| [1] |
LI J, ZOU B, YEO YH, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(5): 389-398. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30039-1. |
| [2] |
ZHENG Q, ZOU B, WU Y, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: prevalence of hepatic steatosis, fibrosis and associated factors in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 54(9): 1100-1109. DOI: 10.1111/apt.16595. |
| [3] |
KLEINER DE, BRUNT EM, VAN NATTA M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2005, 41(6): 1313-1321. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20701. |
| [4] |
WANG MM, WANG GS, SHEN F, et al. Hepatic steatosis is highly prevalent in hepatitis B patients and negatively associated with virological factors[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59(10): 2571-2579. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-014-3180-9. |
| [5] |
SCHEUER PJ. Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: a need for reassessment[J]. J Hepatol, 1991, 13(3): 372-374. DOI: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90084-o. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
SARIN SK, KUMAR M, LAU GK, et al. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: a 2015 update[J]. Hepatol Int, 2016, 10(1): 1-98. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-015-9675-4. |
| [8] |
LEE MH, YANG HI, LIU J, et al. Prediction models of long-term cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B patients: risk scores integrating host and virus profiles[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(2): 546-554. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26385. |
| [9] |
WONG GL, CHAN HL, YU Z, et al. Coincidental metabolic syndrome increases the risk of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis B-a prospective cohort study with paired transient elastography examinations[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 39(8): 883-893. DOI: 10.1111/apt.12658. |
| [10] |
YEN YH, CHANG KC, TSAI MC, et al. Elevated body mass index is a risk factor associated with possible liver cirrhosis across different etiologies of chronic liver disease[J]. J Formos Med Assoc, 2018, 117(4): 268-275. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfma.2017.09.002. |
| [11] |
CHEN YC, HSU CW, JENG WJ, et al. Advanced liver fibrosis is associated with necroinflammatory grade but not hepatic steatosis in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(12): 4492-4500. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06761-x. |
| [12] |
SETO WK, FUNG J, CHEUNG KS, et al. Body-mass index is associated with fibrosis regression during long-term nucleoside analogue therapy in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 44(10): 1071-1079. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13804. |
| [13] |
ZHU L, JIANG J, ZHAI X, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based cohort study[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(1): 70-80. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13933. |
| [14] |
PAIS R, RUSU E, ZILISTEANU D, et al. Prevalence of steatosis and insulin resistance in patients with chronic hepatitis B compared with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2015, 26(1): 30-36. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.12.001. |
| [15] |
NAU AL, SOARES JC, SHIOZAWA MB, et al. Clinical and laboratory characteristics associated with dyslipidemia and liver steatosis in chronic HBV carriers[J]. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop, 2014, 47(2): 158-164. DOI: 10.1590/0037-8682-0009-2014. |
| [16] |
YILMAZ B, KOKLU S, BUYUKBAYRAM H, et al. Chronic hepatitis B associated with hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, necroinflammation and fibrosis[J]. Afr Health Sci, 2015, 15(3): 714-718. DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v15i3.3. |
| [17] |
CHEN Y, CAO D, LI C, et al. A nomogram for discrimination of non- alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 33(1): 69-75. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001691. |
| [18] |
YUAN H, YU C, LI X, et al. Serum uric acid levels and risk of metabolic syndrome: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 100(11): 4198-4207. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2015-2527. |
| [19] |
HWANG IC, SUH SY, SUH AR, et al. The relationship between normal serum uric acid and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2011, 26(3): 386-391. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.3.386. |
| [20] |
XU CF, YU CH, XU L, et al. High serum uric acid increases the risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective observational study[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(7): e11578. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011578. |
| [21] |
ZHENG X, GONG L, LUO R, et al. Serum uric acid and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-obesity Chinese adults[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2017, 16(1): 202. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0531-5. |
| [22] |
ZHOU M, YANG N, XING X, et al. Obesity interacts with hyperuricemia on the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21(1): 43. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01615-w. |
| [23] |
PETTA S, CAMMÀ C, CABIBI D, et al. Hyperuricemia is associated with histological liver damage in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 34(7): 757-766. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04788.x. |
| [24] |
FERNÁNDEZ RODRÍGUEZ CM, ALLER R, GUTIÉRREZ GARCÍA ML, et al. Higher levels of serum uric acid influences hepatic damage in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2019, 111(4): 264-269. DOI: 10.17235/reed.2019.5965/2018. |
| [25] |
BALLESTRI S, NASCIMBENI F, ROMAGNOLI D, et al. The independent predictors of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and its individual histological features. : Insulin resistance, serum uric acid, metabolic syndrome, alanine aminotransferase and serum total cholesterol are a clue to pathogenesis and candidate targets for treatment[J]. Hepatol Res, 2016, 46(11): 1074-1087. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12656. |
| [26] |
DUAN H, ZHANG R, CHEN X, et al. Associations of uric acid with liver steatosis and fibrosis applying vibration controlled transient elastography in the united states: a nationwide cross-section study[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2022, 13: 930224. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.930224. |










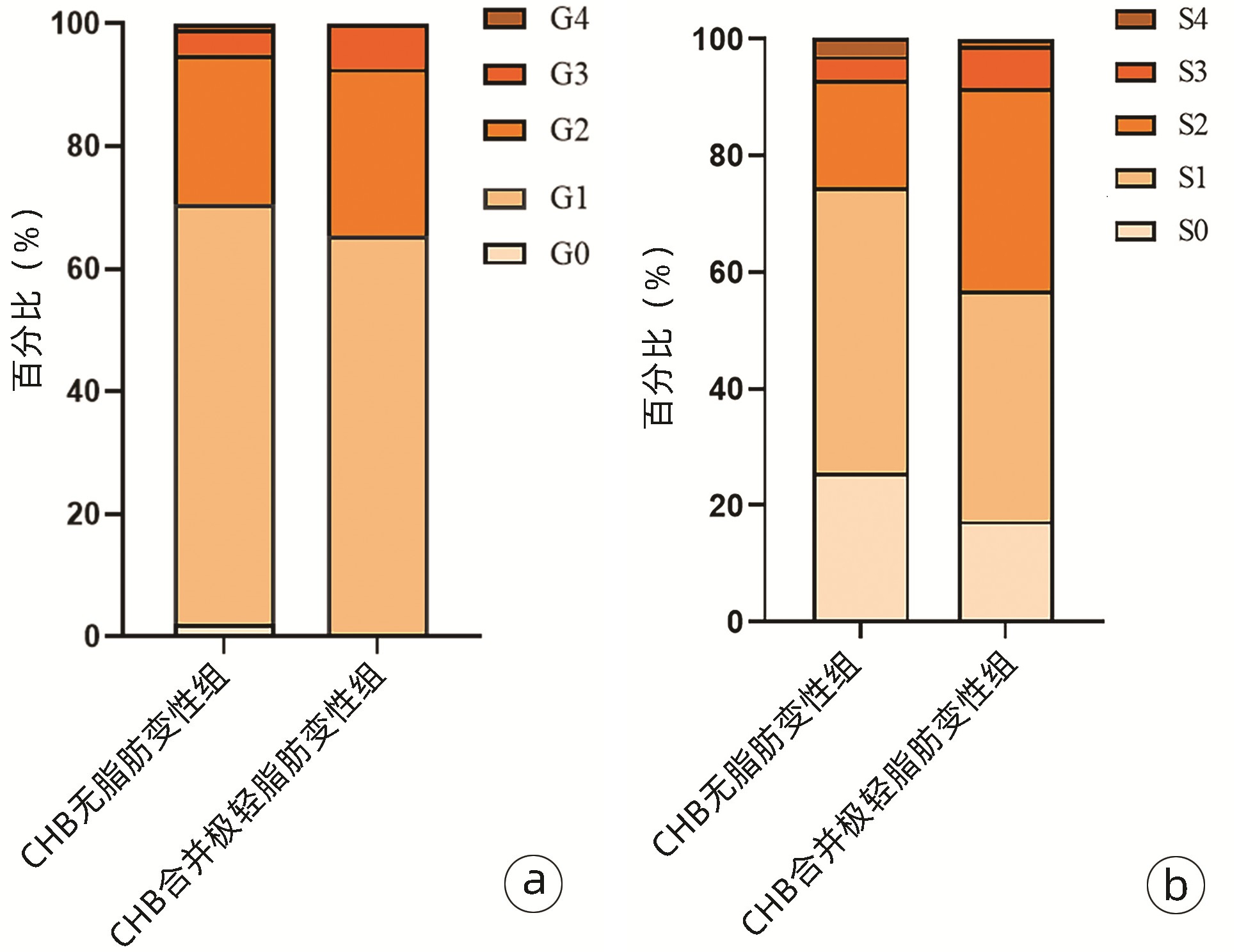




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:

