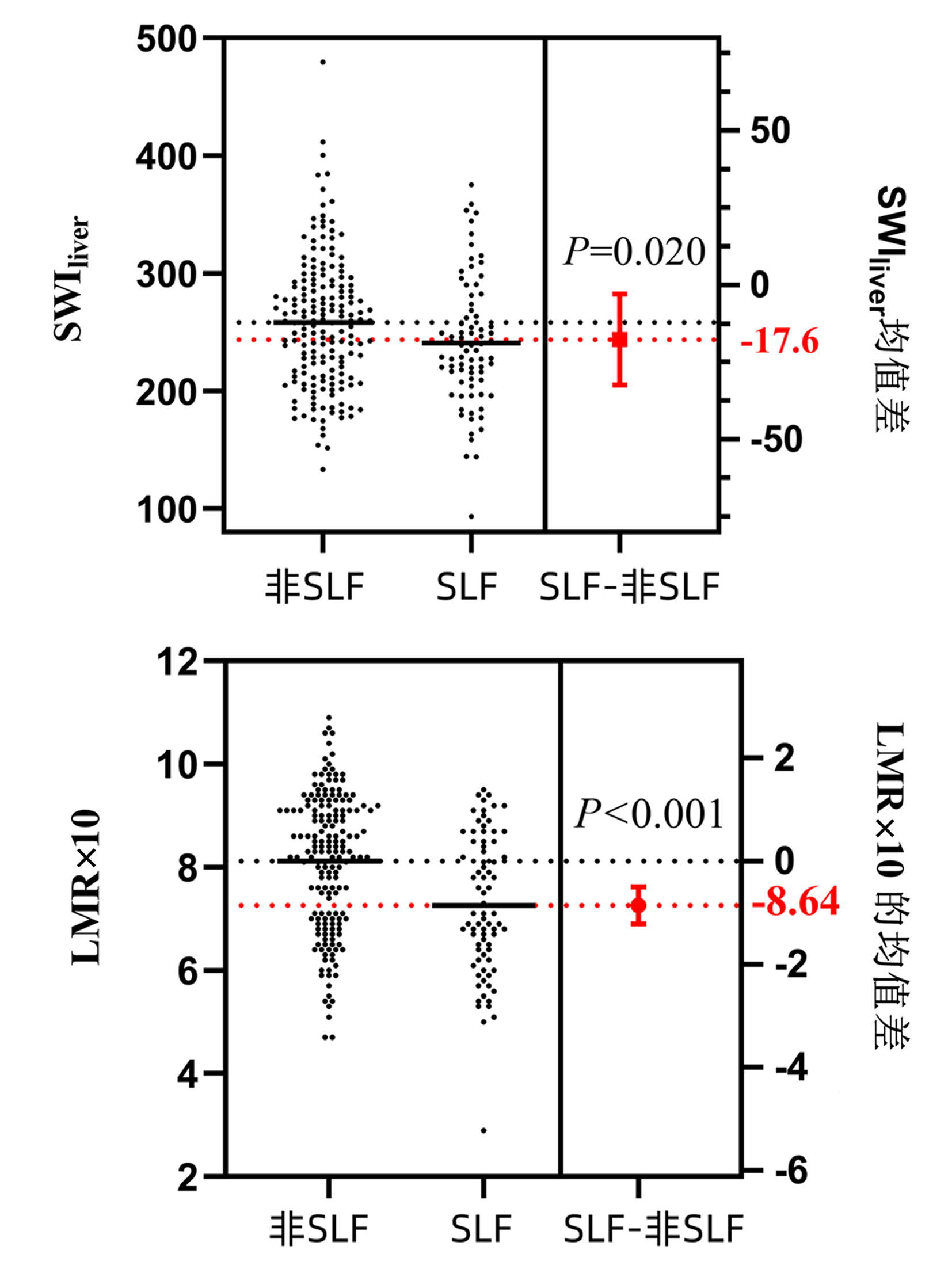
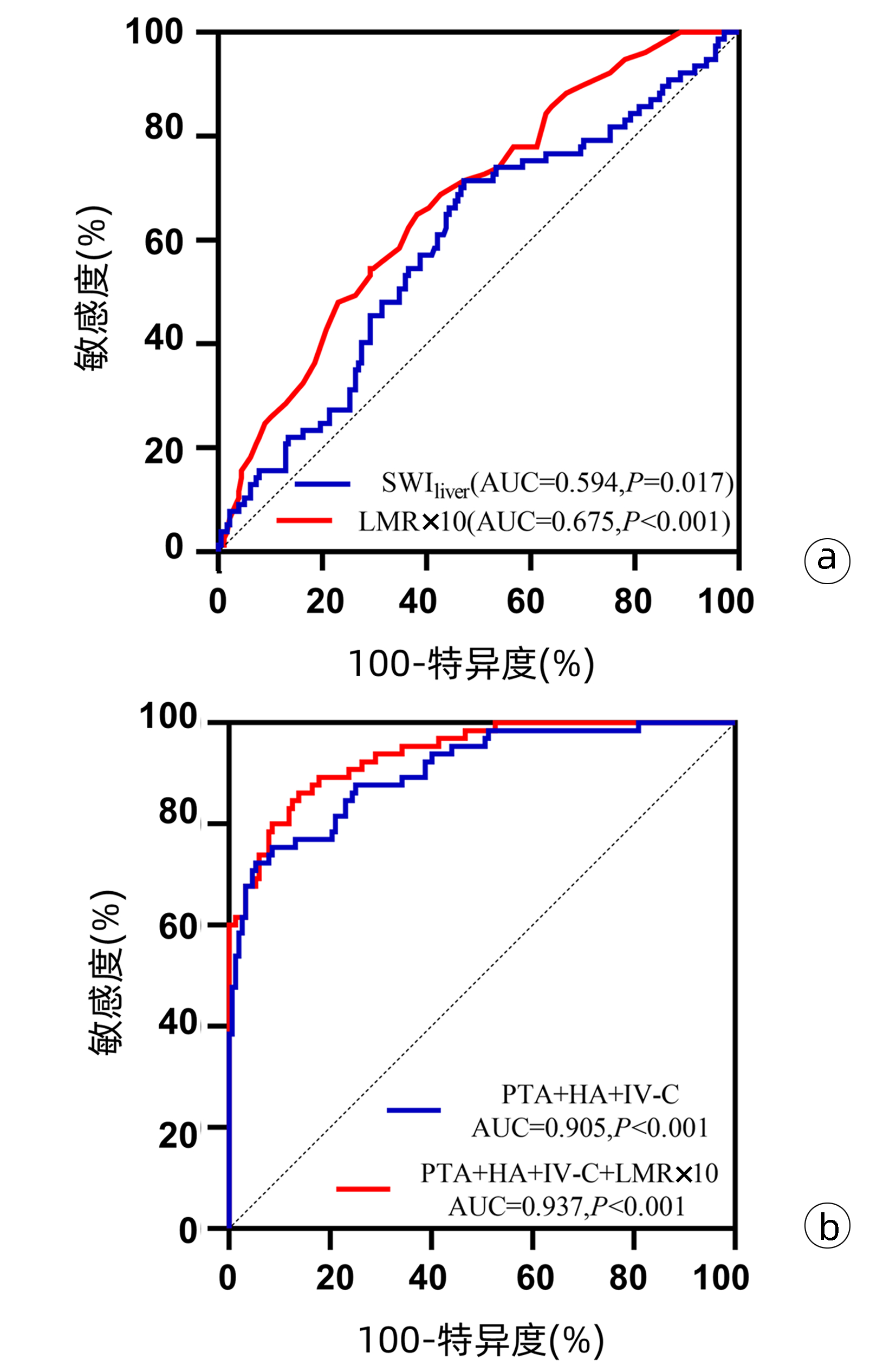
| [1] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [2] |
SHIHA G, IBRAHIM A, HELMY A, et al. Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) consensus guidelines on invasive and non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: a 2016 update[J]. Hepatol Int, 2017, 11(1): 1-30. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-016-9760-3. |
| [3] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and therapy of hepatic fibrosis(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(10): 2163-2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007. |
| [4] |
European Association for Study of Liver, Asociacion Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Higado. EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(1): 237-264. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.006. |
| [5] |
WANG L, ZHU M, CAO L, et al. Liver stiffness measurement can reflect the active liver necroinflammation in population with chronic liver disease: a real-world evidence study[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2019, 7(4): 313-321. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2019.00040. |
| [6] |
HUANG LL, YU XP, LI JL, et al. Effect of liver inflammation on accuracy of FibroScan device in assessing liver fibrosis stage in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27(7): 641-653. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.641. |
| [7] |
SETO WK, HUI R, MAK LY, et al. Association between hepatic steatosis, measured by controlled attenuation parameter, and fibrosis burden in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 16(4): 575-583.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.044. |
| [8] |
CHENG Y, GUO R, LIU MG, et al. Value of MRI and quantitative serological markers detection to the diagnosis of liver fibrosis[J]. J Chin Pract Diagn Ther, 2018, 32 (6): 589-593. DOI: 10.13507/j.ssn.1674-3474.2018.06.021.
|
| [9] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [10] |
CHENG DY, LI B, JI SJ, et al. Application of transient elastography in noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2021, 13(4): 9-13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.04.003.
程丹颖, 李贲, 纪世博, 等. 瞬时弹性成像技术在肝纤维化无创诊断中的应用[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(4): 9-13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.04.003.
|
| [11] |
OBMANN VC, MARX C, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Liver MRI susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) compared to T2* mapping in the presence of steatosis and fibrosis[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2019, 118: 66-74. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.07.001. |
| [12] |
JIANG JZ, DENG LB, RUAN JY, et al. Value of susceptibility weighted imaging in hepatic fibrosis staging by using MR in a rabbit model[J]. J Chin Med, 2016, 96(17): 1371-1376. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.17.015 |
| [13] |
GANDON Y, OLIVIÉ D, GUYADER D, et al. Non-invasive assessment of hepatic iron stores by MRI[J]. Lancet, 2004, 363(9406): 357-362. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15436-6. |
| [14] |
BALASSY C, FEIER D, PECK-RADOSAVLJEVIC M, et al. Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging in the grading of liver fibrosis: a feasibility study[J]. Radiology, 2014, 270(1): 149-158. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.13122440. |
| [15] |
SHI DD, GUO R, LIU YH, et al. The value of gadoxetate disodium enhanced MRI in the quantitative assessment of liver fibrosis[J]. Chin J Radio, 2022, 56(3): 273-278. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20210316-00236. |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
YANG XZ, GEN AW, XIAN JC, et al. Diagnostic value of various noninvasive indexes in the diagnosis of chronic hepatic fibrosis[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(2): 479-485. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_201801_14198. |















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: