG DQ, MATHURIN P, CORTEZ-PINTO H, et al. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: Trends, projections and risk factors[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20( 1): 37- 49. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-022-00688-6. |
| [5] |
HUANG DQ, TERRAULT NA, TACKE F, et al. Global epidemiology of cirrhosis- aetiology, trends and predictions[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20( 6): 388- 398. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-023-00759-2. |
| [6] |
2019 VIEWPOINT COLLABORATORS GBD. Five insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396( 10258): 1135- 1159. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31404-5. |
| [7] |
2019 RISK FACTORS COLLABORATORS GBD. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396( 10258): 1223- 1249. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30752-2. |
| [8] |
KIM HJ, FAY MP, FEUER EJ, et al. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates[J]. Stat Med, 2000, 19( 3): 335- 351. DOI: 3.0.co;2-z">10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(20000215)19: 3<335: aid-sim336>3.0.co;2-z.
|
| [9] |
LI HZ, DU LB. Application of Joinpoint regression model in cancer epidemiological time trend analysis[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2020, 54( 8): 908- 912. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200616-00889. |
| [10] |
XU D, HU JC, WANG SY, et al. Trends in the prevalence of hypertensive heart disease in China from 1990 to 2019: A joinpoint and age-period-cohort analysis[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 833345. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.833345. |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
ROSENBERG PS. A new age-period-cohort model for cancer surveillance research[J]. Stat Methods Med Res, 2019, 28( 10-11): 3363- 3391. DOI: 10.1177/0962280218801121. |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
2017 CIRRHOSIS COLLABORATORS GBD. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5( 3): 245- 266. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8. |
| [15] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, et al. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2023, 26( 3): 457- 478. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01. |
| [16] |
LIU ZH, LIANG XE, HOU JL. Thoughts on expert opinion on expanding antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 1): 14- 21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.01.002. |
| [17] |
WANG GS, XIE W, WAN G, et al. Diseases spectrum changes of inpatients with liver diseases in a general hospital during 15 years[J/OL]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis Electron Ed, 2021, 15( 1): 29- 36. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2021.01.006. |
| [18] |
CHEN QQ, RUI FJ, NI WJ, et al. Research progress in epidemiology and risk factors of primary liver cancer[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2024, 27( 6): 637- 642. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0479. |
| [19] |
LI YR, WANG M, HE FL, et al. Etiological and non-etiological therapies for cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 6): 1224- 1228. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.003. |
| [20] |
FALLOWFIELD JA, JIMENEZ-RAMOS M, ROBERTSON A. Emerging synthetic drugs for the treatment of liver cirrhosis[J]. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs, 2021, 26( 2): 149- 163. DOI: 10.1080/14728214.2021.1918099. |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
WANG SY, DONG C, CHANG CD, et al. Opportunities and challenges of surveillance for liver cancer in primary care institutions in China[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2023, 26( 36): 4498- 4504, 4520. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0337. |
| [23] |
TONG YN, ZHENG JM, HAN D, et al. Analysis of etiology and clinical characteristics in 986 patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2022, 27( 8): 871- 873, 880. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2022.08.008. |
| [24] |
LIN Y. Epidemiological Analysis of the Etiology of Cirrhosis in Central China[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2022.
林易. 华中地区肝硬化病因的流行病学变化趋势分析: 单中心研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2022.
|
| [25] |
HUANG DQ, MATHURIN P, CORTEZ-PINTO H, et al. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: Trends, projections and risk factors[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20( 1): 37- 49. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-022-00688-6. |
| [26] |
ZHOU EH. The Effect of Drinking on the Progress of Hepatitis B to Cirrhosis[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2021.
周恩豪. 饮酒对慢乙肝进展为肝硬化的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2021.
|
| [27] |
BUZZETTI E, PARIKH PM, GERUSSI A, et al. Gender differences in liver disease and the drug-dose gender gap[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2017, 120: 97- 108. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.03.014. |
| [28] |
YUE TT, ZHANG QQ, CAI T, et al. Trends in the disease burden of HBV and HCV infection in China from 1990-2019[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2022, 122: 476- 485. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.017. |
| [29] |
LIU YB, CHEN MK. Epidemiology of liver cirrhosis and associated complications: Current knowledge and future directions[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28( 41): 5910- 5930. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i41.5910. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: