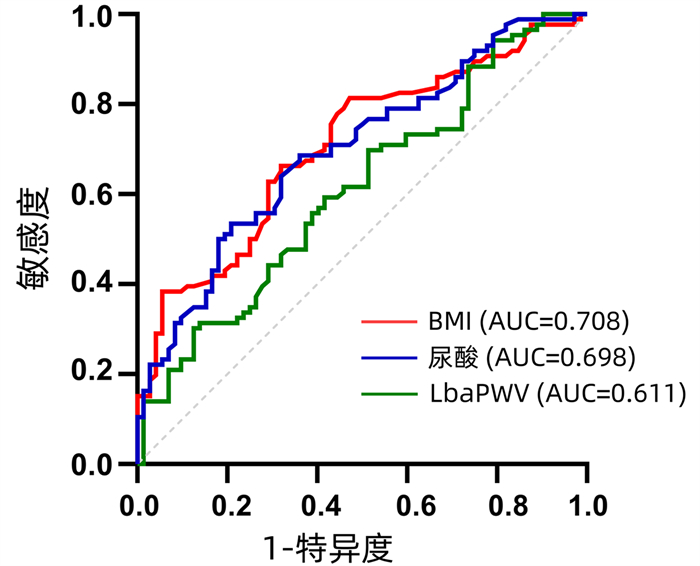
| [1] |
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition[EB/OL]. (2021-11-08)[2022-08-16]. https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/world/.
|
| [2] |
Chinese Society of Endocrinology, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus for diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases and metabolic disorders (2nd Edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(10): 2103-2108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.010. |
| [3] |
ZHOU Q, WANG Y, WANG J, et al. Prevalence and risk factor analysis for the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021, 100(10): e24940. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024940. |
| [4] |
SONG T, JIA Y, LI Z, et al. Effects of liraglutide on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Ther, 2021, 12(6): 1735-1749. DOI: 10.1007/s13300-021-01072-4. |
| [5] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, de AVILA L, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71(4): 793-801. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021. |
| [6] |
Chinese Society of Diabetes, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and control of type 2 diabetes in China (2017 Edition)[J]. Chin J Diabetes Mellitus, 2018, 10(1): 4-67. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2018.01.003. |
| [7] |
National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(5): 947-957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. |
| [8] |
WANG L, PENG W, ZHAO Z, et al. Prevalence and treatment of diabetes in China, 2013-2018[J]. JAMA, 2021, 326(24): 2498-2506. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2021.22208. |
| [9] |
NAN Y, AN J, BAO J, et al. The Chinese Society of Hepatology position statement on the redefinition of fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(2): 454-461. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.003. |
| [10] |
BUZZETTI E, PINZANI M, TSOCHATZIS EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Metabolism, 2016, 65(8): 1038-1048. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012. |
| [11] |
TARGHER G, COREY KE, BYRNE CD, et al. The complex link between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus-mechanisms and treatments[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(9): 599-612. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-021-00448-y. |
| [12] |
ZHANG M, CHEN L, QU MD, et al. Analysis of the risk factors for NAFLD in patients with T2DM[J]. Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2019, 26(5): 271-275. DOI: 10.16151/j.1007-810x.2019.05.004. |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
MANGLA N, AJMERA VH, CAUSSY C, et al. Liver stiffness severity is associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(3): 744-746. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.05.003. |
| [15] |
MUZICA CM, SFARTI C, TRIFAN A, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a bidirectional relationship[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 2020: 6638306. DOI: 10.1155/2020/6638306. |
| [16] |
ALEMANY-PAGÈS M, MOURA-RAMOS M, ARAÚJO S, et al. Insights from qualitative research on NAFLD awareness with a cohort of T2DM patients: time to go public with insulin resistance?[J]. BMC Public Health, 2020, 20(1): 1142. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-09249-5. |
| [17] |
VUSIRIKALA A, THOMAS T, BHALA N, et al. Impact of obesity and metabolic health status in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A United Kingdom population-based cohort study using the health improvement network (THIN)[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2020, 20(1): 96. DOI: 10.1186/s12902-020-00582-9. |
| [18] |
AMPUERO J, RANCHAL I, GALLEGO-DURÁN R, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein antibodies/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is linked to advanced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease lean patients[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 31(9): 1611-1618. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13335. |
| [19] |
ALONSO-DOMÍNGUEZ R, SÁNCHEZ-AGUADERO N, PATINO-ALONSO MC, et al. Association between measurements of arterial stiffness and target organ damage in a general Spanish population[J]. Ann Med, 2021, 53(1): 345-356. DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1881812. |
| [20] |
CAUSSY C, AUBIN A, LOOMBA R. The relationship between type 2 diabetes, NAFLD, and cardiovascular risk[J]. Curr Diab Rep, 2021, 21(5): 15. DOI: 10.1007/s11892-021-01383-7. |
| [21] |
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Addendum. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45(Suppl. 1): S144-S174[J]. Diabetes Care, 2022, 45(9): 2178-2181. DOI: 10.2337/dc22-ad08.
|
| [22] |
CUI Y, LIU J, SHI H, et al. Serum uric acid is positively associated with the prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver in non-obese type 2 diabetes patients in a Chinese population[J]. J Diabetes Complications, 2021, 35(5): 107874. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.107874. |
| [23] |
HE J, YE J, SUN Y, et al. The additive values of the classification of higher serum uric acid levels as a diagnostic criteria for metabolic-associated fatty liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(17): 3587. DOI: 10.3390/nu14173587. |










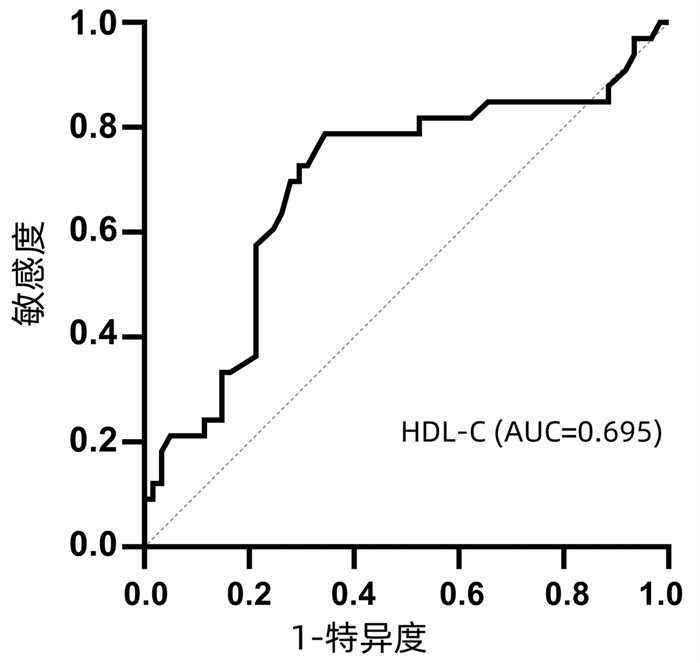




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: