| [1] |
LOZANO R, NAGHAVI M, FOREMAN K, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9859): 2095-2128. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 |
| [2] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B:A 2015 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 23(12): 1941-1960. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.12.002 |
| [3] |
PAPATHEODORIDIS G, VLACHOGIANNAKOS I, CHOLONGITAS E, et al. Discontinuation of oral antivirals in chronic hepatitis B: A systematic review[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63(5): 1481-1492. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28438 |
| [4] |
TERRAULT NA, LOK ASF, MCMAHON BJ, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance[J]. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md), 2018, 67(4): 1560-1599. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29800 |
| [5] |
BERSOFF-MATCHA SJ, CAO K, JASON M, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation associated with direct-acting antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus: A review of cases reported to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2017, 166(11): 792-798. DOI: 10.7326/M17-0377 |
| [6] |
ZHAO DF.Relationship between ALT, AST, HBeAg and serum HBV DNA content in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers[J/CD]. Chin J Clin Lab Sci(Electronic Edition), 2017, 6(1): 11-13. (in Chinese)
赵冬凤. 慢性乙肝病毒携带者ALT、AST及HBeAg与血清HBV DNA含量的关系[J/CD]. 临床检验杂志(电子版), 2017, 6(1): 11-13.
|
| [7] |
ZHOU LL, LIU N, LI CX, et al. Current status of the diagnosis and treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with immune control[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(5): 1134-1137. (in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.05.041 |
| [8] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007 |
| [9] |
LI Q, CHEN L, ZHOU Y. Diagnostic accuracy of liver stiffness measurement in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal or mildly elevated alanine transaminase levels[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 5224. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-23646-2 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
BEDOSSA P, POYNARD T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group[J]. Hepatology, 1996, 24(2): 289-293. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510240201 |
| [12] |
CASTERA L, FORNS X, ALBERTI A. Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using transient elastography[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48(5): 835-847. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.02.008 |
| [13] |
ZHAO Y, LI YE, QI L, et al. Antiviral curative effects of tenofovir and entecavir in treatment of aged patients with chronic hepatitis B and their regulation on inflammation factors[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2019, 45(1): 117-122. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BQEB201901022.htm |
| [14] |
LIM SG. Influencing factors of initiation and timing of discontinuation of treatment for chronic hepatitis B[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis (Electronic Edition), 2019, 13(6):528.(in Chinese)
Seng-Gee LIM. 慢性乙型肝炎治疗开始和停药时机的影响因素[J/CD]. 中华实验和临床感染病杂志(电子版), 2019, 13(6): 528.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
KUMAR M, SARIN SK, HISSAR S, et al. Virologic and histologic features of chronic hepatitis B virus-infected asymptomatic patients with persistently normal ALT[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 134(5): 1376-1384. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.075 |
| [17] |
WANG H, RU GQ, YAN R, et al. Histologic disease in chinese chronic hepatitis B patients with low viral loads and persistently normal alanine aminotransferase levels[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2016, 50(9): 790-796. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000544 |
| [18] |
BAI XX, DONG B, GAO HY, et al. Clinical features of immune escape phase and immune control phase of chronic HBV infection[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(12): 2568-2571. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.12.012 |
| [19] |
LIU WR, TIAN MX, JIN L, et al. High levels of hepatitis B surface antigen are associated with poorer survival and early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low hepatitis B viral loads[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2015, 22(3): 843-850. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-014-4043-5 |
| [20] |
TSENG T C, LIU C J, YANG H C, et al. High levels of hepatitis B surface antigen increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low HBV load[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 142(5): 1140-1149. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.02.007 |
| [21] |
CHOI GH, KIM GA, CHOI J, et al. High risk of clinical events in untreated HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with high viral load and no significant ALT elevation[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(2): 215-226. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15311 |
| [22] |
NAKAZAWA T, SHIBUYA A, TAKEUCHI A, et al. Viral level is an indicator of long-term outcome of hepatitis B virus e antigen-negative carriers with persistently normal serum alanine aminotransferase levels[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2011, 18(7): e191-e199. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21692932/ |









 本站查看
本站查看
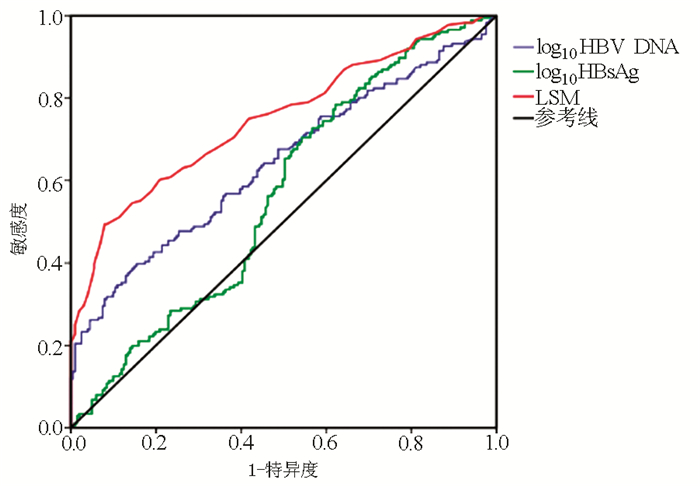




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: