| [1] |
Chinese Society of Spleen and Portal Hypertension Surgery, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese expert consensus on clinical diagnosis and treatment of portal hypertension with hepatocellular carcinoma (2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2022, 21(4): 444-455. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20220223-00104. |
| [2] |
HUANG D, CAO JG, YE HY, et al. Occurrence and progression of hemodynamic dysfunction in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(10): 1117-1122. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210813-00394. |
| [3] |
XU JH, YU YY, XU XY. Current status of the clinical management of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(7): 1457-1459. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.001. |
| [4] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: vascular diseases of the liver[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(1): 179-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.040. |
| [5] |
KAMATH PS, WIESNER RH, MALINCHOC M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 33(2): 464-470. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2001.22172. |
| [6] |
WAI CT, GREENSON JK, FONTANA RJ, et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. Hepatology, 2003, 38(2): 518-526. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50346. |
| [7] |
TESHALE E, LU M, RUPP LB, et al. APRI and FIB-4 are good predictors of the stage of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: the Chronic Hepatitis Cohort Study (CHeCS)[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2014, 21(12): 917-920. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12279. |
| [8] |
SATO Y, REN XS, HARADA K, et al. Induction of elastin expression in vascular endothelial cells relates to hepatoportal sclerosis in idiopathic portal hypertension: possible link to serum anti-endothelial cell antibodies[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2012, 167(3): 532-542. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04530.x. |
| [9] |
SCHOUTEN JN, GARCIA-PAGAN JC, VALLA DC, et al. Idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54(3): 1071-1081. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24422. |
| [10] |
GOEL A, ELIAS JE, EAPEN CE, et al. Idiopathic non-cirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension (NCIPH)-newer insights into pathogenesis and emerging newer treatment options[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2014, 4(3): 247-256. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.07.005. |
| [11] |
de GOTTARDI A, RAUTOU PE, SCHOUTEN J, et al. Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: proposal and description of a novel entity[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(5): 399-411. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30047-0. |
| [12] |
OKUDAIRA M, OHBU M, OKUDA K. Idiopathic portal hypertension and its pathology[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2002, 22(1): 59-72. DOI: 10.1055/s-2002-23207. |
| [13] |
PULVIRENTI F, PENTASSUGLIO I, MILITO C, et al. Idiopathic non cirrhotic portal hypertension and spleno-portal axis abnormalities in patients with severe primary antibody deficiencies[J]. J Immunol Res, 2014, 2014: 672458. DOI: 10.1155/2014/672458. |
| [14] |
GUIDO M, SARCOGNATO S, SACCHI D, et al. Pathology of idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Virchows Arch, 2018, 473(1): 23-31. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-018-2355-8. |
| [15] |
EAPEN CE, NIGHTINGALE P, HUBSCHER SG, et al. Non-cirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension: associated gut diseases and prognostic factors[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2011, 56(1): 227-235. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-010-1278-2. |
| [16] |
CAZALS-HATEM D, HILLAIRE S, RUDLER M, et al. Obliterative portal venopathy: portal hypertension is not always present at diagnosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 54(3): 455-461. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.038. |
| [17] |
VERNIER-MASSOUILLE G, COSNES J, LEMANN M, et al. Nodular regenerative hyperplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with azathioprine[J]. Gut, 2007, 56(10): 1404-1409. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.114363. |
| [18] |
SANTRA A, DAS GUPTA J, DE BK, et al. Hepatic manifestations in chronic arsenic toxicity[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 1999, 18(4): 152-155.
|
| [19] |
GUIDO M, ALVES V, BALABAUD C, et al. Histology of portal vascular changes associated with idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension: nomenclature and definition[J]. Histopathology, 2019, 74(2): 219-226. DOI: 10.1111/his.13738. |
| [20] |
MADHU K, AVINASH B, RAMAKRISHNA B, et al. Idiopathic non-cirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension: common cause of cryptogenic intrahepatic portal hypertension in a Southern Indian tertiary hospital[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 2009, 28(3): 83-87. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-009-0030-3. |
| [21] |
NAYAK NC, JAIN D, SAIGAL S, et al. Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis: one disease with many names? An analysis from morphological study of native explant livers with end stage chronic liver disease[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2011, 64(7): 592-598. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2010.087395. |
| [22] |
de FRANCHIS R, BOSCH J, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Baveno VⅡ - Renewing consensus in portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(4): 959-974. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.022. |
| [23] |
SEIJO S, REVERTER E, MIQUEL R, et al. Role of hepatic vein catheterisation and transient elastography in the diagnosis of idiopathic portal hypertension[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2012, 44(10): 855-860. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2012.05.005. |
| [24] |
KHANNA R, SARIN SK. Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension - diagnosis and management[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60(2): 421-441. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.08.013. |









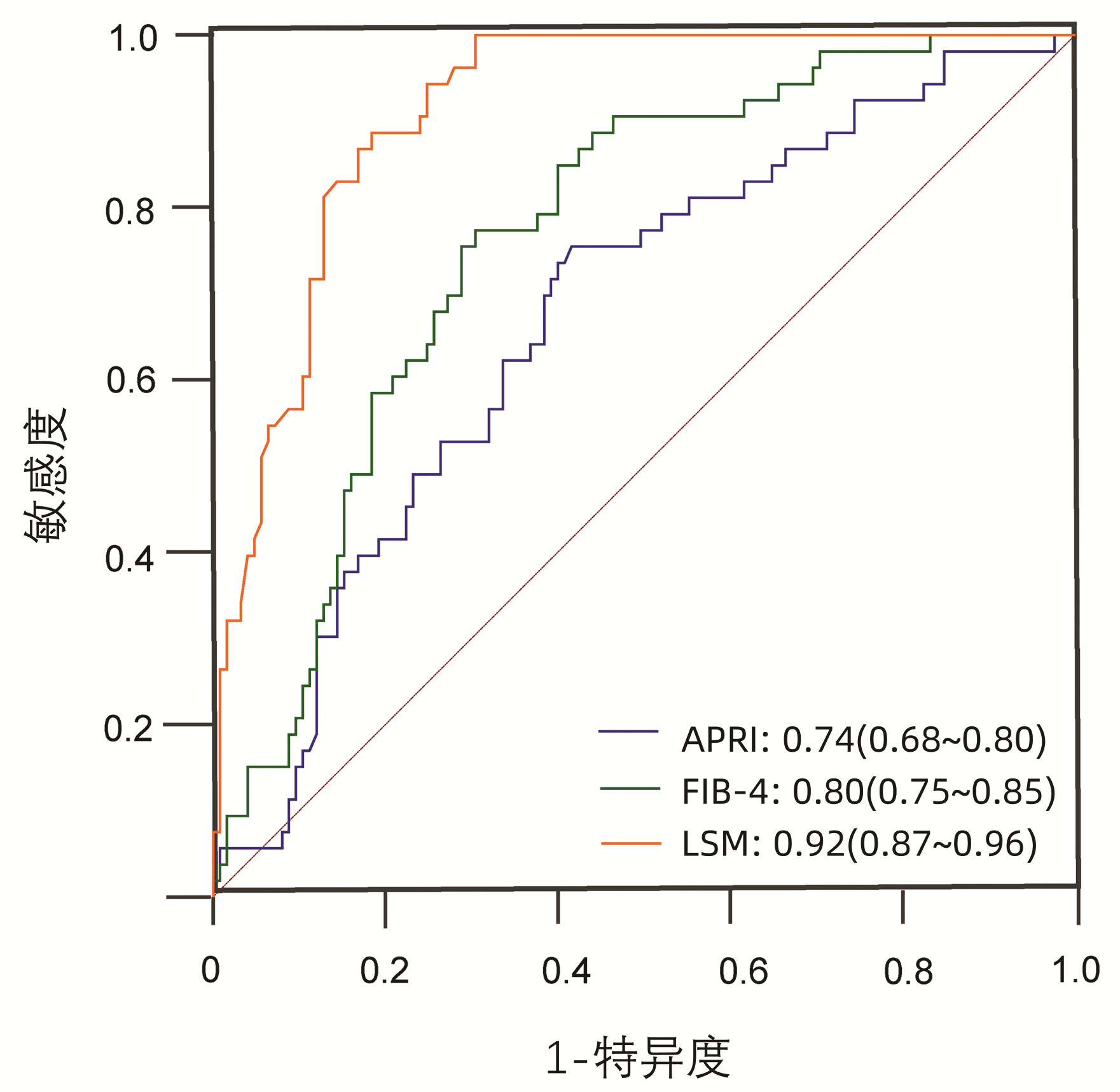




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: