| [1] |
RATHI S, BROCCO S, FORMENTIN C, et al. Spontaneous portosystemic shunts in cirrhosis: Detection, implications, and clinical associations[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2021, 53( 11): 1468- 1475. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.11.020. |
| [2] |
AMIN AA, ALABSAWY EI, JALAN R, et al. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management of hepatorenal syndrome[J]. Semin Nephrol, 2019, 39( 1): 17- 30. DOI: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2018.10.002. |
| [3] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. |
| [4] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of ascites and complications in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33( 10): 1847- 1863. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.10.003. |
| [5] |
WANG Y, XU Y, SUN W, et al. Value of interleukin-6 combined with Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score in predicting the prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 8): 1774- 1779. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.08.011. |
| [6] |
NARDELLI S, RIGGIO O, TURCO L, et al. Relevance of spontaneous portosystemic shunts detected with CT in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Radiology, 2021, 299( 1): 133- 140. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2021203051. |
| [7] |
LI WG, XU XY. Management of renal injury include hepatorenal syndrome in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2020, 28( 5): 381- 385. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200427-00216. |
| [8] |
LIANG JQ, LIU W. Integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 9): 1974- 1979. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.005. |
| [9] |
YANG LH, YANG JH. Mechanism and treatment of portal-systemic circulatory imbalance in hepatorenal syndrome[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 12): 2770- 2773. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.12.006. |
| [10] |
Hepatobiliary Study Group of Chinese Society of Gastroenterology of Chinese Medical Association, Hepatology Committee of Chinese Research Hospital Association. Practice guidance for the use of terlipressin for liver cirrhosis related complications(2021)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 8): 1733- 1738. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.08.006. |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
KAZORY A, RONCO C. Hepatorenal syndrome or hepatocardiorenal syndrome: Revisiting basic concepts in view of emerging data[J]. Cardiorenal Med, 2019, 9( 1): 1- 7. DOI: 10.1159/000492791. |
| [13] |
ZHANG XF, HE QJ, WANG HY, et al. An excerpt of report of the Baveno VII Consensus Workshop: Personalized care in portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 6): 1258- 1268. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.010. |
| [14] |
HU JX, HAN T. An excerpt of diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 11): 2548- 2549. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.11.012. |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
ZHU BB, YANG JX, ZHANG Q, et al. Risk factors for the 90-day prognosis of patients with type I hepatorenal syndrome and establishment of a predictive model[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 7): 1561- 1565. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.019. |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, and Chinese Society of Digestive Endoscopology of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of esophagogastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 3): 527- 538.
中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会消化内镜学分会. 肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 3): 527- 538.
|
| [19] |
SHANG YY, XU WT, GUO XZ, et al. Research progress on application of terlipressin in complications of liver cirrhosis[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 9): 884- 886. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.02. |
| [20] |
ANGELI P, GARCIA-TSAO G, NADIM MK, et al. News in pathophysiology, definition and classification of hepatorenal syndrome: A step beyond the International Club of Ascites(ICA) consensus document[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71( 4): 811- 822. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.07.002. |









 本站查看
本站查看
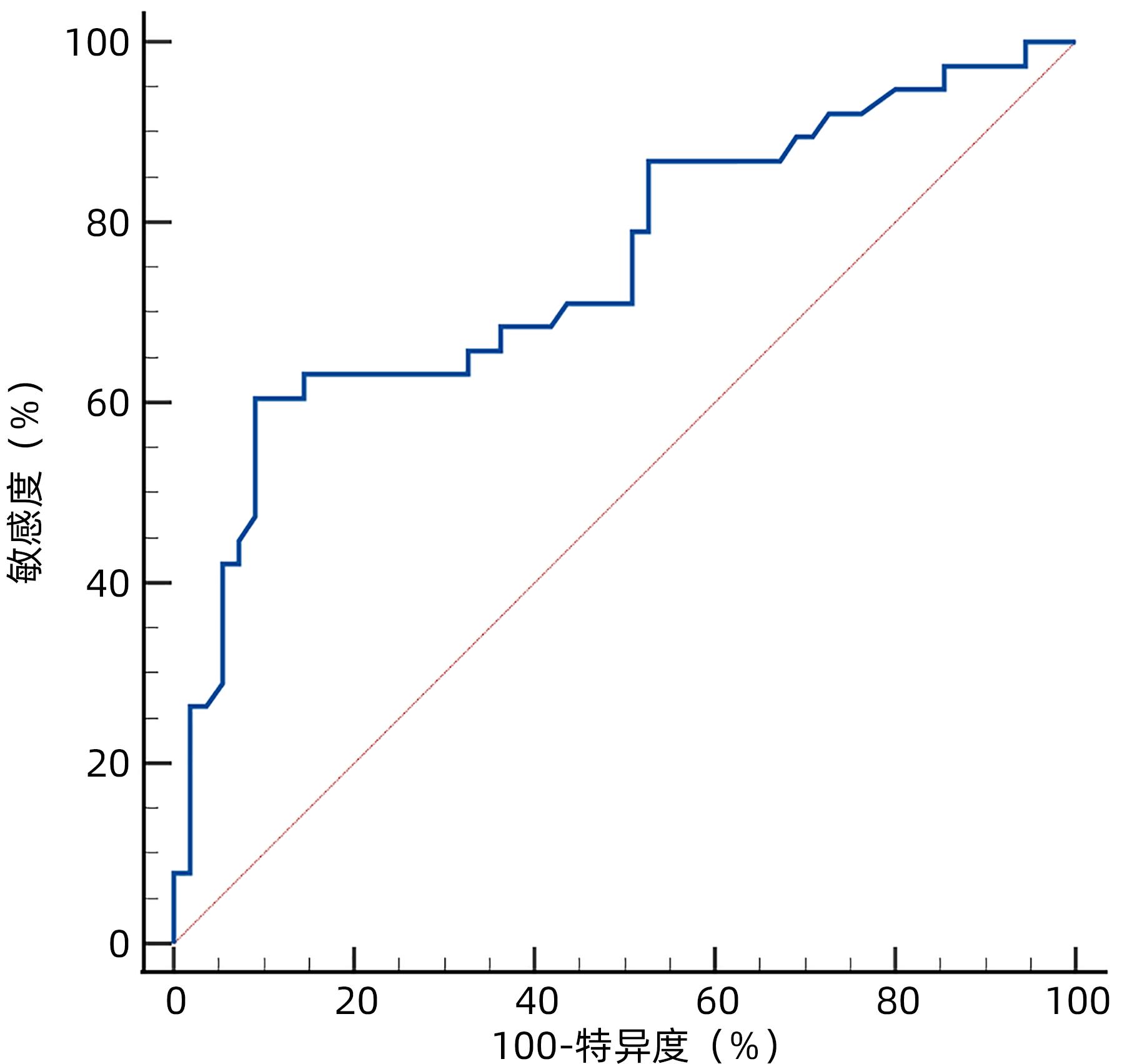




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
