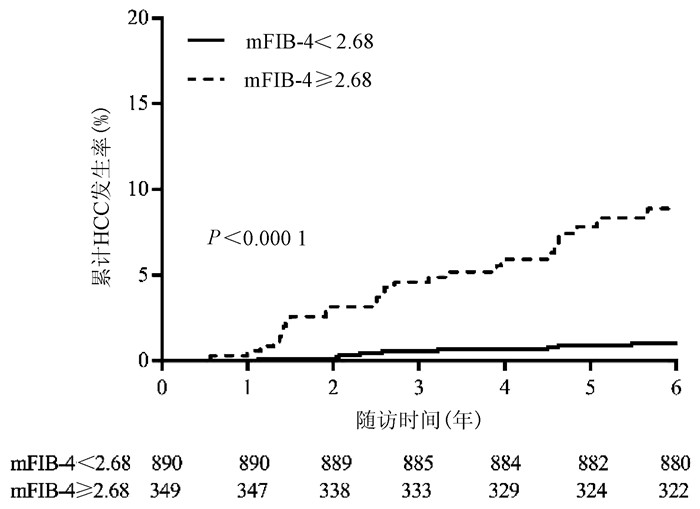
| [1] |
SINGAL AG, El-SERAG HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma from epidemiology to prevention: Translating knowledge into practice[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13(12): 2140-2151. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.08.014. |
| [2] |
HEIMBACH JK, KULIK LM, FINN RS, et al. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(1): 358-380. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29086. |
| [3] |
ARENDS P, SONNEVELD MJ, ZOUTENDIJK R, et al. Entecavir treatment does not eliminate the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B: Limited role for risk scores in Caucasians[J]. Gut, 2015, 64(8): 1289-1295. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307023. |
| [4] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 57(1): 167-185. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.02.010. |
| [5] |
JUNG KS, KIM SU, SONG K, et al. Validation of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma prediction models in the era of antiviral therapy[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62(6): 1757-1766. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28115. |
| [6] |
VALLET-PICHARD A, MALLET V, NALPAS B, et al. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 46(1): 32-36. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21669. |
| [7] |
WAI CT, GREENSON JK, FONTANAL RJ, et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. Hepatology, 2003, 38(2): 518-526. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50346. |
| [8] |
PAIK N, SINN DH, LEE JH, et al. Non-invasive tests for liver disease severity and the hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B patients with low level viremia[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38(1): 68-75. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13489. |
| [9] |
WANG HW, PENG CY, LAI HC, et al. New noninvasive index for predicting liver fibrosis in Asian patients with chronic viral hepatitis[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 3259. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03589-w. |
| [10] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases and Chinese Society of Hepatology Chinese, Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: A 2019 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35 (12): 2648-2669. DOI: 1001-5256(2019)12-2648-22. 中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 1001-5256(2019) 12-2648-22.
|
| [11] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases Chinese, Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 1001-5256(2019)11-2408-18.
中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35 (11): 2408-2425. DOI: 1001-5256(2019) 11-2408-18.
|
| [12] |
OMATA M, CHENG AL, KOKUDO N, et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma, a 2017 update[J]. Hepatol Int, 2017, 11(4): 317-370. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9799-9. |
| [13] |
CHAN SL, WONG VW, QIN S, et al. Infection and cancer: The case of hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(1): 83-90. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.61.5724. |
| [14] |
CHAN HLY. Okuda lecture: Challenges of hepatitis B in the era of antiviral therapy[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34(3): 501-506. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14534. |
| [15] |
PAPATHEODORIDIS GV, IDILMAN R, DALEKOS GN, et al. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma decreases after the first 5 years of entecavir or tenofovir in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(5): 1444-1453. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29320. |
| [16] |
PAPATHEODORIDIS GV, MANOLAKOPOULOS S, TOULOUMI G, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma risk in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with or without cirrhosis treated with entecavir: HepNet. Greece cohort[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2015, 22(2): 120-127. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12283. |
| [17] |
CHEN CF, LEE WC, YANG HI, et al. Changes in serum levels of HBV DNA and alanine aminotransferase determine risk for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2011, 141(4): 1240-1248, 1248. e1-e2. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.036. |
| [18] |
TSENG TC. Risk factors of liver cancer progression in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis (Electronic Edition), 2019, 13(5): 440. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2019.05.017. |
| [19] |
KIM JH, KIM YD, LEE M, et al. Modified PAGE-B score predicts the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asians with chronic hepatitis B on antiviral therapy[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(5): 1066-1073. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.07.018. |
| [20] |
BERZIGOTTI A, SEIJO S, ARENA U, et al. Elastography, spleen size, and platelet count identify portal hypertension in patients with compensated cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(1): 102-111. e101. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.001. |
| [21] |
THOMOPOULOS KC, LABROPOULOU-KARATZA C, MIMIDIS KP, et al. Non-invasive predictors of the presence of large oesophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2003, 35(7): 473-478. DOI: 10.1016/s1590-8658(03)00219-6. |
| [22] |
TANDON P, GARCIA-TSAO G. Portal hypertension and hepatocellular carcinoma: Prognosis and beyond[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2006, 4(11): 1318-1319. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2006.09.009. |
| [23] |
SUH B, PARK S, SHIN DW, et al. High liver fibrosis index FIB-4 is highly predictive of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B carriers[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(4): 1261-1268. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27654. |
| [24] |
KIM MN, KIM SU, KIM BK, et al. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients with transient elastography-defined subclinical cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(6): 1851-1859. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27735. |
| [25] |
BAGLIERI J, BRENNER DA, KISSELEVA T. The role of fibrosis and liver-associated fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(7): 1723. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20071723. |
| [26] |
GABELE E, BRENNER DA, RIPPE RA. Liver fibrosis: Signals leading to the amplification of the fibrogenic hepatic stellate cell[J]. Front Biosci, 2003, 8: d69-d77. DOI: 10.2741/887. |
| [27] |
SAKURAI T, HE G, MATSUZAWA A, et al. Hepatocyte necrosis induced by oxidative stress and IL-1 alpha release mediate carcinogen-induced compensatory proliferation and liver tumorigenesis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2008, 14(2): 156-165. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.06.016. |
| [28] |
FARAZI PA, DEPINHO RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2006, 6(9): 674-87. DOI: 10.1038/nrc1934. |








 下载:
下载:




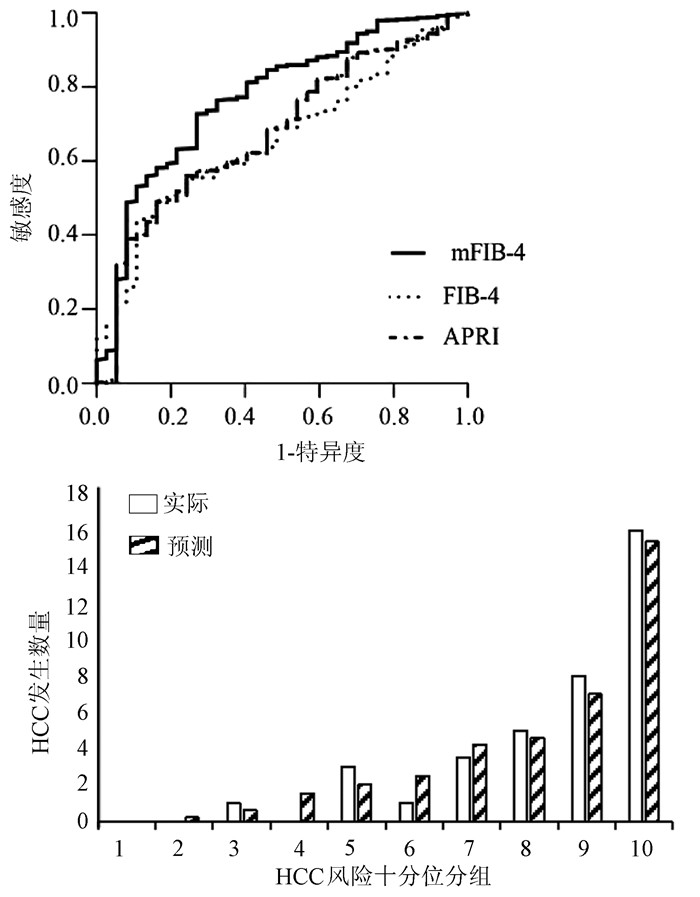




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: