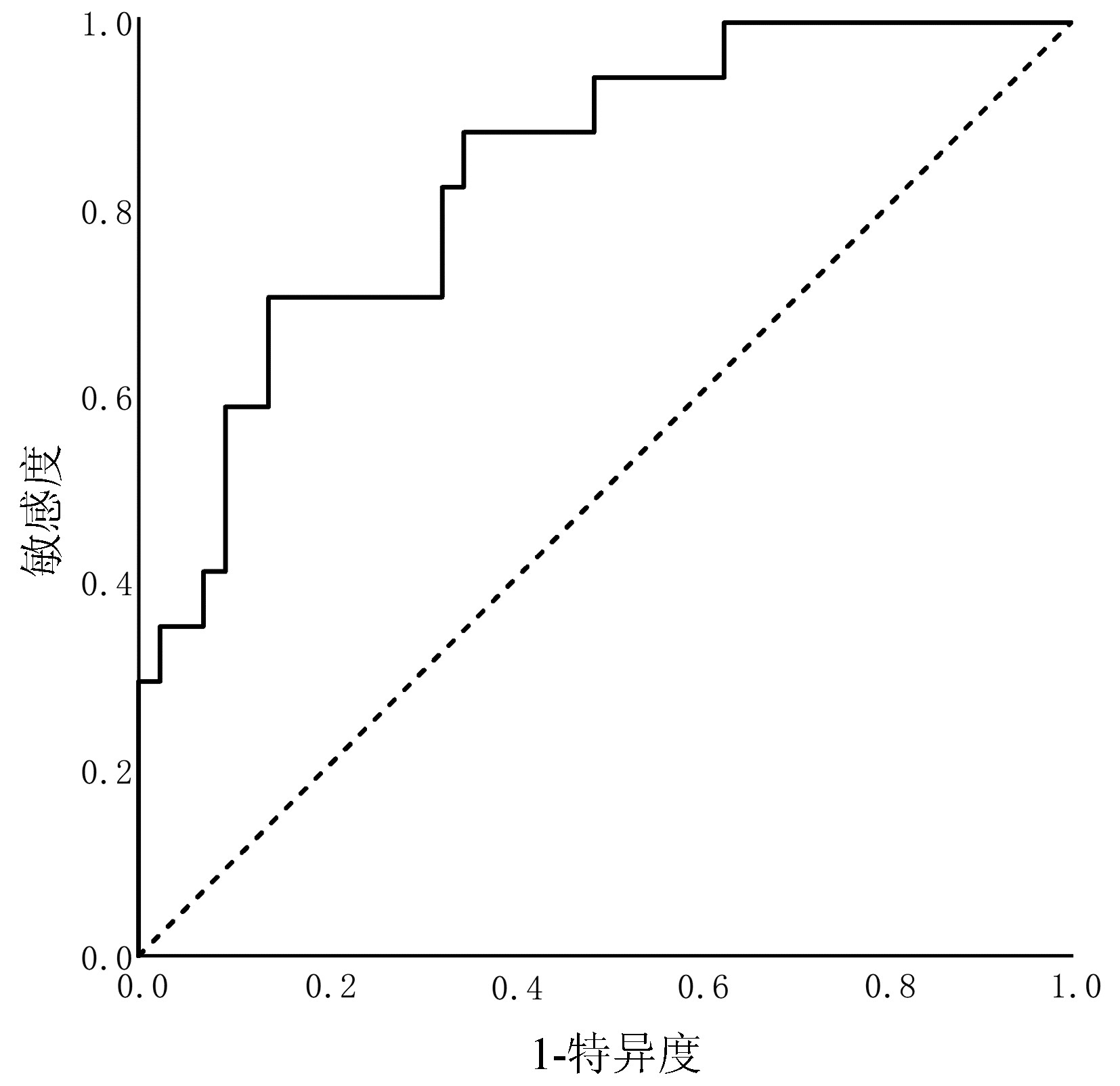
| [1] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of ascites and complications in cirrhosis[J]. J Chin Hepatol, 2017, 33(10): 1847-1863. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.10.003. |
| [2] |
BIGGINS SW, ANGELI P, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74(2): 1014-1048. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31884. |
| [3] |
FIORE M, GENTILE I, MARAOLO AE, et al. Are third-generation cephalosporins still the empirical antibiotic treatment of community-acquired spontaneous bacterial peritonitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 30(3): 329-336. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001057. |
| [4] |
PUGH RN, MURRAY-LYON IM, DAWSON JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices[J]. Br J Surg, 1973, 60(8): 646-649. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. |
| [5] |
KAMATH PS, WIESNER RH, MALINCHOC M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 33(2): 464-470. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2001.22172. |
| [6] |
SUNJAYA DB, LENNON RJ, SHAH VH, et al. Prevalence and predictors of third- generation cephalosporin resistance in the empirical treatment of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2019, 94(8): 1499-1508. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.12.036.. |
| [7] |
PEDUZZI P, CONCATO J, KEMPER E, et al. A simulation study of the number of events per variable in Logistic regression analysis[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 1996, 49(12): 1373-1379. DOI: 10.1016/s0895-4356(96)00236-3. |
| [8] |
TAY P, XIAO J, TAN D, et al. An epidemiological meta-analysis on the worldwide prevalence, resistance, and outcomes of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2021, 8: 693652. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.693652. |
| [9] |
SARWAR S, TARIQUE S, WARIS U, et al. Cephalosporin resistance in community acquired spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Pak J Med Sci, 2019, 35(1): 4-9. DOI: 10.12669/pjms.35.1.17. |
| [10] |
Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. Regulations for clinical application of antibacterial agents[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2012, 5(4): 193-196. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn. 1674-2397.2012.04.001.
|
| [11] |
ZHU LC, GAN DK, HU QQ, et al. Predictive factors for third-generation cephalosporin- resistant spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. J Chin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1501-1504. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.016. |
| [12] |
ARIZA X, LORA-TAMAYO J, CASTELLOTE J, et al. Polymorphonuclear counts in ascitic fluid and microorganisms producing spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: an under-recognized relationship[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2013, 48(10): 1213-1221. DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2013.832367. |
| [13] |
ZHANG GY, TIAN CY, HU H. Recent progress in immune dysfunction of neutrophils in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2021, 24(21): 2734-2743. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn. 1007-9572.2021.00.457.
|
| [14] |
MISHRA D, DAS AK, CHAPAGAIN RH, et al. Thrombocytosis as a predictor of serious bacterial infection in febrile infants[J]. J Nepal Health Res Counc, 2019, 16(41): 401-404. DOI: 10.33314/jnhrc.v16i41.1673. |
| [15] |
YUAN SN, ZHAO JJ, HAN XY, et al. Influence of bacterial and fungal infections on platelets[J]. Chin J Nosocomiol, 2016, 26(22): 5083-5086. DOI: 10.11816/cn.ni.2016-154312. |










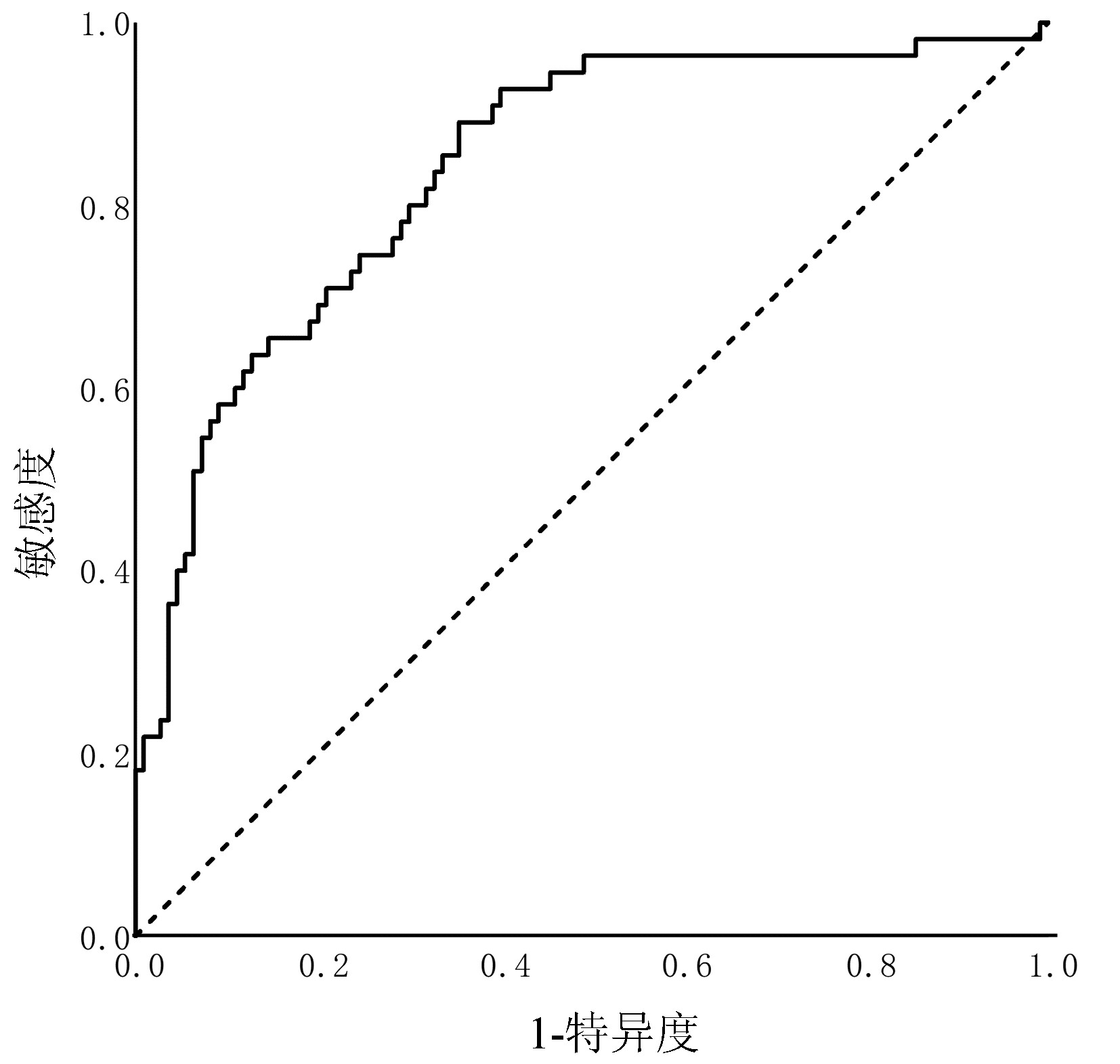




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: