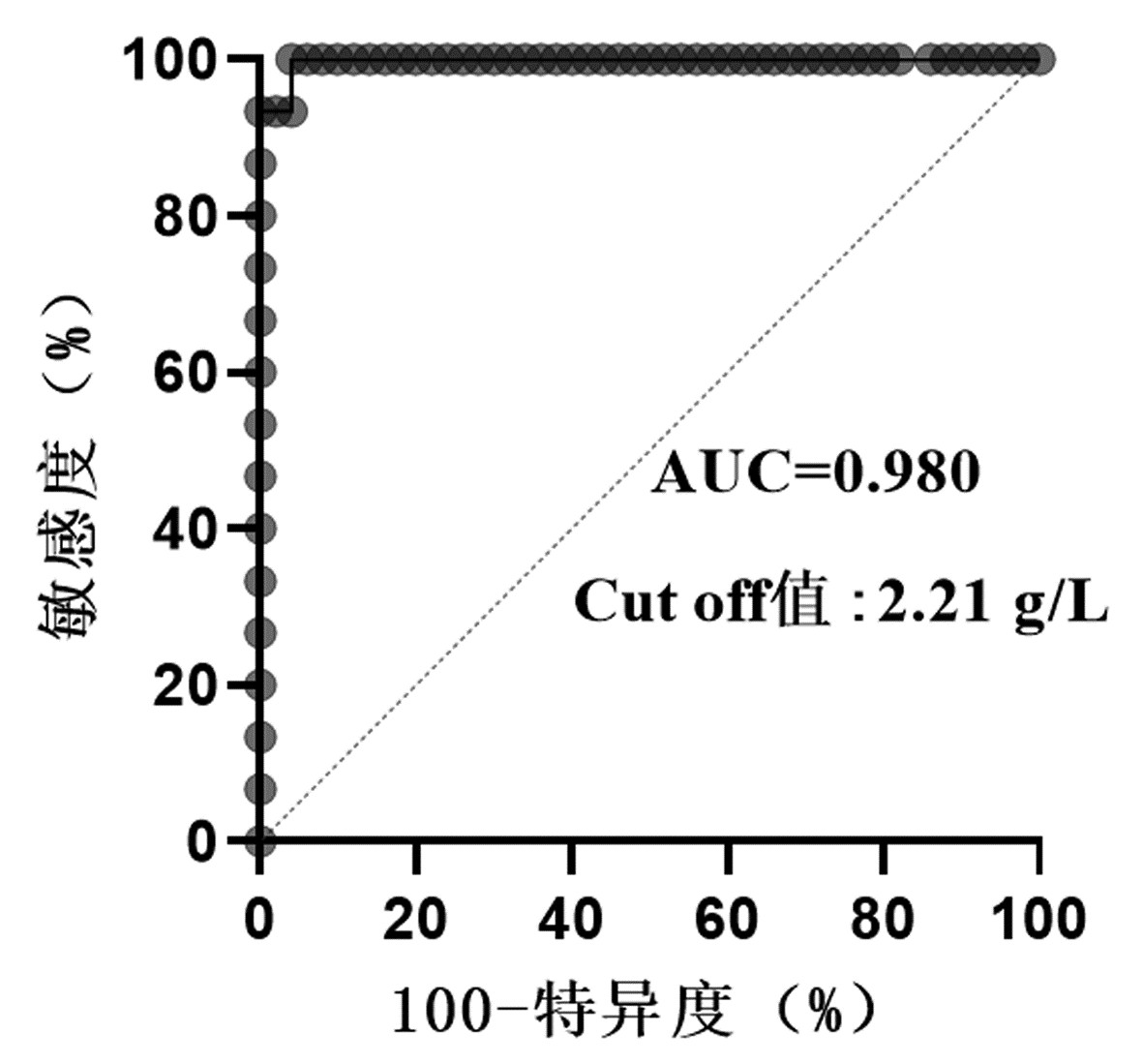
| [1] |
LANZILLOTTA M, MANCUSO G, DELLA-TORRE E. Advances in the diagnosis and management of IgG4 related disease[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369: m1067. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.m1067. |
| [2] |
YANG C, LI J, ZHANG YY, et al. Imaging findings of IgG4-related sclerosing mass pancreatitis and analysis of misdiagnosis[J]. Clin Misdiagn Misther, 2021, 305(1): 13-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2021.01.004. |
| [3] |
DELLA-TORRE E, LANZILLOTTA M, DOGLIONI C. Immunology of IgG4-related disease[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2015, 181(2): 191-206. DOI: 10.1111/cei.12641. |
| [4] |
WALLACE ZS, ZHANG Y, PERUGINO CA, et al. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: an analysis of two international cross- sectional cohorts[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78(3): 406-412. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214603. |
| [5] |
LANZILLOTTA M, CAMPOCHIARO C, MANCUSO G, et al. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease reflect different prognostic outcomes[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2020, 59(9): 2435-2442. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa221. |
| [6] |
MILOSLAVSKY EM, NADEN RP, BIJLSMA JW, et al. Development of a Glucocorticoid Toxicity Index (GTI) using multicriteria decision analysis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76(3): 543-546. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210002. |
| [7] |
GHAZALE A, CHARI ST, ZHANG L, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: clinical profile and response to therapy[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 134(3): 706-715. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.12.009. |
| [8] |
OTSUKI M, CHUNG JB, OKAZAKI K, et al. Asian diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: consensus of the Japan-Korea Symposium on Autoimmune Pancreatitis[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2008, 43(6): 403-408. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-008-2205-6. |
| [9] |
WALLACE ZS, NADEN RP, CHARI S, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020, 79(1): 77-87. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216561. |
| [10] |
ZHANG DH, ZHAO J. Pathogenesis of immunoglobulin G4-related hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(6): 1401-1405. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.050. |
| [11] |
OKAZAKI K, UCHIDA K, IKEURA T, et al. Current concept and diagnosis of IgG4-related disease in the hepato-bilio-pancreatic system[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2013, 48(3): 303-314. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-012-0744-3. |
| [12] |
TANAKA A. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Gut Liver, 2019, 13(3): 300-307. DOI: 10.5009/gnl18085. |
| [13] |
XU WL, LING YC, WANG ZK, et al. Diagnostic performance of serum IgG4 level for IgG4-related disease: A meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6(2): 32035. DOI: 10.1038/srep32035. |
| [14] |
KHOSROSHAHI A, WALLACE ZS, CROWE JL, et al. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2015, 67(7): 1688-1699. DOI: 10.1002/art.39132. |
| [15] |
BERNASCONI L, MUNDWILER E, REGENASS S, et al. Variable and inaccurate serum IgG4 levels resulting from lack of standardization in IgG subclass assay calibration[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2019, 57(11): 1777-1783. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2019-0261. |
| [16] |
TANG J, CAI S, YE C, et al. Biomarkers in IgG4-related disease: A systematic review[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2020, 50(2): 354-359. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.06.018. |
| [17] |
VALENZUELA NM, SCHAUB S. The biology of IgG subclasses and their clinical relevance to transplantation[J]. Transplantation, 2018, 102(1S Suppl 1): S7-S13. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001816. |
| [18] |
USAMI Y, SUGANO M, UEHARA T, et al. Cut-off values of serum IgG4 among three reagents, including a novel IgG4 reagent: A multicenter study[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 7280. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86024-5. |
| [19] |
ZEGERS I, KELLER T, SCHREIBER W, et al. Characterization of the new serum protein reference material ERM-DA470k/IFCC: Value assignment by immunoassay[J]. Clin Chem, 2010, 56(12): 1880-1888. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.148809. |










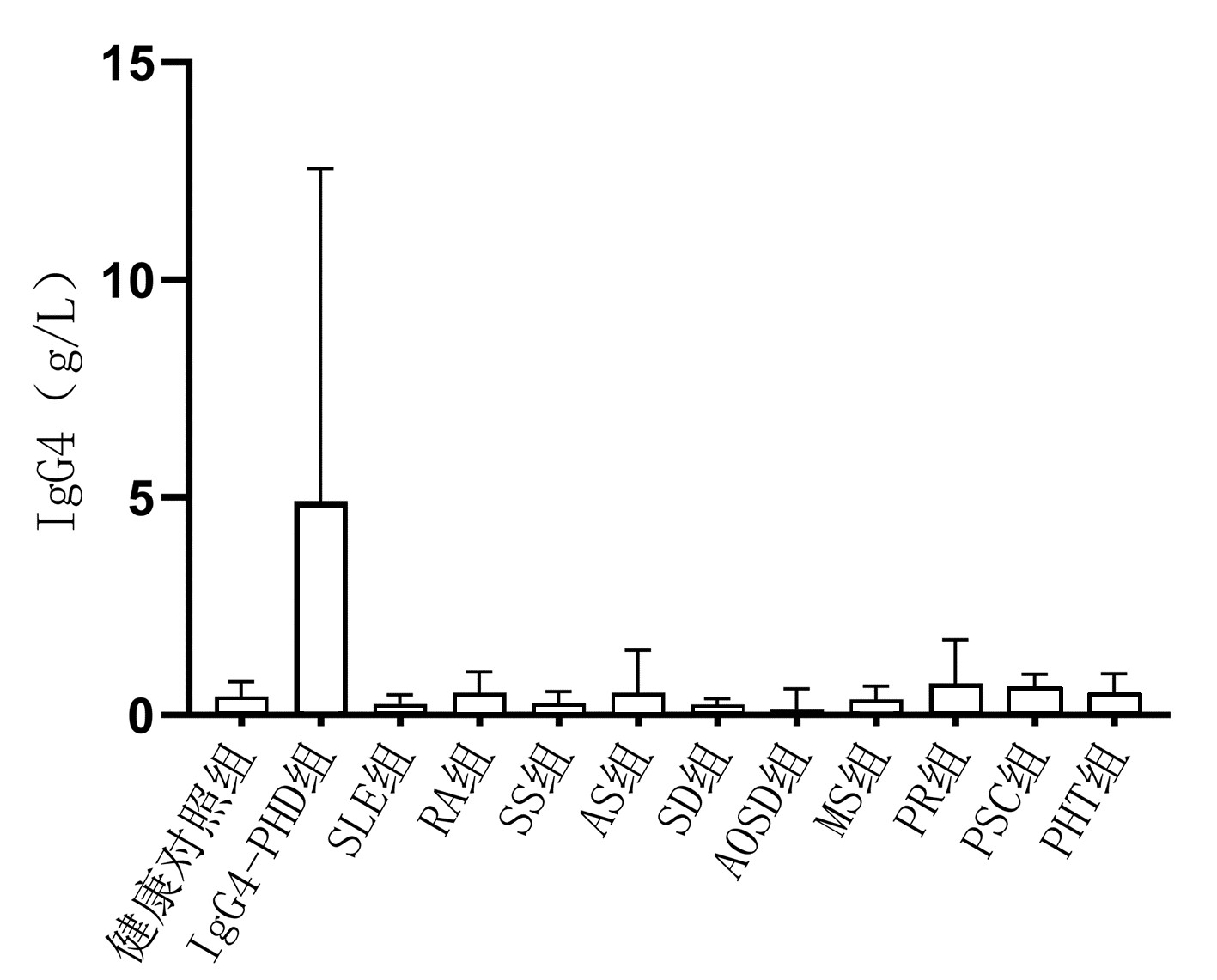




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: