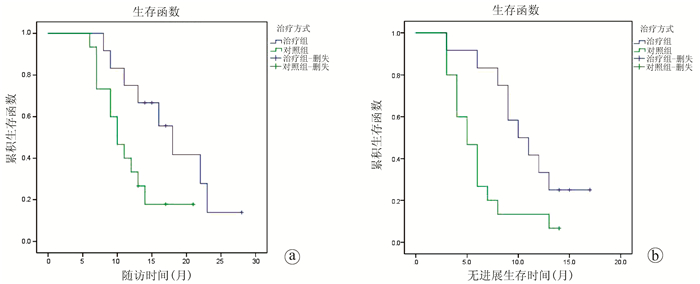
| [1] |
Pancreatic Cancer Committee of Chinese Anti-Cancer Association. Comprehensive guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer (2018 version)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(10): 2109-2120. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.011. |
| [2] |
HE C, WANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparison of combination therapies in the management of locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Induction chemotherapy followed by irreversible electroporation vs radiofrequency ablation[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(13): 4699-4710. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3119. |
| [3] |
PAIELLA S, de PASTENA M, D'ONOFRIO M, et al. Palliative therapy in pancreatic cancer-interventional treatment with radiofrequency ablation/irreversible electroporation[J]. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 3: 80. DOI: 10.21037/tgh.2018.10.05. |
| [4] |
HAMMEL P, HUGUET F, van LAETHEM JL, et al. Effect of chemoradiotherapy vs chemotherapy on survival in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer controlled after 4 months of gemcitabine with or without erlotinib: The LAP07 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(17): 1844-1853. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2016.4324. |
| [5] |
VROOMEN L, PETRE EN, CORNELIS FH, et al. Irreversible electroporation and thermal ablation of tumors in the liver, lung, kidney and bone: What are the differences?[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2017, 98(9): 609-617. DOI: 10.1016/j.diii.2017.07.007. |
| [6] |
VOGEL JA, van VELDHUISEN E, AGNASS P, et al. Time-dependent impact of irreversible electroporation on pancreas, liver, blood vessels and nerves: A systematic review of experimental studies[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0166987. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166987. |
| [7] |
van ROESSEL S, KASUMOVA GG, VERHEIJ J, et al. International validation of the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging system in patients with resected pancreatic cancer[J]. JAMA Surg, 2018, 153(12): e183617. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.3617. |
| [8] |
LENCIONI R, LLOVET JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2010, 30(1): 52-60. DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1247132. |
| [9] |
RUARUS A, VROOMEN L, PUIJK R, et al. Locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A review of local ablative therapies[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2018, 10(1): 16. DOI: 10.3390/cancers10010016. |
| [10] |
Chinese Society of Interventional and Minimally Invasive Therapy, China Medicine Education Association. Expert consensus on image-guided irreversible electroporation ablation for pancreatic cancer (2018 version)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(2): 299-302. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.02.011 |
| [11] |
AL EFISHAT M, WOLFGANG CL, WEISS MJ. Stage Ⅲ pancreatic cancer and the role of irreversible electroporation[J]. BMJ, 2015, 350: h521. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.h521. |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
BELFIORE MP, RONZA FM, ROMANO F, et al. Percutaneous CT-guided irreversible electroporation followed by chemotherapy as a novel neoadjuvant protocol in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Our preliminary experience[J]. Int J Surg, 2015, 21(Suppl 1): s34-s39. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.06.049. |
| [14] |
ZHANG Y, SHI J, ZENG J, et al. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation for ablation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Experience from a Chinese institution[J]. Pancreas, 2017, 46(2): e12-12e14. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000703. |
| [15] |
SCHEFFER HJ, VROOMEN LG, de JONG MC, et al. Ablation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer with percutaneous irreversible electroporation: Results of the Phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ PANFIRE Study[J]. Radiology, 2017, 282(2): 585-597. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2016152835. |
| [16] |
TONG H, LI XY, CHEN YJ, et al. Complications of nano-knife ablation on locally advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2020, 26(4): 270-271. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113884-20190923-00312. |
| [17] |
MORIS D, MACHAIRAS N, TSILIMIGRAS DI, et al. Systematic review of surgical and percutaneous irreversible electroporation in the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2019, 26(6): 1657-1668. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-019-07261-7. |
| [18] |
MARTIN RC 2nd, KWON D, CHALIKONDA S, et al. Treatment of 200 locally advanced (stage Ⅲ) pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients with irreversible electroporation: Safety and efficacy[J]. Ann Surg, 2015, 262(3): 486-494; discussion 492-494. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001441. |
| [19] |
YANG PC, HUANG KW, PUA U, et al. Prognostic factor analysis of irreversible electroporation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer-A multi-institutional clinical study in Asia[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2020, 46(5): 811-817. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.12.006. |










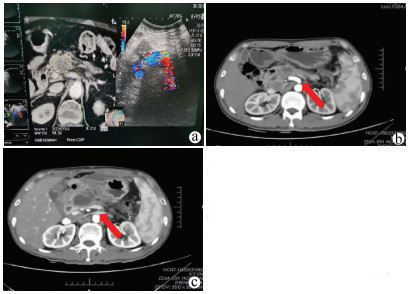




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: