| [1] |
CORDELL HJ, FRYETT JJ, UENO K, et al. An international genome-wide meta-analysis of primary biliary cholangitis: Novel risk loci and candidate drugs[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 3): 572- 581. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.055. |
| [2] |
WONG GL, LAW FM, WONG VW, et al. Health-related quality of life in Chinese patients with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008, 23( 4): 592- 598. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.055. |
| [3] |
BIAGINI MR, TOZZI A, MILANI S, et al. Fatigue in primary biliary cirrhosis: a possible role of comorbidities[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008, 20( 2): 122- 126. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f1cbda. |
| [4] |
SHAHEEN AA, KAPLAN GG, ALMISHRI W, et al. The impact of depression and antidepressant usage on primary biliary cholangitis clinical outcomes[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13( 4): e0194839. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194839. |
| [5] |
BUGANZA-TORIO E, MITCHELL N, ABRALDES JG, et al. Depression in cirrhosis-a prospective evaluation of the prevalence, predictors and development of a screening nomogram[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 49( 2): 194- 201. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15068. |
| [6] |
KRONSTEN VT, TRANAH TH, PARIANTE C, et al. Gut-derived systemic inflammation as a driver of depression in chronic liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76( 3): 665- 680. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.008. |
| [7] |
VOS T, BARBER RM, BELL B, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990—2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386( 9995): 743- 800. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. |
| [8] |
MULLISH BH, KABIR MS, THURSZ MR, et al. Review article: depression and the use of antidepressants in patients with chronic liver disease or liver transplantation[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 40( 8): 880- 892. DOI: 10.1111/apt.12925. |
| [9] |
HARMS MH, de VEER RC, LAMMERS WJ, et al. Number needed to treat with ursodeoxycholic acid therapy to prevent liver transplantation or death in primary biliary cholangitis[J]. Gut, 2020, 69( 8): 1502- 1509. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319057. |
| [10] |
HIRSCHFIELD GM, LIU X, XU C, et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis associated with HLA, IL12A, and IL12RB2 variants[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 360( 24): 2544- 2555. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810440. |
| [11] |
LINDOR KD, BOWLUS CL, BOYER J, et al. Primary biliary cholangitis: 2018 practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69( 1): 394- 419. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30145. |
| [12] |
PARÉS A, CABALLERÍA L, RODÉS J. Excellent long-term survival in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and biochemical response to ursodeoxycholic acid[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130( 3): 715- 720. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.12.029. |
| [13] |
NEGERI ZF, LEVIS B, SUN Y, et al. Accuracy of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for screening to detect major depression: updated systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis[J]. BMJ, 2021, 375: n2183. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.n2183. |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
SCHRAMM C, WAHL I, WEILER-NORMANN C, et al. Health-related quality of life, depression, and anxiety in patients with autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60( 3): 618- 624. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.10.035. |
| [16] |
LIAO J, KANG J, LI F, et al. A cross-sectional study on the association of anxiety and depression with the disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2022, 22( 1): 591. DOI: 10.1186/s12888-022-04236-z. |
| [17] |
MICHELSEN B, KRISTIANSLUND EK, SEXTON J, et al. Do depression and anxiety reduce the likelihood of remission in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis? Data from the prospective multicentre NOR-DMARD study[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76( 11): 1906- 1910. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211284. |
| [18] |
KOCHAR B, BARNES EL, LONG MD, et al. Depression is associated with more aggressive inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2018, 113( 1): 80- 85. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2017.423. |
| [19] |
ROBERTS AL, KUBZANSKY LD, MALSPEIS S, et al. Association of depression with risk of incident systemic lupus erythematosus in women assessed across 2 decades[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2018, 75( 12): 1225- 1233. DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2462. |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
ANANTHAKRISHNAN AN. Epidemiology and risk factors for IBD[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 12( 4): 205- 217. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.34. |
| [22] |
CAUCH-DUDEK K, ABBEY S, STEWART DE, et al. Fatigue in primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Gut, 1998, 43( 5): 705- 710. DOI: 10.1136/gut.43.5.705. |
| [23] |
UMEMURA T, JOSHITA S, ICHIJO T, et al. Human leukocyte antigen class II molecules confer both susceptibility and progression in Japanese patients with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55( 2): 506- 511. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24705. |
| [24] |
CZAJA AJ. Rapidity of treatment response and outcome in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 51( 1): 161- 167. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.02.026. |
| [25] |
MURATORI P, GRANITO A, QUARNETI C, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis in Italy: the Bologna experience[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 50( 6): 1210- 1218. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.01.020. |
| [26] |
KATRINLI S, LORI A, KILARU V, et al. Association of HLA locus alleles with posttraumatic stress disorder[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2019, 81: 655- 658. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.07.016. |
| [27] |
LE CLERC S, LOMBARDI L, BAUNE BT, et al. HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 genetic diversity modulates response to lithium in bipolar affective disorders[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 17823. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-97140-7. |
| [28] |
BANDINELLI F, BENUCCI M, SALAFFI F, et al. Do new and old biomarkers of early undifferentiated arthritis correlate with arthritis impact measurement scales?[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2021, 39( 1): 79- 83. DOI: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/nqqx5k. |










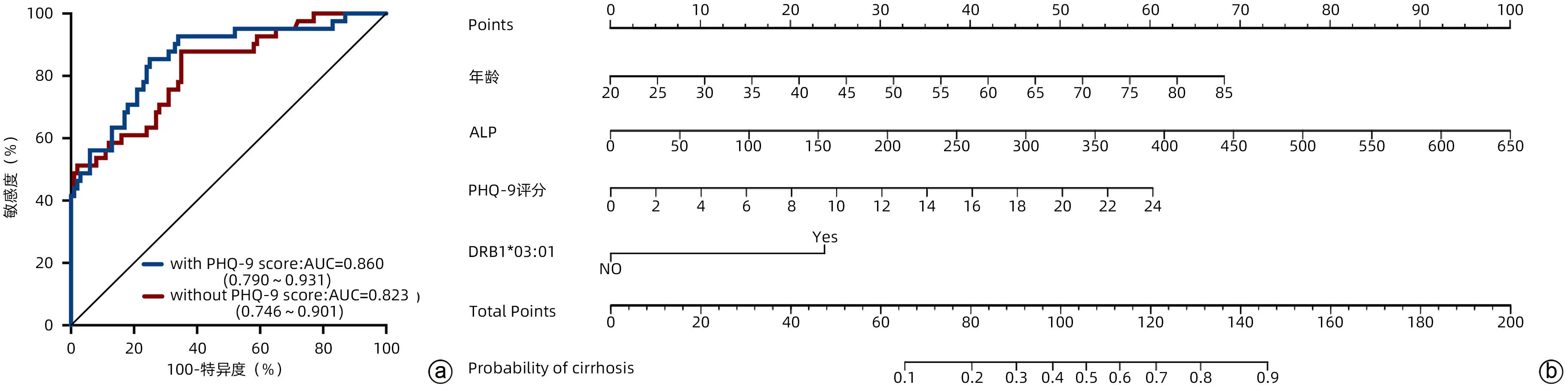




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
