| [1] |
|
| [2] |
ESLAM M, NEWSOME PN, SARIN SK, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 1): 202- 209. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039. |
| [3] |
JIANG DX, CHEN C, LIU XX, et al. Concurrence and impact of hepatic steatosis on chronic hepatitis B patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9( 23): 1718. DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-3052. |
| [4] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. Infect Dis Inf, 2023, 36( 1): 1- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01. |
| [5] |
HUANG SC, LIU CJ. Chronic hepatitis B with concurrent metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Challenges and perspectives[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2023, 29( 2): 320- 331. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0422. |
| [6] |
HUANG SC, SU TH, TSENG TC, et al. Distinct effects of hepatic steatosis and metabolic dysfunction on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatol Int, 2023, 17( 5): 1139- 1149. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-023-10545-6. |
| [7] |
WANG CC, KAO JH. Hepatitis B virus infection and decreased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cohort study[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66( 2): 681. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29252. |
| [8] |
PAIS R, RUSU E, ZILISTEANU D, et al. Prevalence of steatosis and insulin resistance in patients with chronic hepatitis B compared with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2015, 26( 1): 30- 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.12.001. |
| [9] |
HUANG JF, JING ML, WANG CY, et al. The impact of hepatitis B virus infection status on the prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based study[J]. J Med Virol, 2020, 92( 8): 1191- 1197. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.25621. |
| [10] |
LIU WH, LIU H, DING HG, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with chronic hepatitis B combined with metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 10): 2230- 2235. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.007. |
| [11] |
van KLEEF LA, CHOI HSJ, BROUWER WP, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease increases risk of adverse outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3( 5): 100350. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100350. |
| [12] |
HAAM JH, LEE YK, SUH E, et al. Characteristics of urine organic acid metabolites in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease assessed using magnetic resonance imaging with elastography in Korean adults[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2022, 12( 5): 1199. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12051199. |
| [13] |
ZHAO CC, WANG AP, LI LX, et al. Urine uric acid excretion is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. J Diabetes Complications, 2016, 30( 6): 1074- 1080. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.04.017. |
| [14] |
WANG RS, XUE FB, WANG LP, et al. Serum uric acid to creatinine ratio is associated with higher prevalence of NAFLD detected by FibroScan in the United States[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36( 8): e24590. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24590. |
| [15] |
HUI RWH, SETO WK, CHEUNG KS, et al. Inverse relationship between hepatic steatosis and hepatitis B viremia: Results of a large case-control study[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2018, 25( 1): 97- 104. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12766. |
| [16] |
WANG MM, WANG GS, SHEN F, et al. Hepatic steatosis is highly prevalent in hepatitis B patients and negatively associated with virological factors[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59( 10): 2571- 2579. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-014-3180-9. |
| [17] |
ZHENG Q, ZOU BY, WU YK, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Prevalence of hepatic steatosis, fibrosis and associated factors in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 54( 9): 1100- 1109. DOI: 10.1111/apt.16595. |
| [18] |
YI ST, REN GH, ZHU Y, et al. Correlation analysis of hepatic steatosis and hepatitis B virus: A cross-sectional study[J]. Virol J, 2024, 21( 1): 22. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-023-02277-8. |
| [19] |
LIU QC, MU MY, CHEN H, et al. Hepatocyte steatosis inhibits hepatitis B virus secretion via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2022, 477( 11): 2481- 2491. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-021-04143-z. |
| [20] |
YOON S, JUNG J, KIM T, et al. Adiponectin, a downstream target gene of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, controls hepatitis B virus replication[J]. Virology, 2011, 409( 2): 290- 298. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.10.024. |
| [21] |
YANG T, LI J. Chronic hepatitis B comorbid with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Contemporary insights and controversies[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 8): 1797- 1804. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.08.005. |



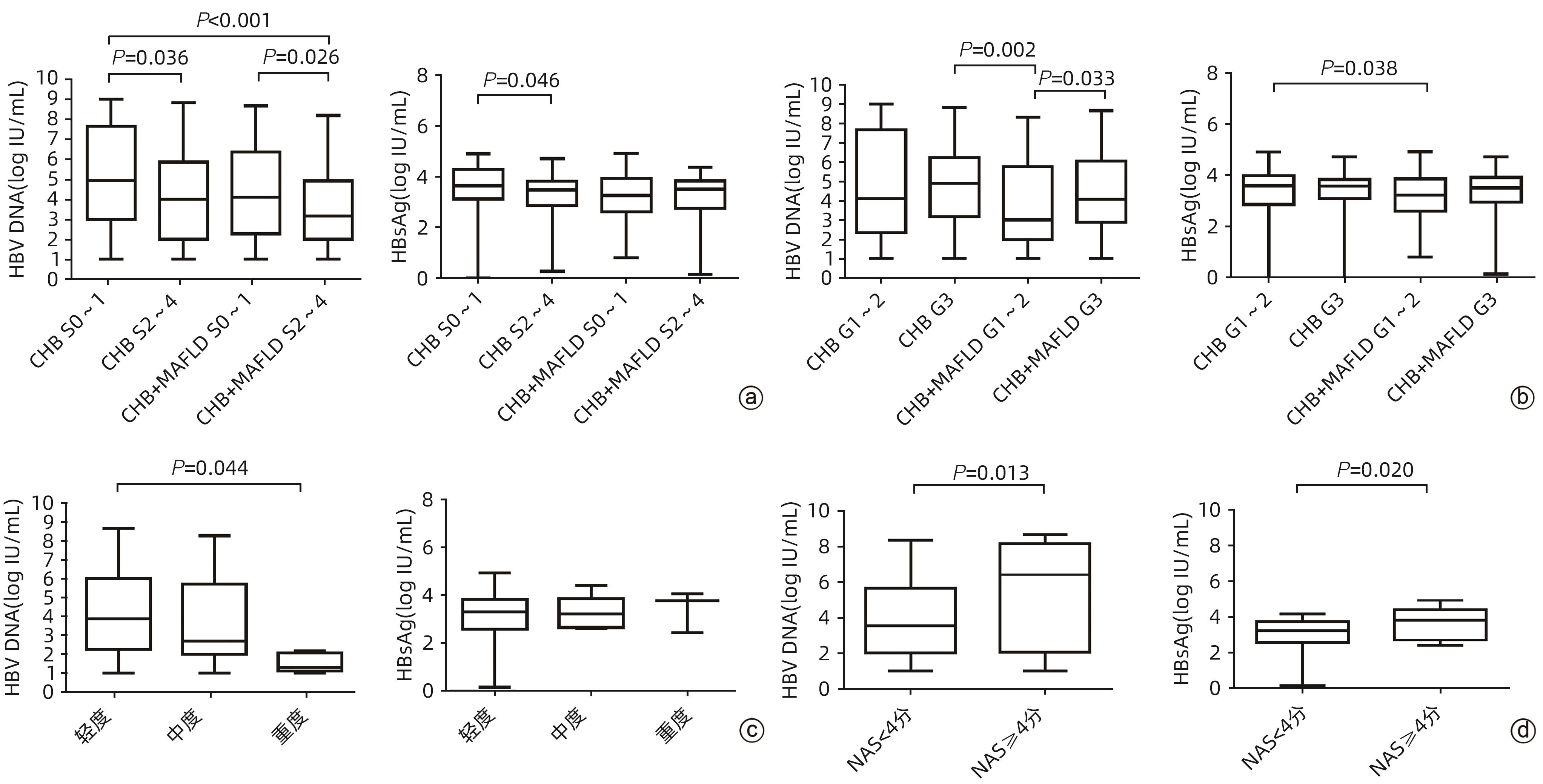




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: