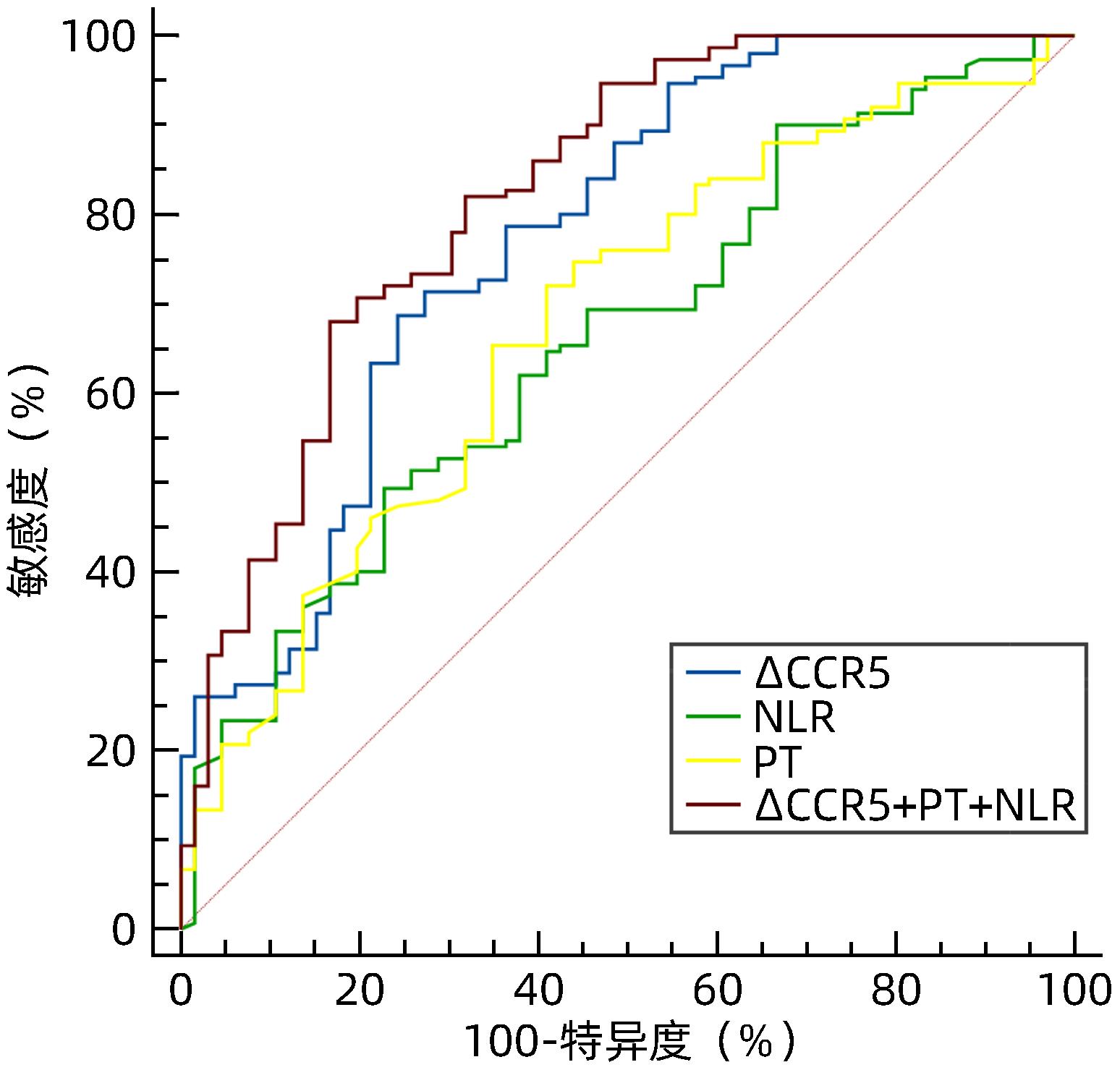
| [1] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Clinical guidelines on nutrition in end-stage liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 6): 1222- 1230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.010. |
| [2] |
MANGANA DEL RIO T, SACLEUX SC, VIONNET J, et al. Body composition and short-term mortality in patients critically ill with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. JHEP Rep, 2023, 5( 8): 100758. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100758. |
| [3] |
NISHIKAWA H, SHIRAKI M, HIRAMATSU A, et al. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease(1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria[J]. Hepatol Res, 2016, 46( 10): 951- 963. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12774. |
| [4] |
PENG H, ZHANG Q, LUO L, et al. A prognostic model of acute-on-chronic liver failure based on sarcopenia[J]. Hepatol Int, 2022, 16( 4): 964- 972. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-022-10363-2. |
| [5] |
SANCHEZ-RODRIGUEZ D, MARCO E, CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ. Defining sarcopenia: Some caveats and challenges[J]. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 2020, 23( 2): 127- 132. DOI: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000621. |
| [6] |
SAYER AA, CRUZ-JENTOFT A. Sarcopenia definition, diagnosis and treatment: Consensus is growing[J]. Age Ageing, 2022, 51( 10): afac220. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afac220. |
| [7] |
KASHANI KB, FRAZEE EN, KUKRÁLOVÁ L, et al. Evaluating muscle mass by using markers of kidney function: Development of the sarcopenia index[J]. Crit Care Med, 2017, 45( 1): e23- e29. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002013. |
| [8] |
WANG S, XIE L, XU J, et al. Predictive value of serum creatinine/cystatin C in neurocritically ill patients[J]. Brain Behav, 2019, 9( 12): e01462. DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1462. |
| [9] |
JUNG CY, KIM HW, HAN SH, et al. Creatinine-cystatin C ratio and mortality in cancer patients: A retrospective cohort study[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2022, 13( 4): 2064- 2072. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.13006. |
| [10] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [11] |
LI JQ, LIANG X, YOU SL, et al. Development and validation of a new prognostic score for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 5): 1104- 1115. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.026. |
| [12] |
GAO FY, ZHANG QQ, LIU Y, et al. Nomogram prediction of individual prognosis of patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2019, 51( 3): 425- 433. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.08.023. |
| [13] |
SUN ZY, LIU XL, WU DX, et al. Circulating proteomic panels for diagnosis and risk stratification of acute-on-chronic liver failure in patients with viral hepatitis B[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9( 4): 1200- 1214. DOI: 10.7150/thno.31991. |
| [14] |
BEER L, BASTATI N, BA-SSALAMAH A, et al. MRI-defined sarcopenia predicts mortality in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40( 11): 2797- 2807. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14648. |
| [15] |
JIN L, LI X. MRI-defined sarcopenia predicts mortality in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Liver Int, 2021, 41( 1): 223. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14691. |
| [16] |
WANG T, ZHANG YG, LI QQ, et al. Evaluation value of area index of the third lumbar psoas major muscle in nutritional status and prognosis of patients with cirrhosis[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 7): 729- 732. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.07.18. |
| [17] |
Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of end-stage liver disease complicated with infections(2021 version)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 304- 310. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.010. |
| [18] |
WANG XB, ZHANG Q, GAO FY. Prediction of acute-on-chronic liver failure and integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine therapy[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 1): 19- 25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.003. |
| [19] |
HAINES RW, ZOLFAGHARI P, WAN Y, et al. Elevated urea-to-creatinine ratio provides a biochemical signature of muscle catabolism and persistent critical illness after major trauma[J]. Intensive care medicine, 2019, 45( 12): 1718- 1731. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-019-05760-5. |
| [20] |
PAGE A, FLOWER L, PROWLE J, et al. Novel methods to identify and measure catabolism[J]. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2021, 27( 4): 361- 366. DOI: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000842. |
| [21] |
VERHAMME FM, FREEMAN CM, BRUSSELLE GG, et al. GDF-15 in pulmonary and critical care medicine[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2019, 60( 6): 621- 628. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0379TR. |
| [22] |
LEE ES, KIM SH, KIM HJ, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 predicts chronic liver disease severity[J]. Gut Liver, 2017, 11( 2): 276- 282. DOI: 10.5009/gnl16049. |
| [23] |
ZHANG IW, CURTO A, LÓPEZ-VICARIO C, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction governs immunometabolism in leukocytes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76( 1): 93- 106. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.08.009. |
| [24] |
WEINERT LS, CAMARGO EG, SOARES AA, et al. Glomerular filtration rate estimation: Performance of serum cystatin C-based prediction equations[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2011, 49( 11): 1761- 1771. DOI: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.670. |
| [25] |
EINHORN D, MENDE CW. Combining creatinine-based EGFR with cystatin C-based EGFR to better assess renal function in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease 3a: Implications for drug selection and dosage in type 2 diabetes[J]. Endocr Pract, 2015, 21( 11): 1301- 1302. DOI: 10.4158/EP15821.ED. |
| [26] |
CHEN XY, SHEN YJ, HOU LS, et al. Sarcopenia index based on serum creatinine and cystatin C predicts the risk of postoperative complications following hip fracture surgery in older adults[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2021, 21( 1): 541. DOI: 10.1186/s12877-021-02522-1. |
| [27] |
ULMANN G, KAÏ J, DURAND JP, et al. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessement of low lean body mass in cancer patients: Comparison to L3-computed tomography scan[J]. Nutrition, 2021, 81: 110895. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110895. |
| [28] |
ZHENG C, WANG E, LI JS, et al. Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio as a screening tool for sarcopenia and prognostic indicator for patients with esophageal cancer[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2022, 22( 1): 207. DOI: 10.1186/s12877-022-02925-8. |
| [29] |
SUN J, YANG H, CAI WT, et al. Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio as a surrogate marker for sarcopenia in patients with gastric cancer[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2022, 22( 1): 26. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02093-4. |



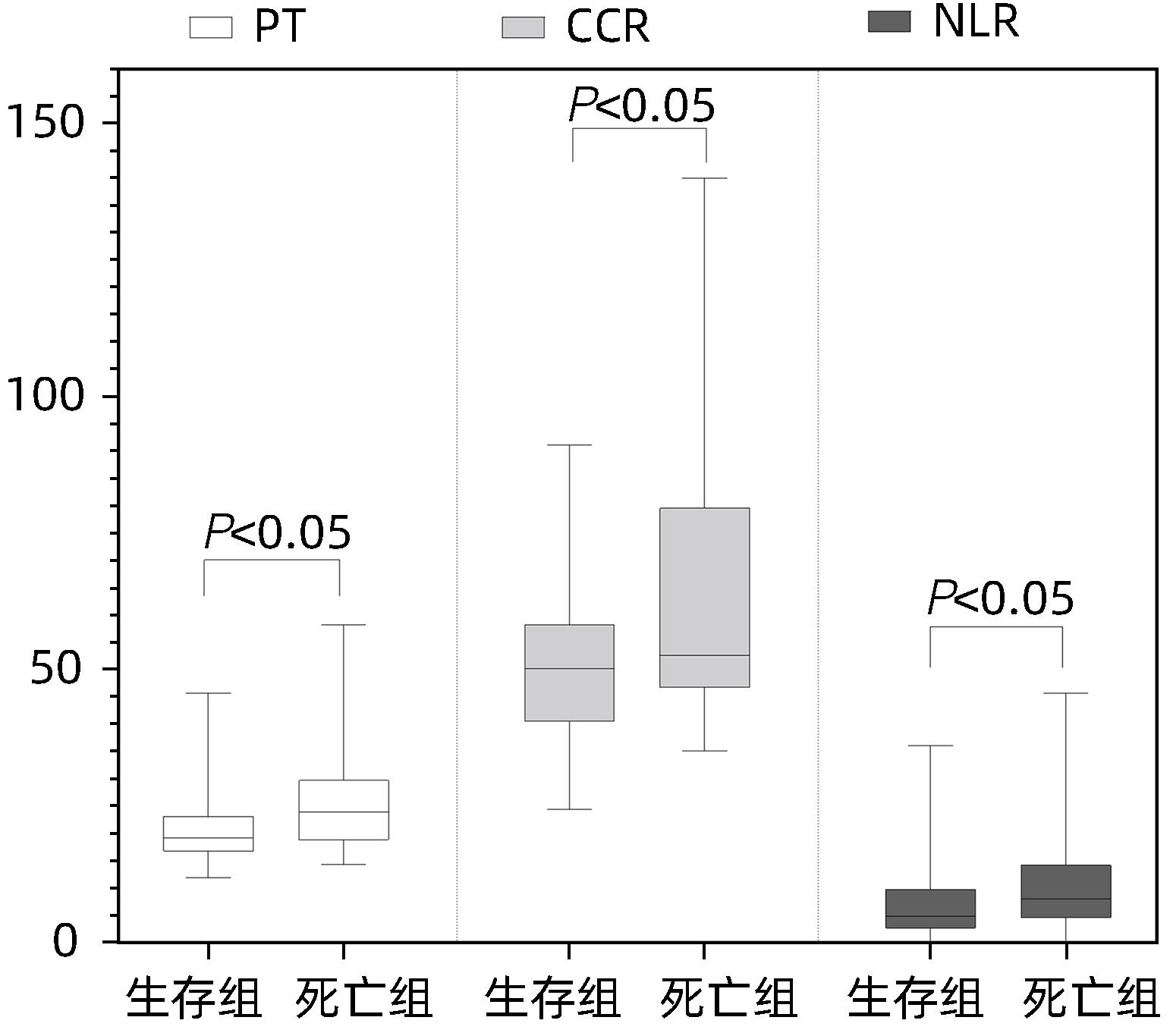




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: