| [1] |
LLOVET JM, KELLEY RK, VILLANUEVA A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7( 1): 6. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3. |
| [2] |
GOH GB, CHANG PE, TAN CK. Changing epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2015, 29( 6): 919- 928. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2015.09.007. |
| [3] |
XIAO L, ZHANG RL, ZHANG H, et al. Comparison of the clinical characteristics and survival between Uyghur patients with hepatitis virus-related and non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma in Xinjiang, China[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2015, 27( 3): 279- 287. DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2015.01.04. |
| [4] |
NAGAOKI Y, HYOGO H, ANDO Y, et al. Increasing incidence of non-HBV- and non-HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: single-institution 20-year study[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21( 1): 306. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01884-5. |
| [5] |
MCGLYNN KA, PETRICK JL, EL-SERAG HB. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73 Suppl 1(Suppl 1): 4- 13. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31288. |
| [6] |
TATEISHI R, UCHINO K, FUJIWARA N, et al. A nationwide survey on non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: 2011-2015 update[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2019, 54( 4): 367- 376. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-018-1532-5. |
| [7] |
WAKIYAMA S, MATSUMOTO M, HARUKI K, et al. Clinical features and outcome of surgical patients with non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Anticancer Res, 2017, 37( 6): 3207- 3213. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.11682. |
| [8] |
GOLABI P, RHEA L, HENRY L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13( 6): 688- 694. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09995-8. |
| [9] |
LIN YP, WANG PM, CHUANG CH, et al. Metabolic risks are increasing in non-B non-C early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a 10-year follow-up study[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 816472. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.816472. |
| [10] |
KIM J, KANG W, SINN DH, et al. Potential etiology, prevalence of cirrhosis, and mode of detection among patients with non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea[J]. Korean J Intern Med, 2020, 35( 1): 65- 78. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2018.040. |
| [11] |
Chinese Diabetes Society. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes in china(2020 edition)[J]. Int J Endocrinol Metab, 2021, 41( 5): 482- 548. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121383-20210825-08063. |
| [12] |
ESLAM M, NEWSOME PN, SARIN SK, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 1): 202- 209. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039. |
| [13] |
VITALE A, SVEGLIATI-BARONI G, ORTOLANI A, et al. Epidemiological trends and trajectories of MAFLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma 2002-2033: the ITA.LI.CA database[J]. Gut, 2023, 72( 1): 141- 152. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324915. |
| [14] |
Chinese Medical Association, Journal of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, et al. Guideline for primary care of alcoholic liver disease(2019)[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2020, 19( 11): 990- 996. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20200812-00898. |
| [15] |
Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China(2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 2): 277- 292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007. |
| [16] |
SHAH AG, LYDECKER A, MURRAY K, et al. Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2009, 7( 10): 1104- 1112. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.05.033. |
| [17] |
JOHNSON PJ, BERHANE S, KAGEBAYASHI C, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33( 6): 550- 558. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.9151. |
| [18] |
ZHOU J, ZHOU F, WANG W, et al. Epidemiological features of NAFLD from 1999 to 2018 in China[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71( 5): 1851- 1864. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31150. |
| [19] |
LIU K, MCCAUGHAN GW. Epidemiology and etiologic associations of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and associated HCC[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1061: 3- 18. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-8684-7_2. |
| [20] |
KANWAL F, KRAMER JR, LI L, et al. Effect of metabolic traits on the risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71( 3): 808- 819. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31014. |
| [21] |
DAVID D, RAGHAVENDRAN A, GOEL A, et al. Risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are common in patients with non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma in India[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 2017, 36( 5): 373- 379. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-017-0785-x. |
| [22] |
YAN SY, FAN JG. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 8): 1748- 1752. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.002. |
| [23] |
LEVRERO M, ZUCMAN-ROSSI J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64( 1 Suppl): S84-S101. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.021. |
| [24] |
YU MW, LIN CL, LIU CJ, et al. Influence of metabolic risk factors on risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related death in men with chronic hepatitis B: A large cohort study[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 153( 4): 1006- 1017.e 5. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.001. |
| [25] |
JIANG LN, LI W, ZHAO JM. Current status and perspectives of the clinical and basic research on concomitant chronic hepatitis B virus infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 7): 1489- 1494. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.07.001. |
| [26] |
CHEN CL, YANG HI, YANG WS, et al. Metabolic factors and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma by chronic hepatitis B/C infection: a follow-up study in Taiwan[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 135( 1): 111- 121. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.073. |
| [27] |
STINE JG, WENTWORTH BJ, ZIMMET A, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis without cirrhosis compared to other liver diseases[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 48( 7): 696- 703. DOI: 10.1111/apt.14937. |
| [28] |
PERUMPAIL RB, LIU A, WONG RJ, et al. Pathogenesis of hepatocarcinogenesis in non-cirrhotic nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Potential mechanistic pathways[J]. World J Hepatol, 2015, 7( 22): 2384- 2388. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i22.2384. |
| [29] |
WHITE DL, KANWAL F, EL-SERAG HB. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk for hepatocellular cancer, based on systematic review[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 10( 12): 1342- 1359.e 2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.10.001. |
| [30] |
WONG DK, CHENG S, MAK LL, et al. Among patients with undetectable hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatocellular carcinoma, a high proportion has integration of HBV DNA into hepatocyte DNA and no cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18( 2): 449- 456. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.06.029. |









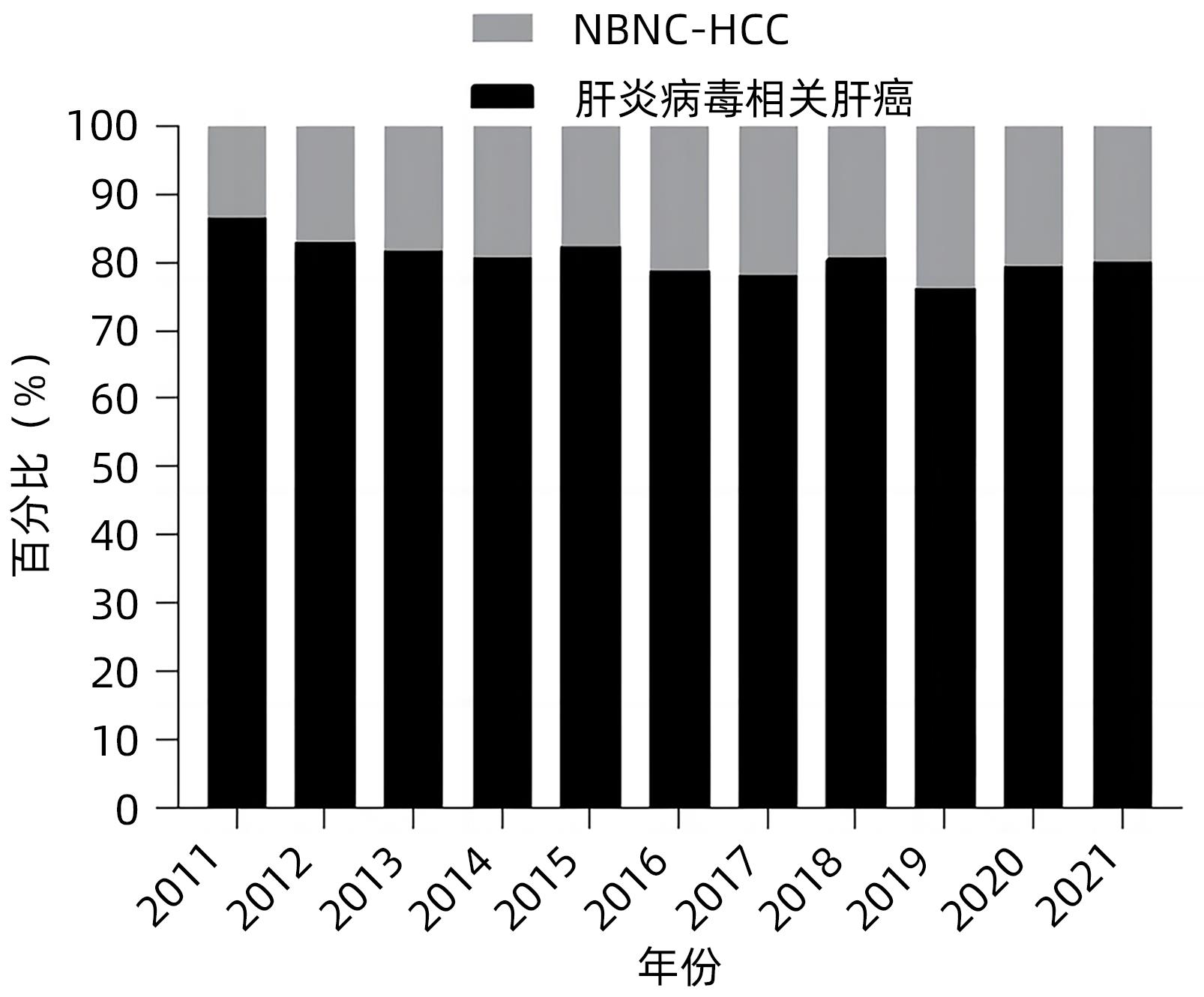




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: