| [1] |
|
| [2] |
VIOLI F, CORAZZA GR, CALDWELL SH, et al. Portal vein thrombosis relevance on liver cirrhosis: Italian venous thrombotic events registry[J]. Intern Emerg Med, 2016, 11(8): 1059-1066. DOI: 10.1007/s11739-016-1416-8. |
| [3] |
VILLA E, CAMMÀ C, MARIETTA M, et al. Enoxaparin prevents portal vein thrombosis and liver decompensation in patients with advanced cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 143(5): 1253-1260. e4. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.07.018. |
| [4] |
VIOLI F, FERRO D. Clotting activation and hyperfibrinolysis in cirrhosis: Implication for bleeding and thrombosis[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2013, 39(4): 426-433. DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1334144. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
WANG JT, ZHAO HY, LIU YL. Portal vein thrombosis[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2005, 4(4): 515-518.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG ZM, LAI EC, ZHANG C, et al. The strategies for treating primary hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus[J]. Int J Surg, 2015, 20: 8-16. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.05.009. |
| [8] |
AKKIZ H, CARR BI, BAG HG, et al. Serum levels of inflammatory markers CRP, ESR and albumin in relation to survival for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Clin Pract, 2021, 75(2): e13593. DOI: 10.1111/ijcp.13593. |
| [9] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(1): 182-236. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019. |
| [10] |
Hepatobiliary Disease Study Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus for management of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis(2020, Shanghai)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(12): 2667-2674. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.007. |
| [11] |
NORTHUP PG, GARCIA-PAGAN JC, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Vascular liver disorders, portal vein thrombosis, and procedural bleeding in patients with liver disease: 2020 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(1): 366-413. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31646. |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
BAǦ IRSAKÇ I E, ŞAHIN E, ATABEY N, et al. Role of albumin in growth inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncology, 2017, 93(2): 136-142. DOI: 10.1159/000471807. |
| [14] |
JOHNSON C, HAN Y, HUGHART N, et al. Interleukin-6 and its receptor, key players in hepatobiliary inflammation and cancer[J]. Transl Gastrointest Cancer, 2012, 1(1): 58-70. DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2224-4778.2011.11.02. |
| [15] |
JANG JW, OH BS, KWON JH, et al. Serum interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cytokine, 2012, 60(3): 686-693. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.07.017. |
| [16] |
GRIVENNIKOV SI, GRETEN FR, KARIN M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer[J]. Cell, 2010, 140(6): 883-899. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025. |
| [17] |
BUDHU A, WANG XW. The role of cytokines in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2006, 80(6): 1197-1213. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0506297. |
| [18] |
KARIN M, GRETEN FR. NF-kappaB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2005, 5(10): 749-759. DOI: 10.1038/nri1703. |
| [19] |
HE G, KARIN M. NF-κB and STAT3-key players in liver inflammation and cancer[J]. Cell Res, 2011, 21(1): 159-168. DOI: 10.1038/cr.2010.183. |
| [20] |
HUANG X, FAN X, ZHANG R, et al. Systemic inflammation and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients with gastroesophageal varices[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 32(3): 401-405. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001526. |
| [21] |
CASTELL JV, GÓMEZ-LECHÓN MJ, DAVID M, et al. Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: Regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6[J]. Hepatology, 1990, 12(5): 1179-1186. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840120517. |
| [22] |
MCKEOWN DJ, BROWN DJ, KELLY A, et al. The relationship between circulating concentrations of C-reactive protein, inflammatory cytokines and cytokine receptors in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2004, 91(12): 1993-1995. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602248. |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
BELL S, MEHTA G, MOORE K, et al. Ten-year alcohol consumption typologies and trajectories of C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist over the following 12 years: A prospective cohort study[J]. J Intern Med, 2017, 281(1): 75-85. DOI: 10.1111/joim.12544. |
| [25] |
CARR BI, AKKIZ H, GUERRA V, et al. C-reactive protein and hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of its relationships to tumor factors[J]. Clin Pract (Lond), 2018, 15(Spec Issue): 625-634. DOI: 10.4172/clinical-practice.1000409. |
| [26] |
BATLIVALA SP. Focus on diagnosis: The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the C-reactive protein test[J]. Pediatr Rev, 2009, 30(2): 72-74. DOI: 10.1542/pir.30-2-72. |
| [27] |
PINATO DJ, NORTH BV, SHARMA R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: The prognostic nutritional index (PNI)[J]. Br J Cancer, 2012, 106(8): 1439-1445. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.92. |
| [28] |
LI X, CHEN ZH, XING YF, et al. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio acts as a prognostic factor for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(4): 2263-2269. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-2833-9. |










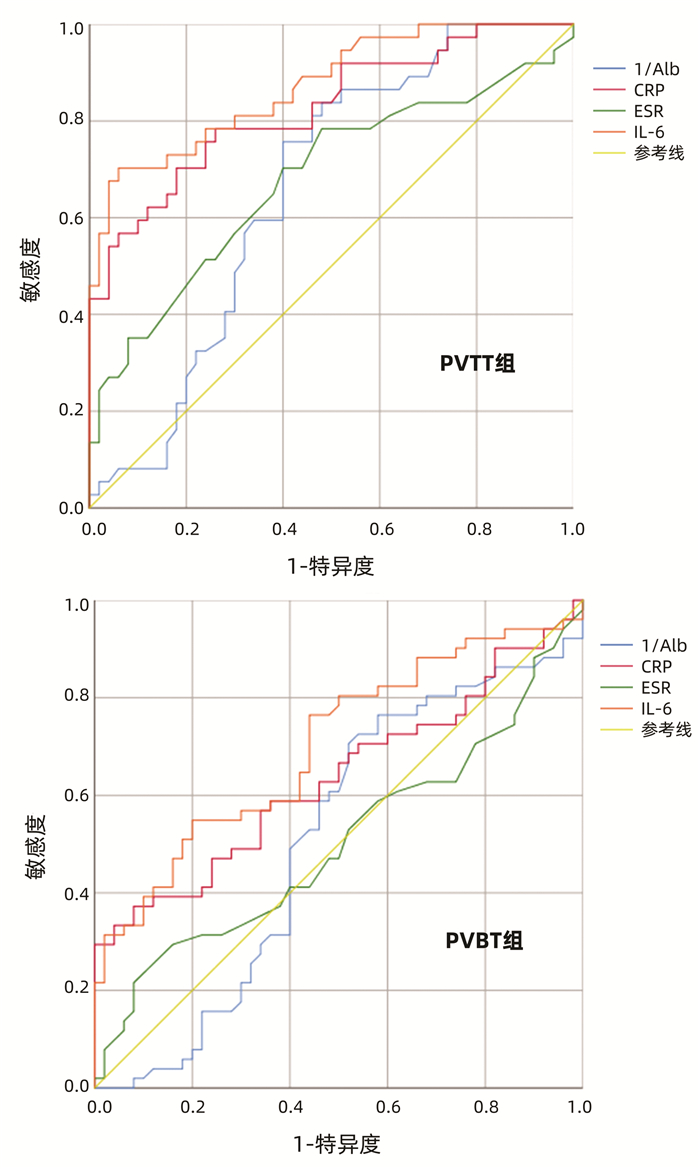




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: