| [1] |
|
| [2] |
YOUNOSSI Z, ANSTEE QM, MARIETTI M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15(1): 11-20. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109. |
| [3] |
SARIN SK, KUMAR M, ESLAM M, et al. Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: a Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5(2): 167-228. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30342-5. |
| [4] |
ESLAM M, VALENTI L, ROMEO S. Genetics and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: Clinical impact[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(2): 268-279. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.09.003. |
| [5] |
ALEXANDER M, LOOMIS AK, van der LEI J, et al. Risks and clinical predictors of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma diagnoses in adults with diagnosed NAFLD: real-world study of 18 million patients in four European cohorts[J]. BMC Med, 2019, 17(1): 95. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-019-1321-x. |
| [6] |
SHEKA AC, ADEYI O, THOMPSON J, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(12): 1175-1183. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.2298. |
| [7] |
LIU SF, LIANG PS, WANG L, et al. Thinking and method of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver[J]. Global Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 13(6): 1047-1049. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2020.06.027. |
| [8] |
Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Hepatology of South China Alliance of TCM, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and treatment scheme of Ganpi (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis)[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Edition), 2021, 13(1): 1-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.01.001.
国家中医药管理局华南区中医肝病诊疗中心联盟. 肝癖(非酒精性脂肪性肝炎)诊疗方案[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(1): 1-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.01.001.
|
| [9] |
HAO WS. The conversion of the Han Dynasty's system of weights and measures and the quantity of classical prescriptions[J]. Chin Med Modern Distance Educ of China, 2005, 3(3): 48-51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2005.03.016. |
| [10] |
TONG XL, MU LC, WU YC, et al. Modern measurement and research on non-unit drug weight in the prescription of treatise on febrile diseases[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2009, 50(S1): 1-2. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2009.s1.090. |
| [11] |
ALVAREZ CS, GRAUBARD BI, THISTLE JE, et al. Attributable fractions of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease for mortality in the United States: Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey with 27 years of follow-up[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72(2): 430-440. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31040. |
| [12] |
TILG H, TARGHER G. NAFLD-related mortality: simple hepatic steatosis is not as 'benign' as thought[J]. Gut, 2021, 70(7): 1212-1213. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323188. |
| [13] |
TILG H, MOSCHEN AR. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the multiple parallel hits hypothesis[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 52(5): 1836-1846. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24001. |
| [14] |
TILG H, ADOLPH TE, MOSCHEN AR. Multiple parallel hits hypothesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: revisited after a decade[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(2): 833-842. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31518. |
| [15] |
HE YN, SHI JP. Research and development of new drugs for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An unmet need in clinical practice[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(6): 1241-1244. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.001. |
| [16] |
JI G, FAN JG, CHEN JJ, et al. Clinical study on treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver of damp-heat syndrome type by Danning tablet[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med, 2005, 25(6): 485-488. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5370.2005.06.001. |
| [17] |
HUANG X, ZHANG ZY. A clinical observation on Dangfei Liganning capsule for 32 cases of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2007, 48(6): 524-525. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1668.2007.06.015. |
| [18] |
YU X, WANG WJ, JIN JY, et al. Linggui Zhugan decoction combined with probiotics in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2019, 35(5): 891-894. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2019.05.022. |
| [19] |
CUI YH. Clinical observation on treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with the Erchen decoction[J]. Clin J Chin Med, 2018, 10(4): 59-60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2018.04.029. |
| [20] |
LI HS, FENG Q, ZHU DD, et al. Clinical observation on Qushi Huayu decoction for 82 cases of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with phlegm-stasis accumulation syndrome[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2013, 31(8): 1764-1767. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2013.08.017. |
| [21] |
DING JL, FANG CY. Based on the synopsis of the golden chamber, discuss the application of classical prescriptions in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Jiangsu J Traditi Chin Med, 2021, 53(2): 21-23. DOI: 10.19844/j.cnki.1672-397X.2021.02.009. |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
LI H, WANG CF. Experimental study on the prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis with Xuanfuhua Kudouzi mixture[J]. Xinjiang J Tradit Chin Med, 2009, 27(1): 21-23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3931.2009.01.010. |
| [24] |
YANG SC, LIU SJ, ZHONG XL, et al. Experimental study on the anti-immune liver injury of Xuanfuhua Kudouzi mixture[J]. Xinjiang J Tradit Chin Med, 2008, 26(1): 7-10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3931.2008.01.005. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
ZHOU F, ZHOU J, WANG W, et al. Unexpected rapid increase in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(4): 1119-1133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30702. |
| [27] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, KOENIG AB, ABDELATIF D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(1): 73-84. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28431. |
| [28] |
ECKARD C, COLE R, LOCKWOOD J, et al. Prospective histopathologic evaluation of lifestyle modification in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized trial[J]. Therap Adv Gastroenterol, 2013, 6(4): 249-259. DOI: 10.1177/1756283X13484078. |
| [29] |
PROMRAT K, KLEINER DE, NIEMEIER HM, et al. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(1): 121-129. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23276. |
| [30] |
TAYLOR RS, TAYLOR RJ, BAYLISS S, et al. Association between fibrosis stage and outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(6): 1611-1625. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.043. |
| [31] |
WANG CE, XU WT, GONG J, et al. Research progress in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Med Offic, 2022, 50(9): 897-899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06. |
| [32] |
SHEN ZY, CAI XB, LU LG. Application of farnesoid X receptor agonists in treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(6): 1402-1405. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.038. |








 下载:
下载:
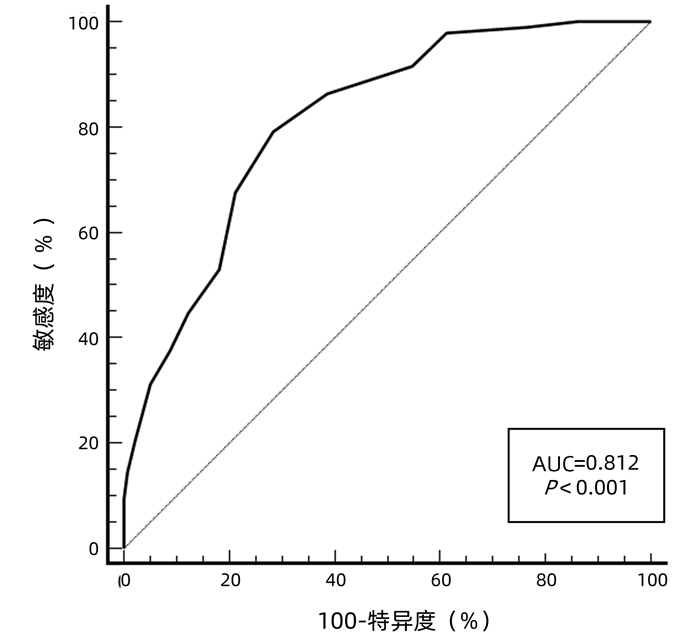
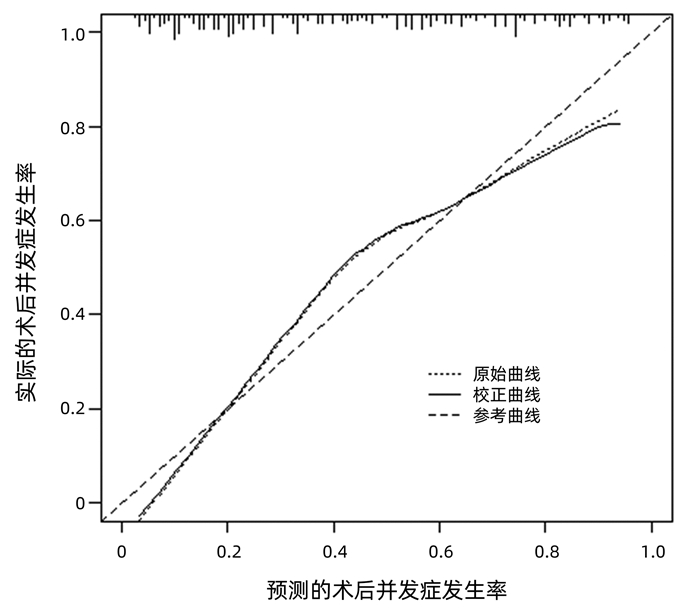
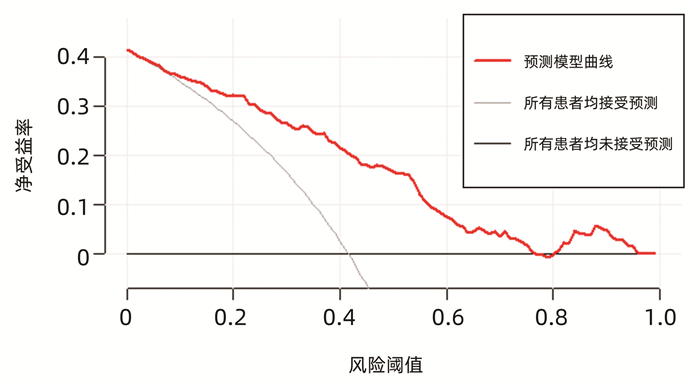







 DownLoad:
DownLoad:


