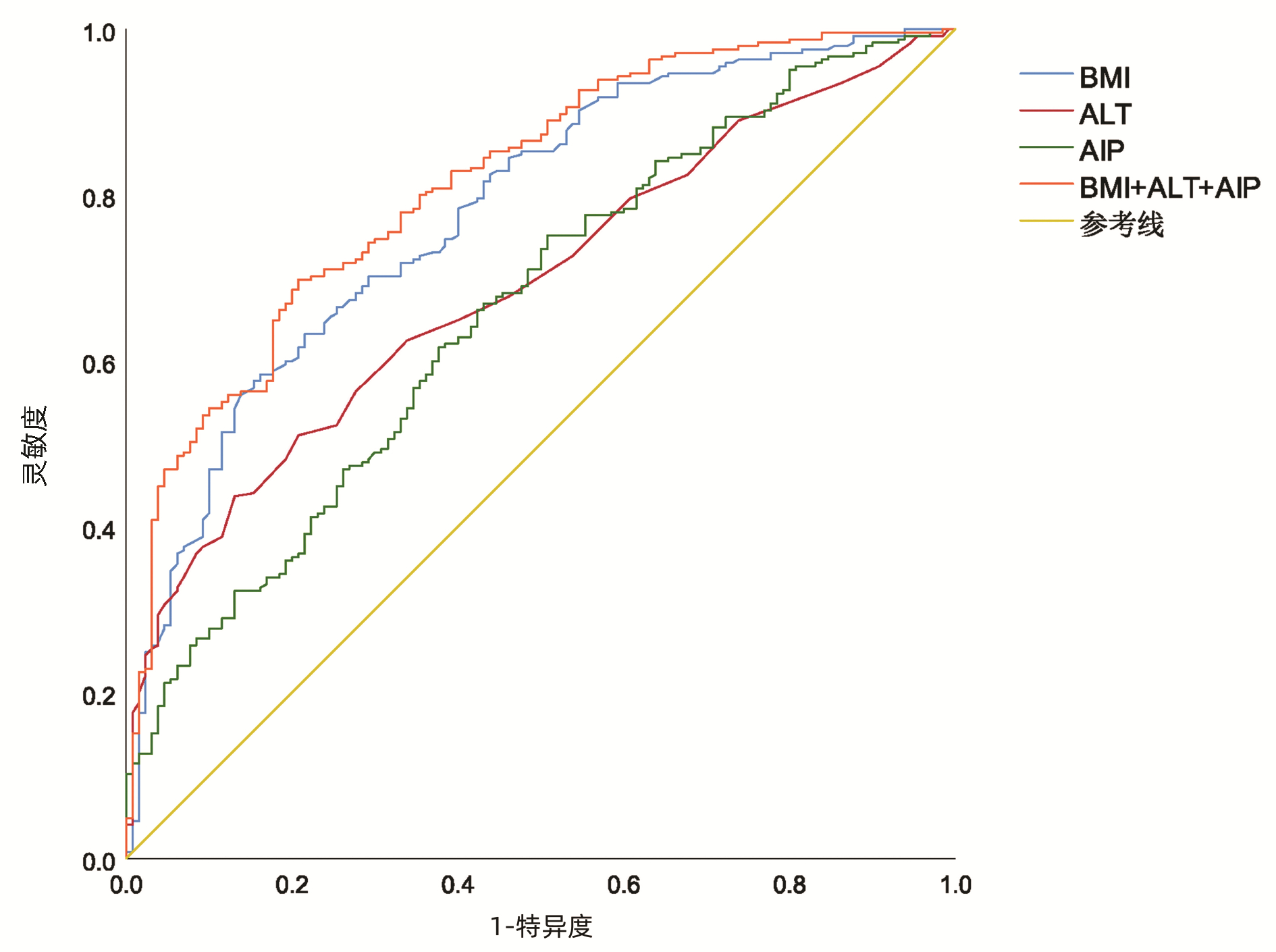
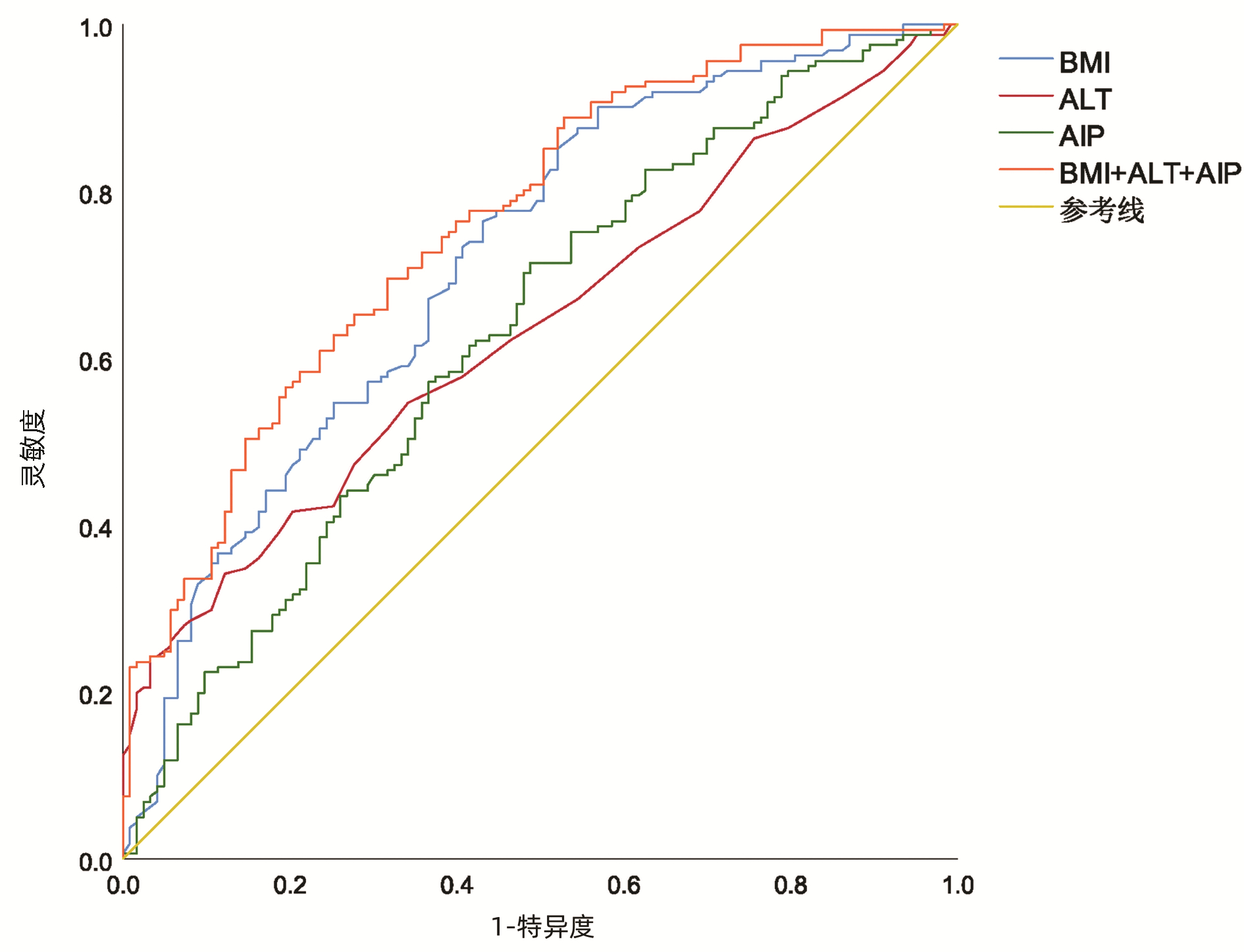
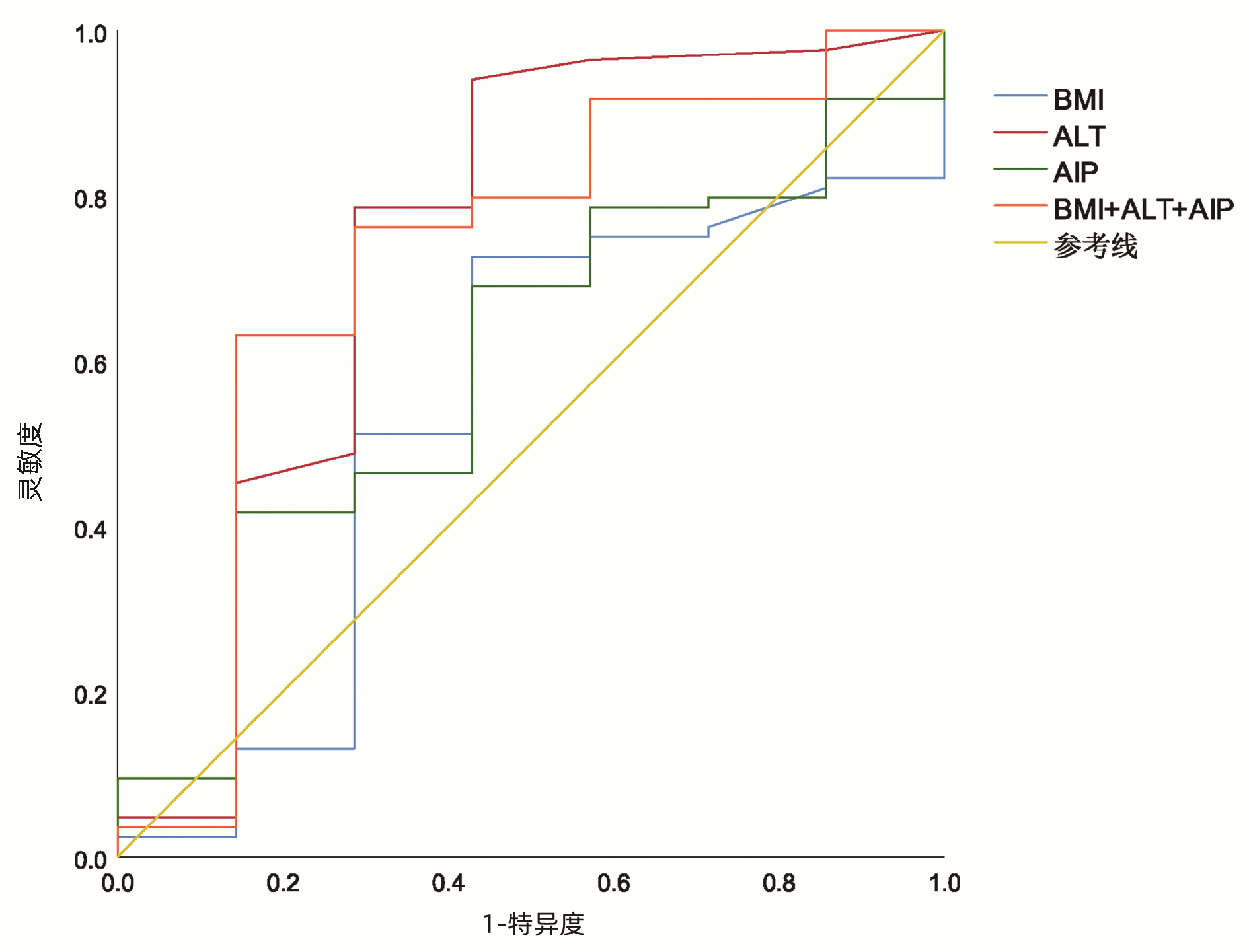
| [1] |
de ALWIS NM, DAY CP. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the mist gradually clears[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48(Suppl 1): S104-S112. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.01.009. |
| [2] |
CHALASANI N, YOUNOSSI Z, LAVINE JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55(6): 2005-2023. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25762. |
| [3] |
DOU KF, YANG XS. Surgeons should attach importance to the understanding of metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(1): 40-45. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20201214-00780. |
| [4] |
XUE R, FAN JG. Brief introduction of an international expert consensus statement: A new definition of metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(6): 1224-1227. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.06.007. |
| [5] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, de AVILA L, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71(4): 793-801. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021. |
| [6] |
FERNÁNDEZ-MACÍAS JC, OCHOA-MARTÍNEZ AC, VARELA-SILVA JA, et al. Atherogenic index of plasma: Novel predictive biomarker for cardiovascular illnesses[J]. Arch Med Res, 2019, 50(5): 285-294. DOI: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2019.08.009. |
| [7] |
CHANG Y, LI Y, GUO X, et al. The association of ideal cardiovascular health and atherogenic index of plasma in rural population: A cross-sectional study from Northeast China[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2016, 13(10): 1027. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13101027. |
| [8] |
LIU H, LIU K, PEI L, et al. Atherogenic index of plasma predicts outcomes in acute ischemic stroke[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12: 741754. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.741754. |
| [9] |
World Health Organization. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications: report of a WHO consultation. Part 1, Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus[R]. World health organization, 1999.
|
| [10] |
XIE J, YANG M, XING Y. Effects of liraglutide on glucose and lipid metabolism and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2021, 13(4): 46-53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.04.008.
谢晶, 杨淼, 邢英. 利拉鲁肽对2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者糖脂代谢及胰岛素抵抗的影响[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(4): 46-53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.04.008.
|
| [11] |
ZHOU F, ZHOU J, WANG W, et al. Unexpected rapid increase in the burden of NAFLD in China From 2008 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(4): 1119-1133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30702. |
| [12] |
DEWIDAR B, KAHL S, PAFILI K, et al. Metabolic liver disease in diabetes - From mechanisms to clinical trials[J]. Metabolism, 2020, 111S: 154299. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154299. |
| [13] |
XIE F, ZHOU H, WANG Y. Atherogenic index of plasma is a novel and strong predictor associated with fatty liver: a cross-sectional study in the Chinese Han population[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2019, 18(1): 170. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-019-1112-6. |
| [14] |
SAMIMI S, RAJABZADEH S, RABIZADEH S, et al. Atherogenic index of plasma is an independent predictor of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2022, 27(1): 112. DOI: 10.1186/s40001-022-00731-x. |
| [15] |
SCHREUDER TC, VERWER BJ, van NIEUWKERK CM, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an overview of current insights in pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(16): 2474-2486. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.2474. |
| [16] |
STEFAN N, KANTARTZIS K, HÄRING HU. Causes and metabolic consequences of fatty liver[J]. Endocr Rev, 2008, 29(7): 939-960. DOI: 10.1210/er.2008-0009. |
| [17] |
POSTIC C, GIRARD J. Contribution of de novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: lessons from genetically engineered mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2008, 118(3): 829-838. DOI: 10.1172/JCI34275. |
| [18] |
ABBASI F, REAVEN GM. Comparison of two methods using plasma triglyceride concentration as a surrogate estimate of insulin action in nondiabetic subjects: triglycerides×glucose versus triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol[J]. Metabolism, 2011, 60(12): 1673-1676. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.04.006. |
| [19] |
DONG BY, MAO YQ, LI ZY, et al. The value of the atherogenic index of plasma in non-obese people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a secondary analysis based on a cross-sectional study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2020, 19(1): 148. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-020-01319-2. |
| [20] |
FRACANZANI AL, PETTA S, LOMBARDI R, et al. Liver and cardiovascular damage in patients with lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and association with visceral obesity[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 15(10): 1604-1611. e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.04.045. |
| [21] |
GAWRIEH S, WILSON LA, CUMMINGS OW, et al. Histologic findings of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease who have normal aminotransferase levels[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2019, 114(10): 1626-1635. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000388. |
| [22] |
CHEN JF, QIN Q, WU ZQ, et al. A cohort study on the correlation between alanine aminotransferase trajectories and new-onset metabolic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2022, 43(2): 234-240. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20210809-00621. |









 本站查看
本站查看
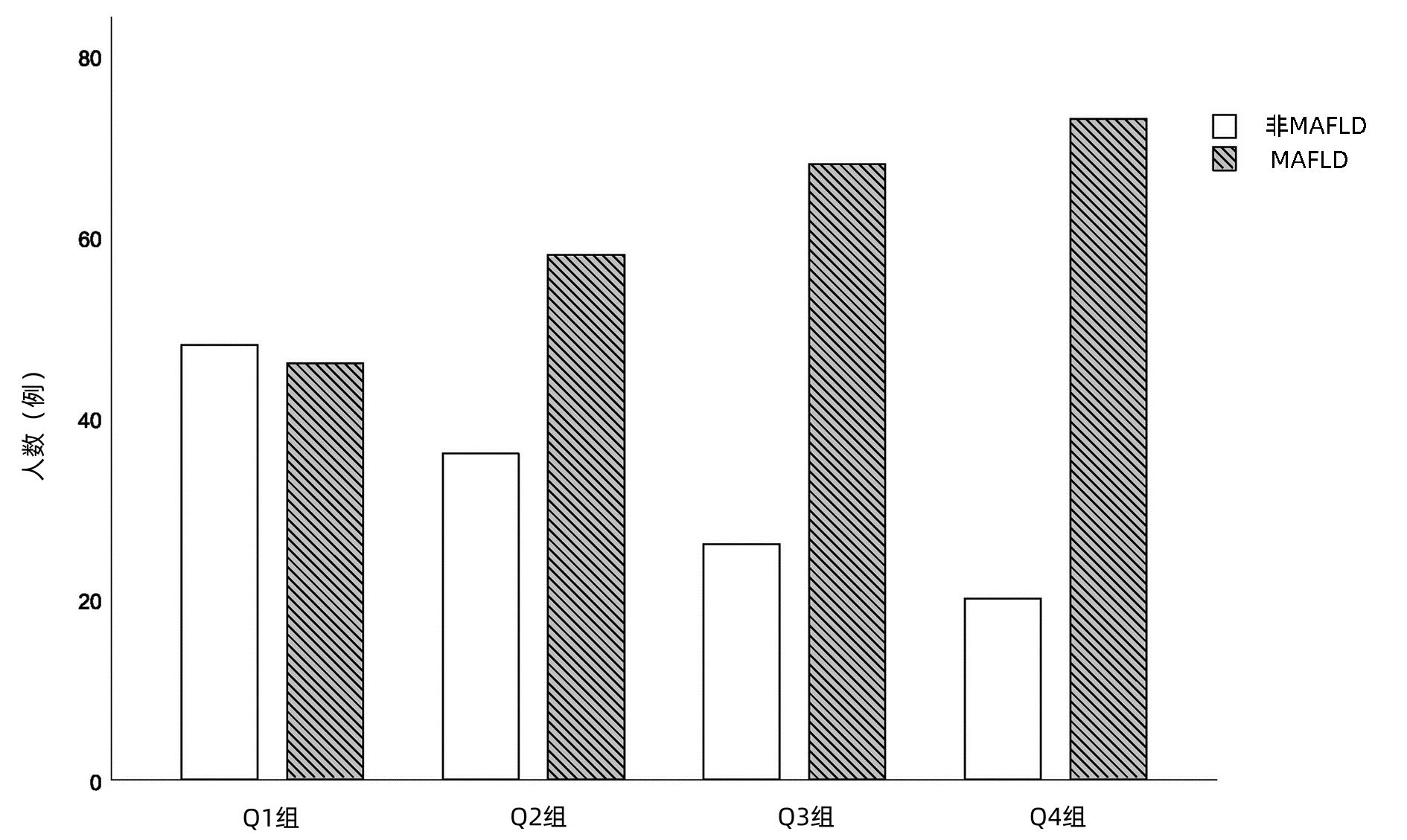




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: