| [1] |
|
| [2] |
BAJAJ JS, O'LEARY JG, REDDY KR, et al. Survival in infection-related acute-on-chronic liver failure is defined by extrahepatic organ failures[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60(1): 250-256. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27077. |
| [3] |
MOREAU R, JALAN R, GINES P, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(7): 1426-1437. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.042. |
| [4] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, CMA; Severe Liver Diseases and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, CMA. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure (2012 version)[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2012, 5(6): 321-327. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2012.06.001. |
| [5] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of ascites and complications in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(10): 1847-1863. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.10.003. |
| [6] |
ANGELI P, GINÈS P, WONG F, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: Revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62(4): 968-974. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.029. |
| [7] |
Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of end-stage liver disease complicated with infections[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(9): 1862-1872. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.09.008. |
| [8] |
FERNÁNDEZ J, ACEVEDO J, WIEST R, et al. Bacterial and fungal infections in acute-on-chronic liver failure: Prevalence, characteristics and impact on prognosis[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(10): 1870-1880. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314240. |
| [9] |
ARVANITI V, D'AMICO G, FEDE G, et al. Infections in patients with cirrhosis increase mortality four-fold and should be used in determining prognosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 139(4): 1246-1256. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.019. |
| [10] |
JALAN R, FERNANDEZ J, WIEST R, et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: A position statement based on the EASL Special Conference 2013[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60(6): 1310-1324. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.01.024. |
| [11] |
BAJAJ JS, O'LEARY JG, TANDON P, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis independent of other extrahepatic organ failures[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 15(4): 565-574. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.09.157. |
| [12] |
LIU XY, XIN SJ, CHEN J, et al. Significance of liver failure staging in predicting the prognosis of HBV-acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Acad J Chin PLA Med Sch, 2014, 35(6): 521-524, 544. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2014.06.001. |
| [13] |
GUPTA S, JASWANI P, SHARMA RK, et al. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic biomarker of sepsis: A tertiary care centre experience[J]. J Infect Public Health, 2019, 12(3): 323-329. DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.11.004. |
| [14] |
CHOI JJ, MCCARTHY MW. Novel applications for serum procalcitonin testing in clinical practice[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2018, 18(1): 27-34. DOI: 10.1080/14737159.2018.1407244. |










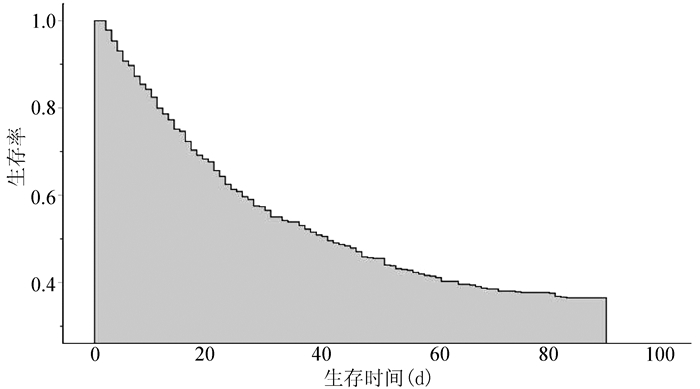




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: