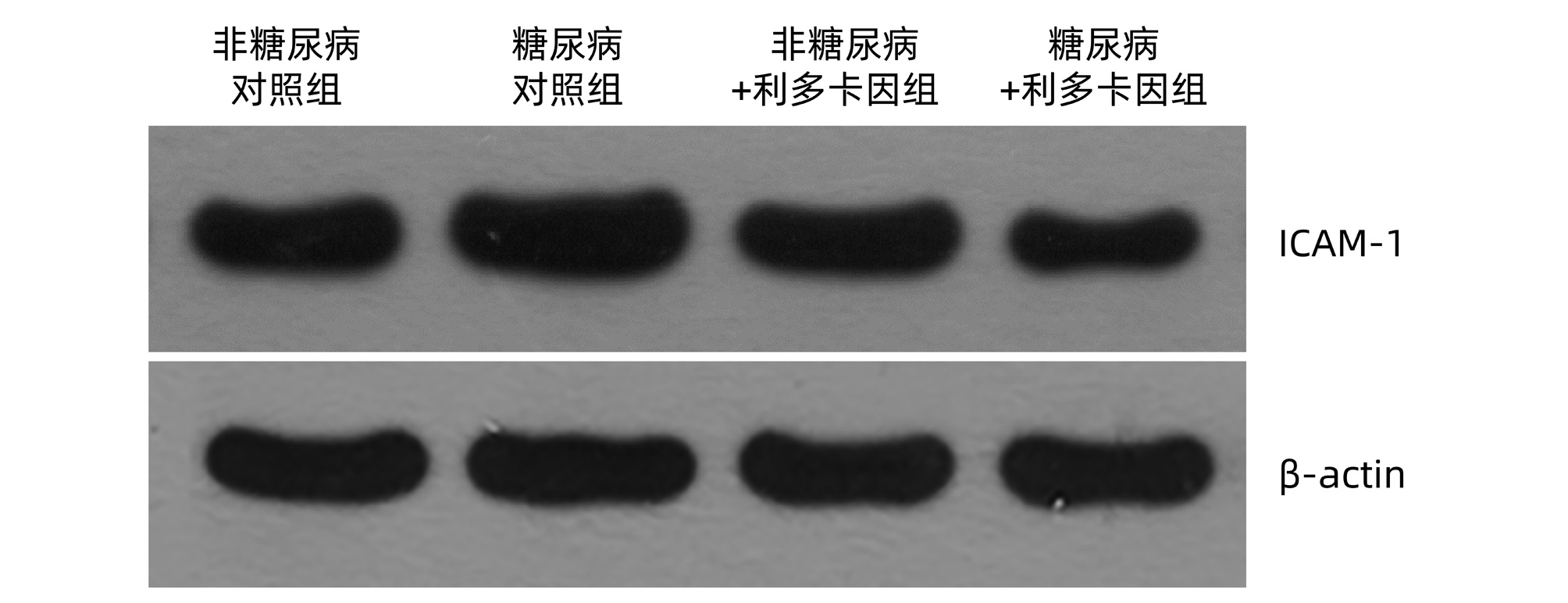
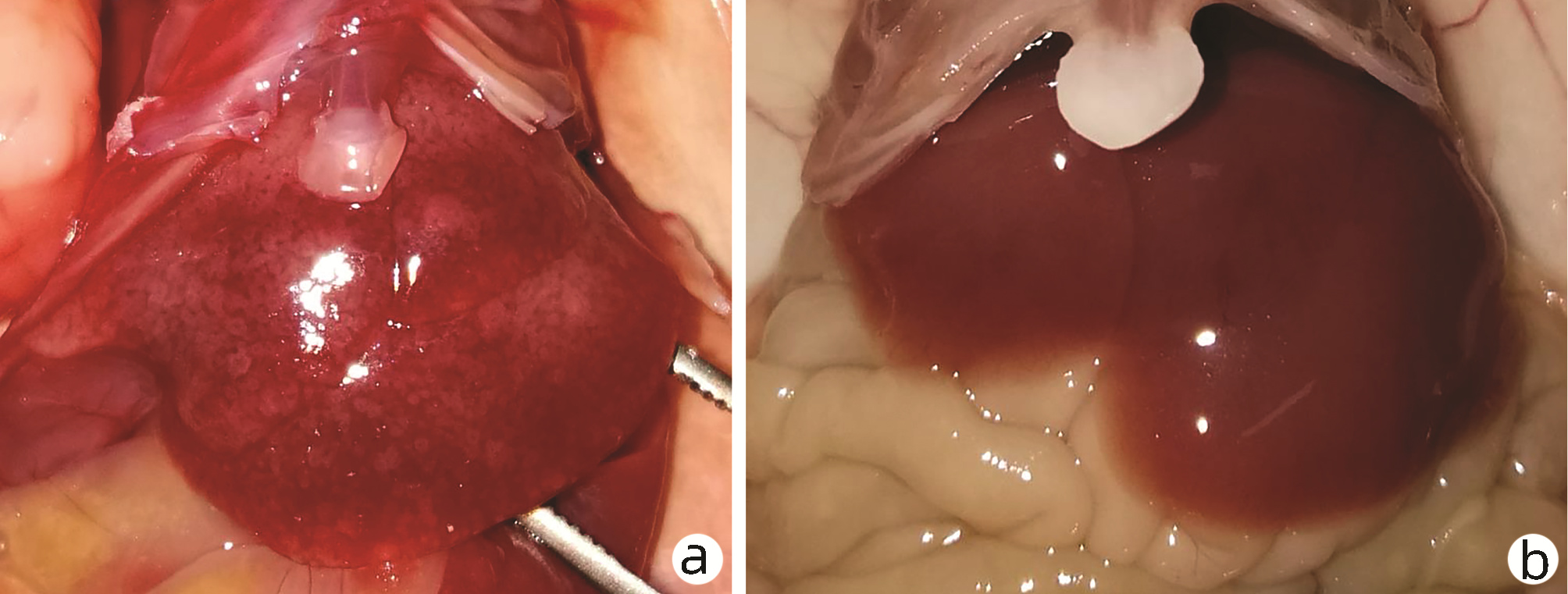
| [1] |
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population- based studies with 4.4 million participants[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10027): 1513-1530. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00618-8. |
| [2] |
FENG J. Retrospective analysis of clinical features and risk factors of patients with diabetic bacterial hepatic abscess complicated with hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases[J]. J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2020, 28(6): 423-426. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4761.2020.06.008. |
| [3] |
ATREJA A, KALRA S. Infections in diabetes[J]. J Pak Med Assoc, 2015, 65(9): 1028-1030.
|
| [4] |
PAN JZ, WANG XM, HUANG YQ, et al. Clinical analysis of 424 cases of diabetes mellitus complicated with bacterial liver abscess[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 14(3): 199-202. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2021.03.007. |
| [5] |
WOHLLEBER D, KNOLLE PA. The role of liver sinusoidal cells in local hepatic immune surveillance[J]. Clin Transl Immunology, 2016, 5(12): e117. DOI: 10.1038/cti.2016.74. |
| [6] |
DONG B, ZHOU Y, WANG W, et al. Vitamin D receptor activation in liver macrophages ameliorates hepatic inflammation, steatosis, and insulin resistance in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(5): 1559-1574. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30937. |
| [7] |
HOTAMISLIGIL GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders[J]. Nature, 2017, 542(7640): 177-185. DOI: 10.1038/nature21363. |
| [8] |
BILZER M, ROGGEL F, GERBES AL. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease[J]. Liver Int, 2006, 26(10): 1175-1186. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01342.x. |
| [9] |
DASU MR, DEVARAJ S, ZHAO L, et al. High glucose induces toll-like receptor expression in human monocytes: Mechanism of activation[J]. Diabetes, 2008, 57(11): 3090-3098. DOI: 10.2337/db08-0564. |
| [10] |
KANETO H, KATAKAMI N, MATSUHISA M, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species in the progression of type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2010, 2010: 453892. DOI: 10.1155/2010/453892. |
| [11] |
TABET F, LAMBERT G, CUESTA TORRES LF, et al. Lipid-free apolipoprotein A-I and discoidal reconstituted high-density lipoproteins differentially inhibit glucose-induced oxidative stress in human macrophages[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2011, 31(5): 1192-1200. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.222000. |
| [12] |
YUAN T, LI Z, LI X, et al. Lidocaine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in microglia[J]. J Surg Res, 2014, 192(1): 150-162. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.05.023. |
| [13] |
International Diabetes Federation: A global emergency. IDF diabetes atlas seventh edition[C]. Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 2015: 11-13.
|
| [14] |
PEARSON-STUTTARD J, BLUNDELL S, HARRIS T, et al. Diabetes and infection: Assessing the association with glycaemic control in population-based studies[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2016, 4(2): 148-158. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00379-4. |
| [15] |
BALMER ML, SLACK E, de GOTTARDI A, et al. The liver may act as a firewall mediating mutualism between the host and its gut commensal microbiota[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2014, 6(237): 237ra66. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008618. |
| [16] |
CHEN YC, LIN CH, CHANG SN, et al. Epidemiology and clinical outcome of pyogenic liver abscess: An analysis from the National Health Insurance Research Database of Taiwan, 2000-2011[J]. J Microbiol Immunol Infect, 2016, 49(5): 646-653. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2014.08.028. |
| [17] |
FOO NP, CHEN KT, LIN HJ, et al. Characteristics of pyogenic liver abscess patients with and without diabetes mellitus[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2010, 105(2): 328-335. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2009.586. |
| [18] |
SOHN SH, KIM KH, PARK JH, et al. Predictors of mortality in Korean patients with pyogenic liver abscess: A single center, retrospective study[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2016, 67(5): 238-244. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2016.67.5.238. |
| [19] |
GREGORY SH, COUSENS LP, van ROOIJEN N, et al. Complementary adhesion molecules promote neutrophil-Kupffer cell interaction and the elimination of bacteria taken up by the liver[J]. J Immunol, 2002, 168(1): 308-315. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.1.308. |
| [20] |
OZCAN U, CAO Q, YILMAZ E, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5695): 457-461. DOI: 10.1126/science.1103160. |
| [21] |
LOHMANN-MATTHES ML, STEINMVLLER C, FRANKE-ULLMANN G. Pulmonary macrophages[J]. Eur Respir J, 1994, 7(9): 1678-1689.
|
| [22] |
GALASSETTI P. Inflammation and oxidative stress in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes[J]. Exp Diabetes Res, 2012, 2012: 943706. DOI: 10.1155/2012/943706. |
| [23] |
HOTAMISLIGIL GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders[J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7121): 860-867. DOI: 10.1038/nature05485. |
| [24] |
ESSER N, LEGRAND-POELS S, PIETTE J, et al. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2014, 105(2): 141-150. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.006. |
| [25] |
DUSTIN ML, ROTHLEIN R, BHAN AK, et al. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-γ: Tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1)[J]. J Immunol, 1986. 137: 245-254.
|
| [26] |
BAKER RG, HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease[J]. Cell Metab, 2011, 13(1): 11-22. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.12.008. |
| [27] |
KAUPPINEN A, SUURONEN T, OJALA J, et al. Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders[J]. Cell Signal, 2013, 25(10): 1939-1948. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007. |
| [28] |
PIEGELER T, VOTTA-VELIS EG, BAKHSHI FR, et al. Endothelial barrier protection by local anesthetics: Ropivacaine and lidocaine block tumor necrosis factor-α-induced endothelial cell Src activation[J]. Anesthesiology, 2014, 120(6): 1414-1428. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000174. |
| [29] |
PIEGELER T, VOTTA-VELIS EG, LIU G, et al. Antimetastatic potential of amide- linked local anesthetics: Inhibition of lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and inflammatory Src signaling independent of sodium channel blockade[J]. Anesthesiology, 2012, 117(3): 548-559. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182661977. |









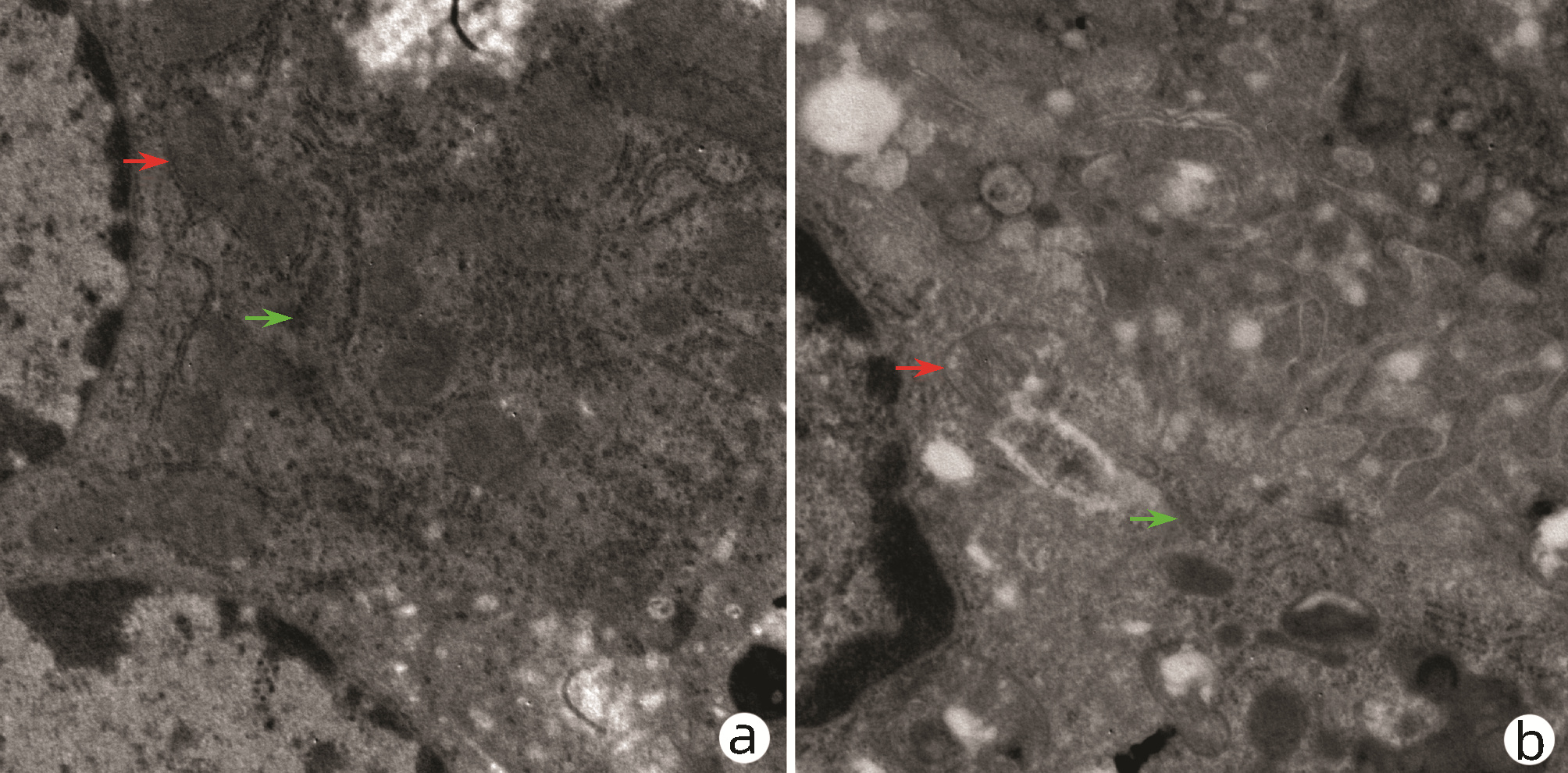




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: