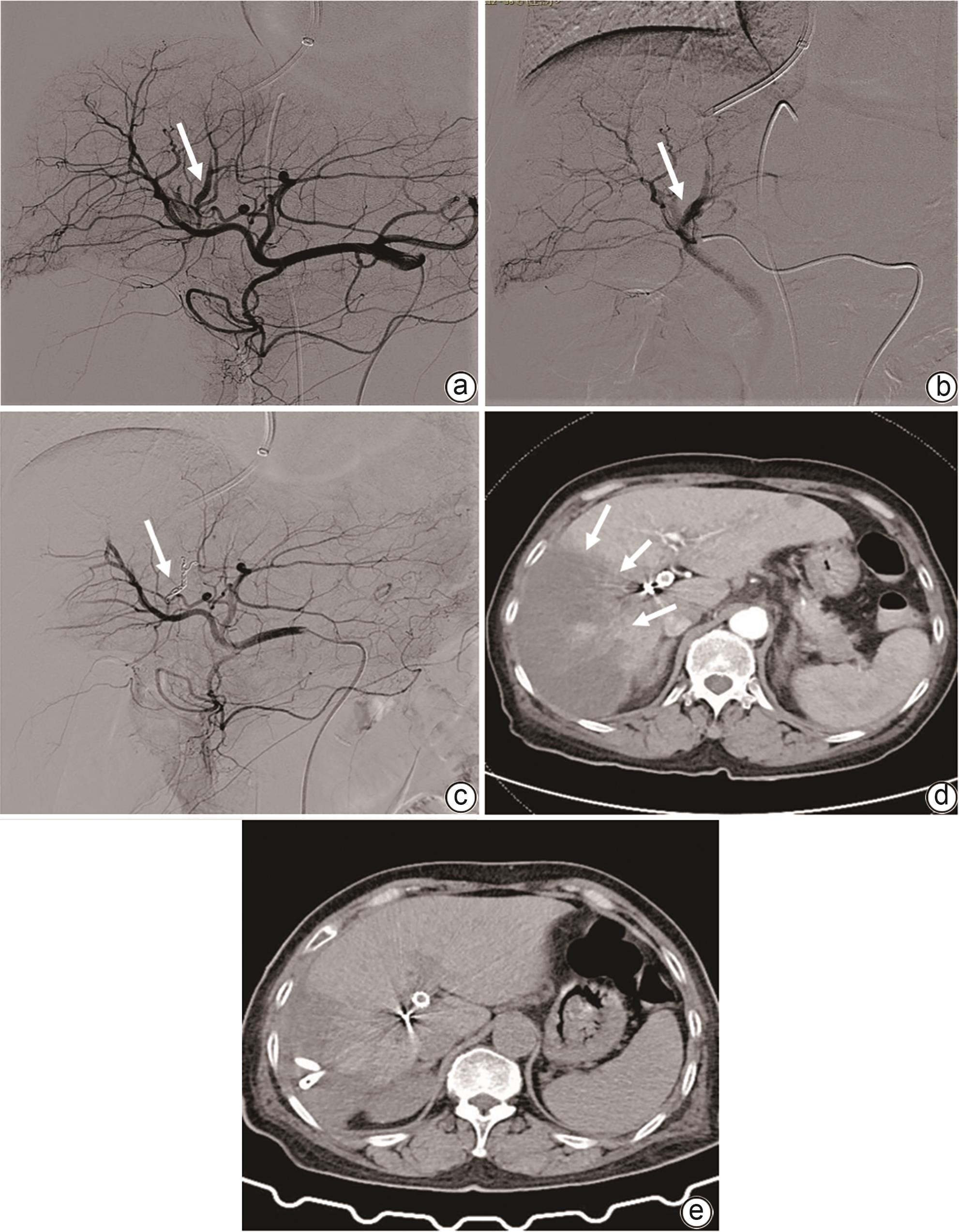
| [1] |
CURET P, BAUMER R, ROCHE A, et al. Hepatic hemobilia of traumatic or iatrogenic origin: Recent advances in diagnosis and therapy, review of the literature from 1976 to 1981[J]. World J Surg, 1984, 8( 1): 2- 8. DOI: 10.1007/BF01658356. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
MUKUND A, RANA S, CHOUDHURY A, et al. Outcome of percutaneous transhepatic biliary interventions in the management of biliary enteric anastomotic strictures with hepatolithiasis[J]. Clin Radiol, 2023, 78( 1): e6- e12. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2022.08.125. |
| [4] |
KIM KH, KIM TN. Etiology, clinical features, and endoscopic management of hemobilia: A retrospective analysis of 37 cases[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2012, 59( 4): 296- 302. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2012.59.4.296. |
| [5] |
THAI BINH N, TRA MY TT, LAN OANH DT, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic endoscopic thulium laser vaporesection for management of severe and focal benign biliary strictures[J]. Clin Ter, 2023, 174( 4): 360- 364. DOI: 10.7417/CT.2023.2451. |
| [6] |
LIU TT, HOU MC, LIN HC, et al. Life-threatening hemobilia caused by hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: A rare complication of chronic cholangitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2003, 9( 12): 2883- 2884. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2883. |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
BERRY R, HAN J, GIROTRA M, et al. Hemobilia: Perspective and role of the advanced endoscopist[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2018, 2018: 3670739. DOI: 10.1155/2018/3670739. |
| [9] |
ZHORNITSKIY A, BERRY R, HAN JY, et al. Hemobilia: Historical overview, clinical update, and current practices[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39( 8): 1378- 1388. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14111. |
| [10] |
CATHCART S, BIRK JW, TADROS M, et al. Hemobilia: An uncommon but notable cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2017, 51( 9): 796- 804. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000876. |
| [11] |
YASUDA M, SATO H, KOYAMA Y, et al. Late-onset severe biliary bleeding after endoscopic pigtail plastic stent insertion[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23( 4): 735- 739. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.735. |
| [12] |
PUNTEL G, PUPPINI G, PERANDINI S, et al. Diagnosis and management of iatrogenic hemobilia secondary to transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedure[J]. Cureus, 2020, 12( 4): e7629. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.7629. |
| [13] |
KURNIAWAN K, WIBAWA IDN, SOMAYANA G, et al. Massive hemobilia caused by rupture of gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm, a delayed complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A case report[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2021, 15( 1): 331. DOI: 10.1186/s13256-021-02915-1. |
| [14] |
ABIKO T, EBIHARA Y, TAKEUCHI M, et al. Hemobilia-a rare complication after laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J]. Surg Case Rep, 2020, 6( 1): 91. DOI: 10.1186/s40792-020-00837-6. |
| [15] |
VACHHANI PG, COPELAN A, REMER EM, et al. Iatrogenic hepatopancreaticobiliary injuries: A review[J]. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2015, 32( 2): 182- 194. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1549377. |
| [16] |
HU XW, LI T. Diagnosis and treatment of common biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation in adults[J]. Ogran Transplant, 2022, 13( 5): 569- 576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.05.004. |
| [17] |
LEE YT, LIN H, CHEN KY, et al. Life-threatening hemobilia caused by hepatic pseudoaneurysm after T-tube choledochostomy: Report of a case[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2010, 10: 81. DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-81. |
| [18] |
HU Y, GAO Q, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography combined with lithotomy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the treatment of bile duct stones[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2023, 39( 10): 1146- 1149. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2023.10.018. |
| [19] |
VULTAGGIO F, MORÈRE PH, CONSTANTIN C, et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding and obstructive jaundice: Think of hepatic artery aneurysm[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2016, 8( 6): 467- 471. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i6.467. |
| [20] |
QUENCER KB, TADROS AS, MARASHI KB, et al. Bleeding after percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage: Incidence, causes and treatments[J]. J Clin Med, 2018, 7( 5): 94. DOI: 10.3390/jcm7050094. |
| [21] |
BERRY R, HAN JY, KARDASHIAN AA, et al. Hemobilia: Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Liver Res, 2018, 2( 4): 200- 208. DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2018.09.007. |
| [22] |
SINGH P, SCIBELLI N, GOSAL K, et al. Hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm presenting as gastrointestinal hemorrhage[J]. Cureus, 2021, 13( 3): e14190. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14190. |
| [23] |
KHOT R, MORGAN MA, NAIR RT, et al. Radiologic findings of biliary complications post liver transplantation[J]. Abdom Radiol(NY), 2023, 48( 1): 166- 185. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-022-03714-y. |
| [24] |
WEN F, DONG Y, LU ZM, et al. Iatrogenic hemobilia: Imaging features and management with transcatheter arterial embolization in 30 patients[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2016, 22( 4): 371- 377. DOI: 10.5152/dir.2016.15295. |



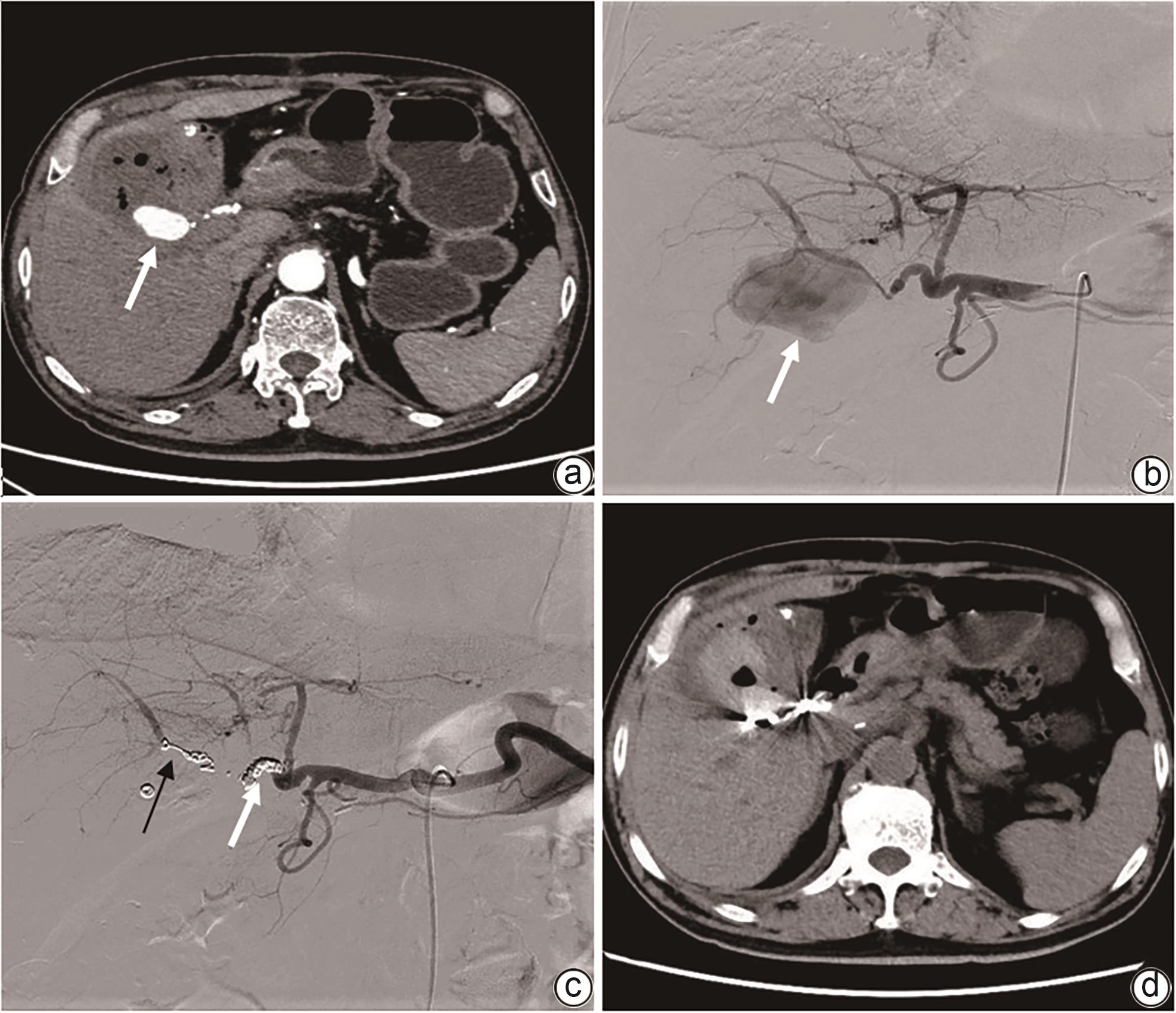




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: