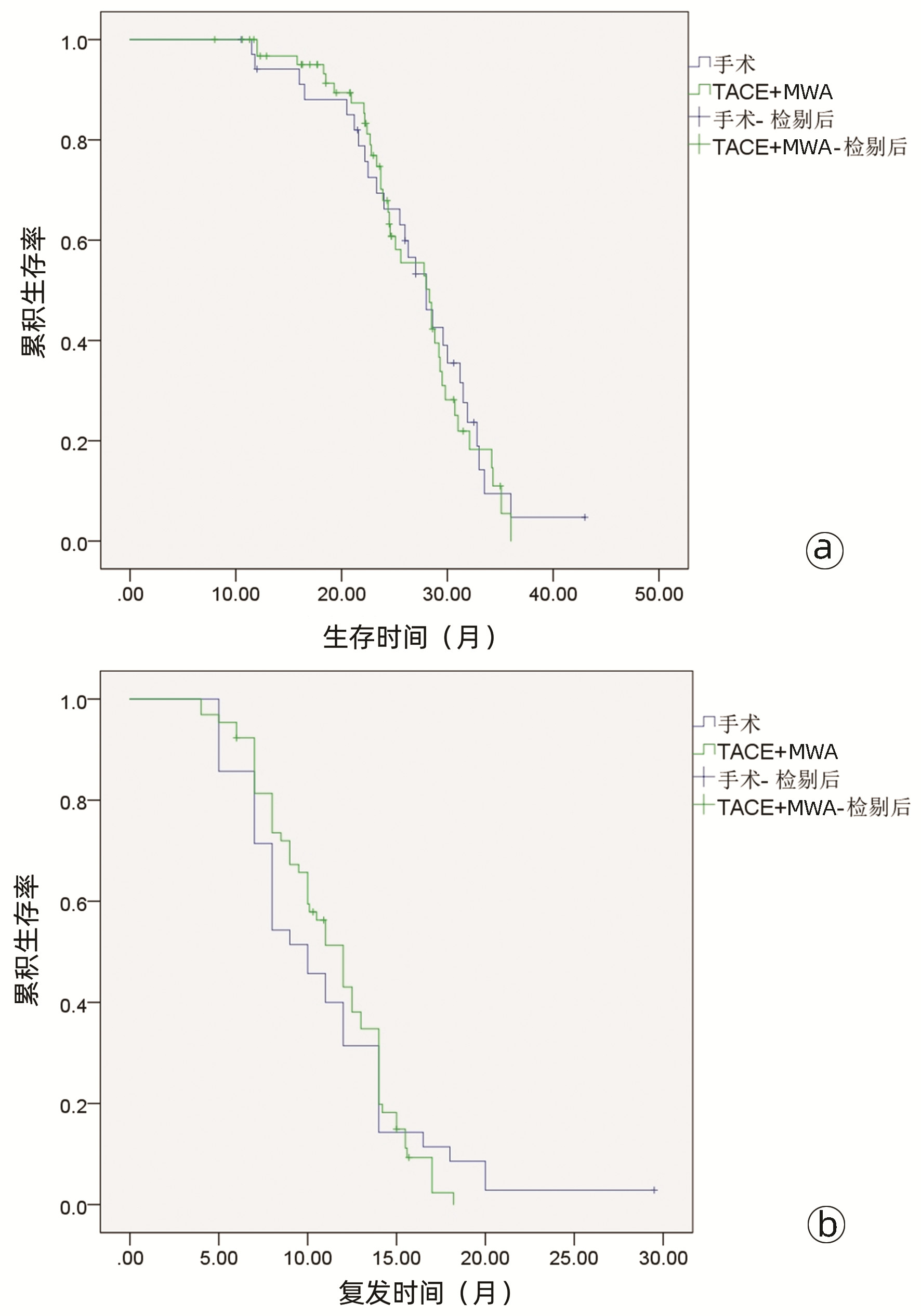
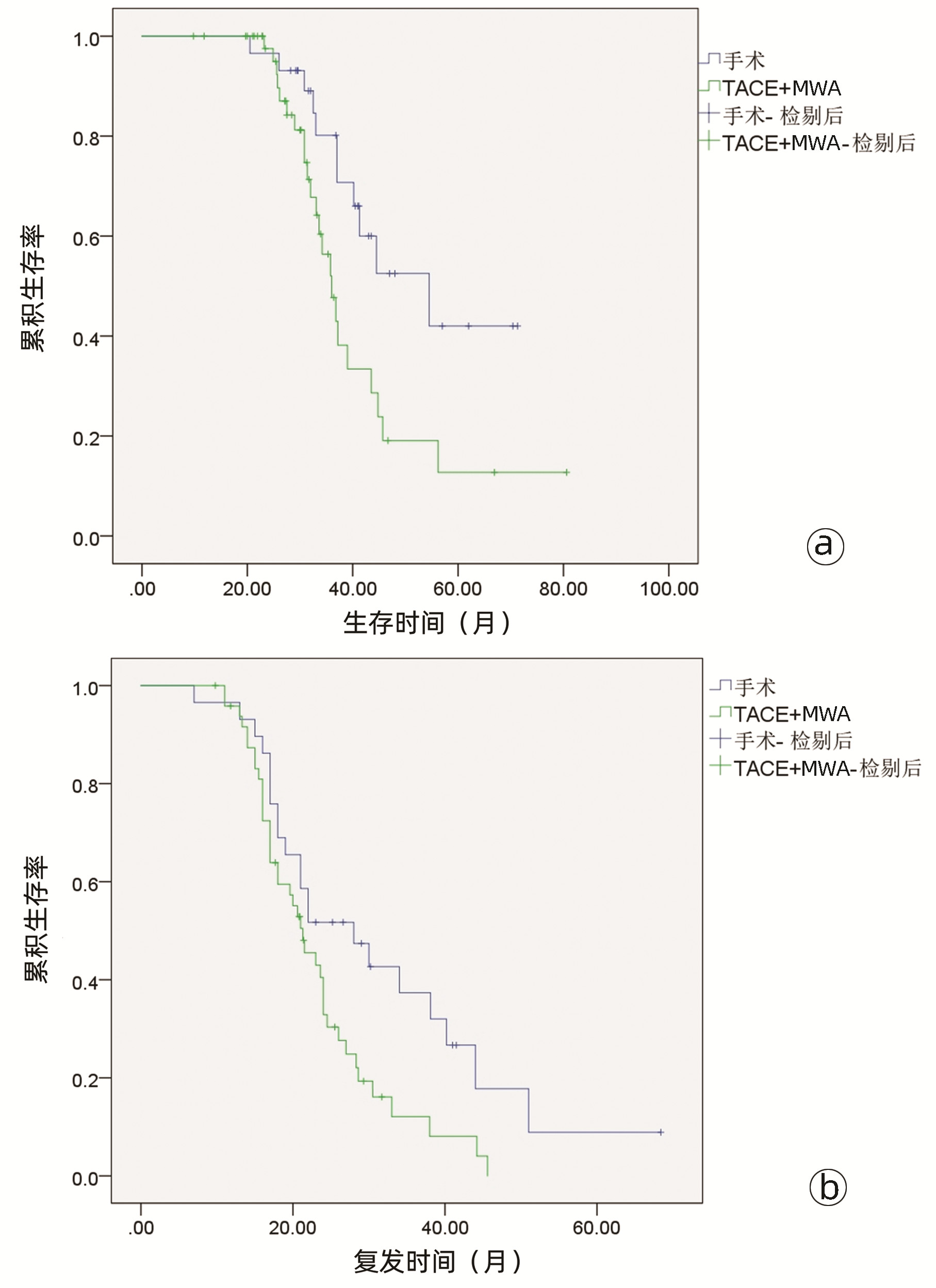
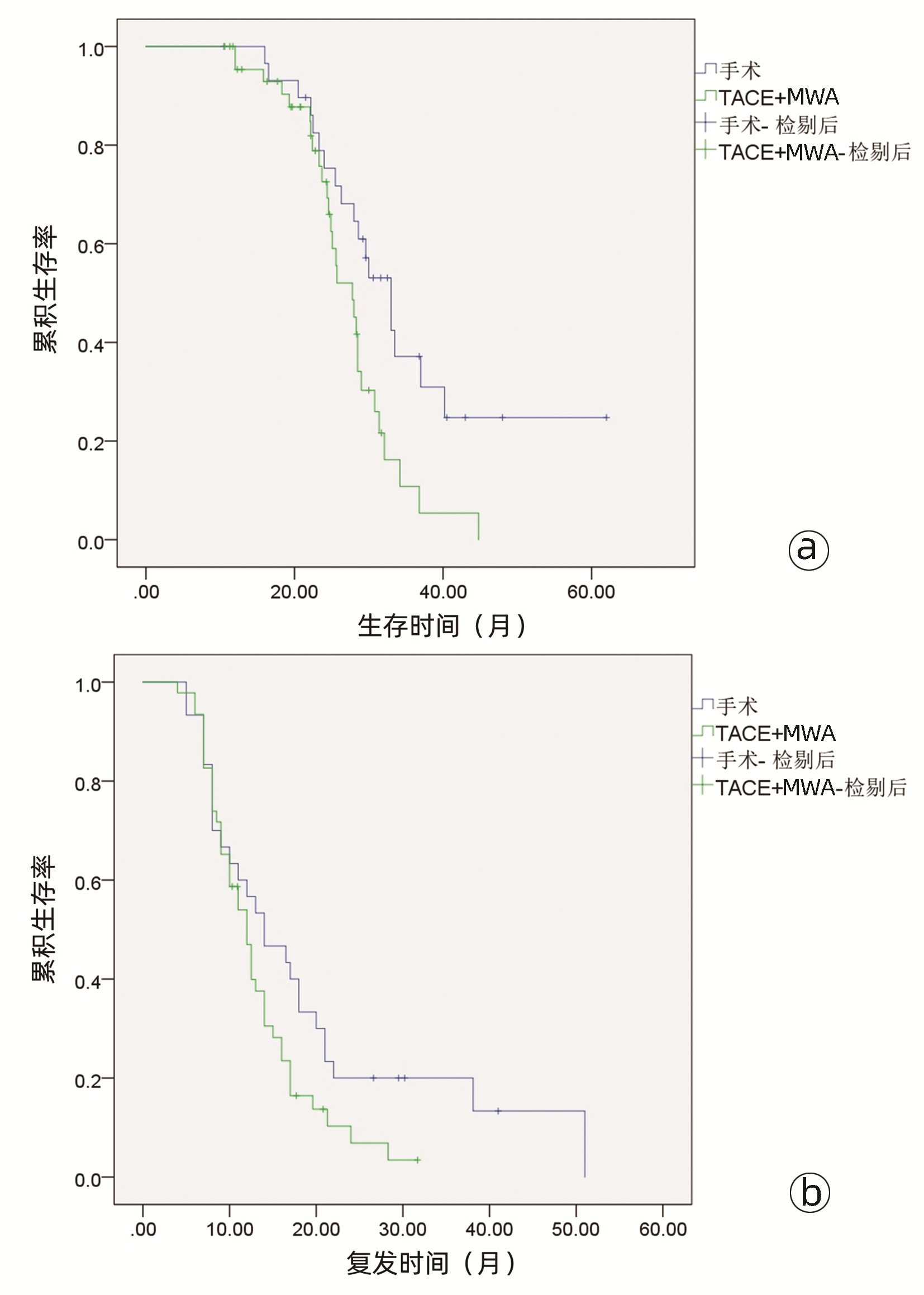
| [1] |
LURJE I, CZIGANY Z, BEDNARSCH J, et al. Treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma—a multidisciplinary approach[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(6): 1465. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20061465. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
GUPTA S, KHAN S, KAWKA M, et al. Clinical utility of clonal origin determination in managing recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 15(10): 1159-1167. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1967144. |
| [4] |
ZHENG J, CAI J, TAO L, et al. Comparison on the efficacy and prognosis of different strategies for intrahepatic recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis[J]. Int J Surg, 2020, 83: 196-204. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.09.031. |
| [5] |
RIZZO A, RICCI AD, BRANDI G. Immune-based combinations for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: shaping the direction of first-line therapy[J]. Future Oncol, 2021, 17(7): 755-757. DOI: 10.2217/fon-2020-0986. |
| [6] |
WANG X, LIANG H, LU Z. Efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization compared with radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation[J]. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol, 2020, 29(6): 344-352. DOI: 10.1080/13645706.2019.1649286. |
| [7] |
JIN YJ, LEE JW, LEE OH, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization versus surgery/radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma with or without microvascular invasion[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 29(5): 1056-1064. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12507. |
| [8] |
TUNG-PING POON R, FAN ST, WONG J. Risk factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2000, 232(1): 10-24. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-200007000-00003. |
| [9] |
PENG ZW, ZHANG YJ, LIANG HH, et al. Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sequential transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and RF ablation versus RF ablation alone: a prospective randomized trial[J]. Radiology, 2012, 262(2): 689-700. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.11110637. |
| [10] |
European Association for Study of Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48(5): 599-641. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.12.021. |
| [11] |
HEIMBACH JK, KULIK LM, FINN RS, et al. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(1): 358-380. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29086. |
| [12] |
EISENHAUER EA, THERASSE P, BOGAERTS J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1)[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2009, 45(2): 228-247. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026. |
| [13] |
DINDO D, DEMARTINES N, CLAVIEN PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey[J]. Ann Surg, 2004, 240(2): 205-213. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. |
| [14] |
CHO JY, HAN HS, CHOI Y, et al. Association of remnant liver ischemia with early recurrence and poor survival after liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. JAMA Surg, 2017, 152(4): 386-392. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2016.5040. |
| [15] |
CALDERARO J, PETITPREZ F, BECHT E, et al. Intra-tumoral tertiary lymphoid structures are associated with a low risk of early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(1): 58-65. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.09.003. |
| [16] |
JUNG SM, KIM JM, CHOI GS, et al. Characteristics of early recurrence after curative liver resection for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2019, 23(2): 304-311. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-018-3927-2. |
| [17] |
ZHANG X, LI C, WEN T, et al. Appropriate treatment strategies for intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma initially within the Milan criteria: according to the recurrence pattern[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 27(8): 933-940. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000383. |
| [18] |
PENG Z, CHEN S, WEI M, et al. Advanced recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: Treatment with sorafenib alone or in combination with transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation[J]. Radiology, 2018, 287(2): 705-714. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2018171541. |
| [19] |
LIU Y, REN Y, GE S, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization in treatment-naïve and recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity-matched outcome and risk signature analysis[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 662408. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.662408. |
| [20] |
TANG C, SHEN J, FENG W, et al. Combination therapy of radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016, 95(20): e3754. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003754. |
| [21] |
YUAN W, YANG MJ, XU J, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transarterial chemoembolization for specially located small hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2018, 17: 1533033818788529. DOI: 10.1177/1533033818788529. |
| [22] |
YAN L, REN Y, QIAN K, et al. Sequential transarterial chemoembolization and early radiofrequency ablation improves clinical outcomes for early-intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma in a 10-year single-center comparative study[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21(1): 182. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01765-x. |
| [23] |
HASSANIN TM, FOUAD Y, HASSNINE A, et al. Quality of life after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma compared with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization alone[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2021, 22(4): 1255-1261. DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.4.1255. |
| [24] |
JIANG C, CHENG G, LIAO M, et al. Individual or combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a time-to-event meta-analysis[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19(1): 81. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-021-02188-4. |
| [25] |
MATSUDA M, FUJⅡ H, KONO H, et al. Surgical treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma based on the mode of recurrence: repeat hepatic resection or ablation are good choices for patients with recurrent multicentric cancer[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg, 2001, 8(4): 353-359. DOI: 10.1007/s005340170008. |
| [26] |
HUANG ZY, LIANG BY, XIONG M, et al. Long-term outcomes of repeat hepatic resection in patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma and analysis of recurrent types and their prognosis: a single-center experience in China[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2012, 19(8): 2515-2525. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-012-2269-7. |
| [27] |
ZHENG X, REN Y, HU H, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation versus repeat hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection: A 10-year single-center comparative study[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 713432. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.713432. |
| [28] |
BRUIX J, TAKAYAMA T, MAZZAFERRO V, et al. Adjuvant sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma after resection or ablation (STORM): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(13): 1344-1354. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00198-9. |
| [29] |
LUO P, WU S, YU Y, et al. Current status and perspective biomarkers in AFP negative HCC: Towards screening for and diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma at an earlier stage[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2020, 26(2): 599-603. DOI: 10.1007/s12253-019-00585-5. |
| [30] |
ZHENG Y, ZHU M, LI M. Effects of alpha-fetoprotein on the occurrence and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2020, 146(10): 2439-2446. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03331-6. |
| [31] |
CHEN ZH, ZHANG XP, ZHOU TF, et al. Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization improves survival outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2019, 45(11): 2188-2196. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.06.031. |















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: