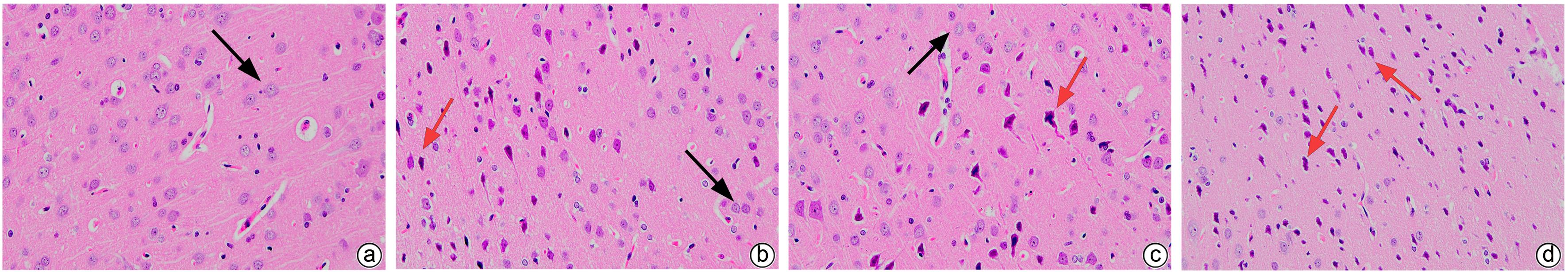
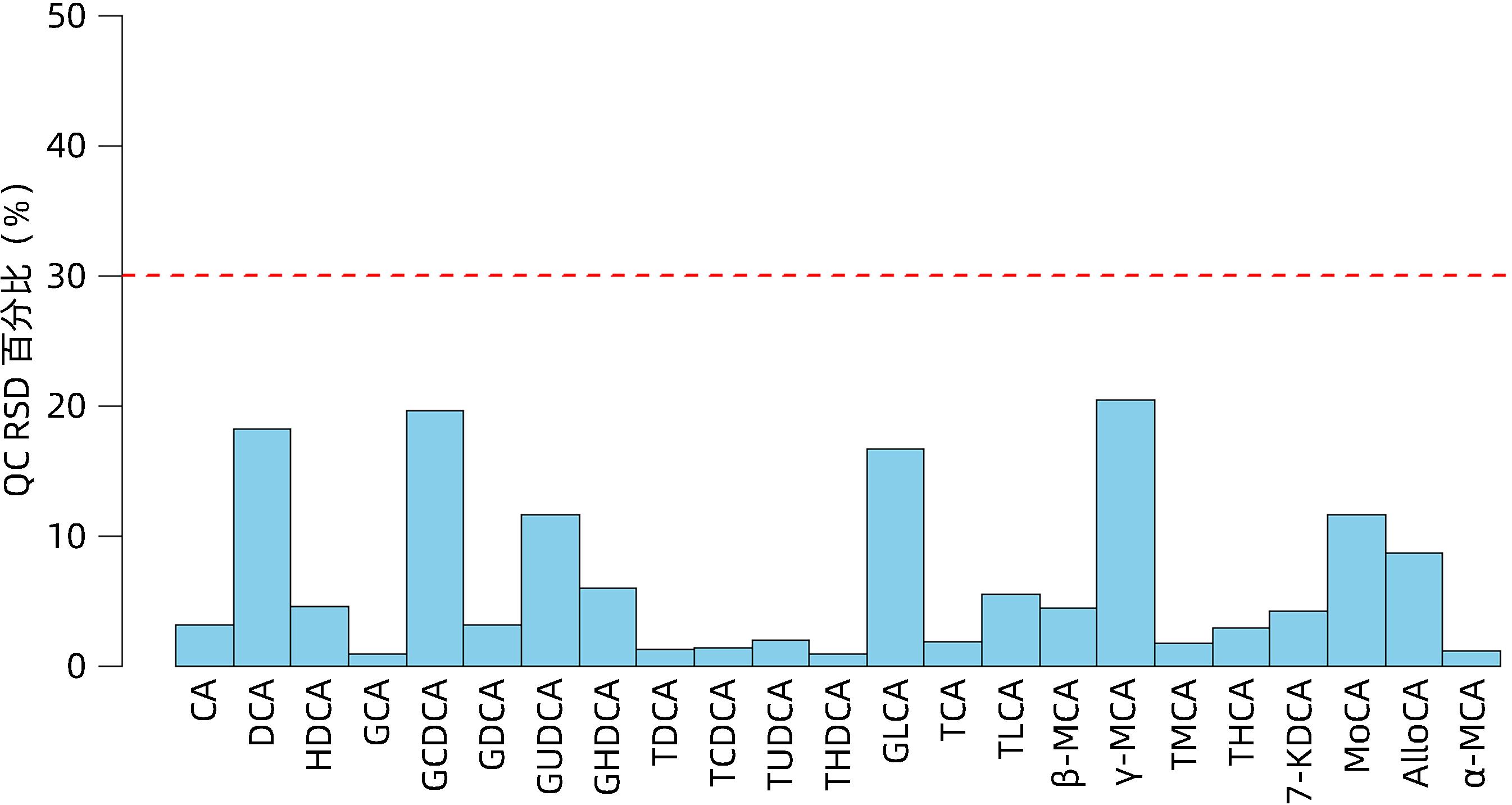
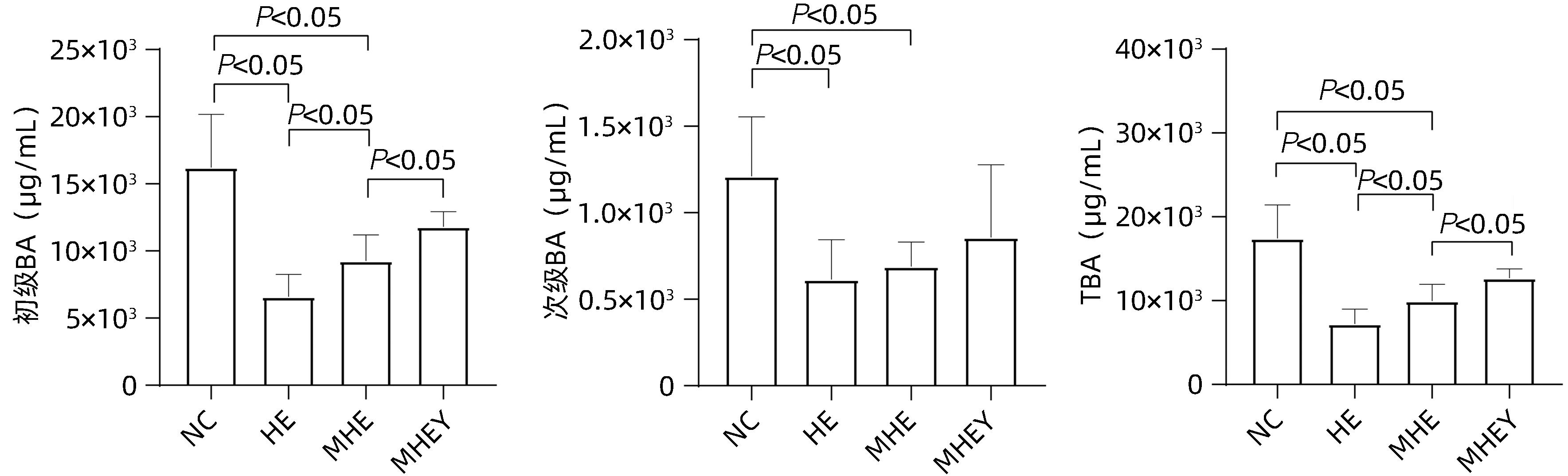
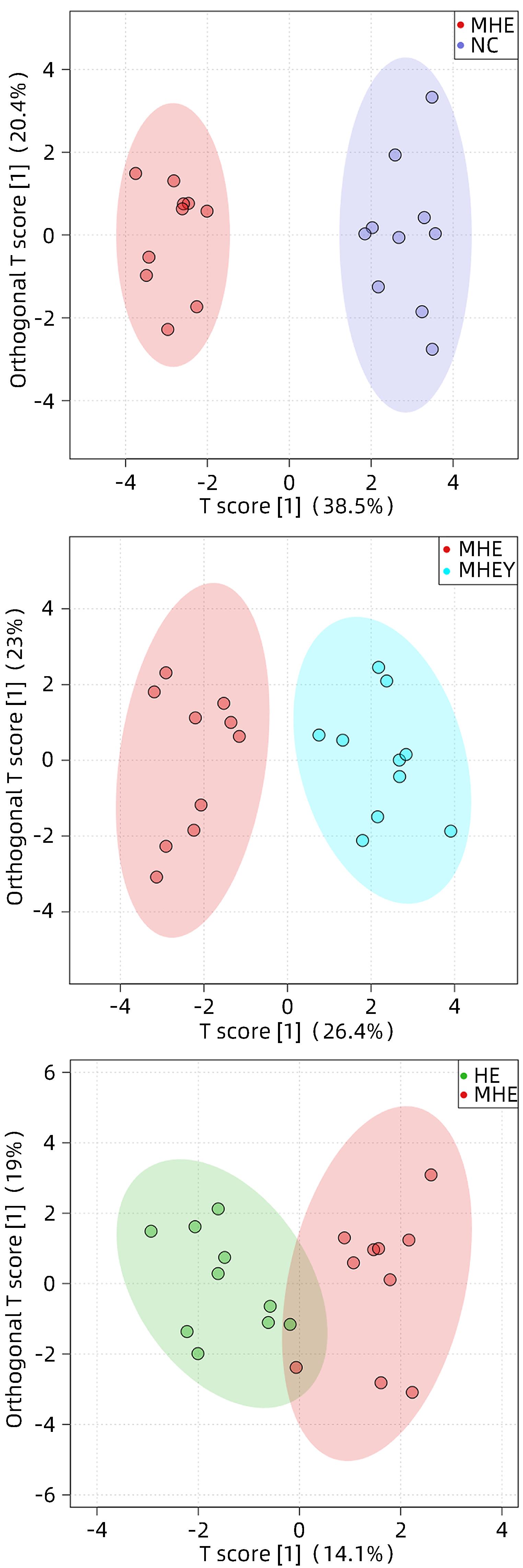
| [1] |
BAJAJ JS, WADE JB, SANYAL AJ. Spectrum of neurocognitive impairment in cirrhosis: Implications for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50( 6): 2014- 2021. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23216. |
| [2] |
ELSAID MI, RUSTGI VK. Epidemiology of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2020, 24( 2): 157- 174. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2020.01.001. |
| [3] |
DHAREL N, BAJAJ JS. Definition and nomenclature of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2015, 5( Suppl 1): S37-S41. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.10.001. |
| [4] |
BAJAJ JS, DUARTE-ROJO A, XIE JJ, et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy and mild cognitive impairment worsen quality of life in elderly patients with cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18( 13): 3008- 3016. e 2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.033. |
| [5] |
PATEL D, MCPHAIL MJ, COBBOLD JF, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Br J Hosp Med(Lond), 2012, 73( 2): 79- 85. DOI: 10.12968/hmed.2012.73.2.79. |
| [6] |
HOLECEK M. Evidence of a vicious cycle in glutamine synthesis and breakdown in pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy-therapeutic perspectives[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2014, 29( 1): 9- 17. DOI: 10.1007/s11011-013-9428-9. |
| [7] |
JOHANSSON M, AGUSTI A, LLANSOLA M, et al. GR3027 antagonizes GABAA receptor-potentiating neurosteroids and restores spatial learning and motor coordination in rats with chronic hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2015, 309( 5): G400-G409. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00073.2015. |
| [8] |
LLANSOLA M, MONTOLIU C, AGUSTI A, et al. Interplay between glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission alterations in cognitive and motor impairment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Neurochem Int, 2015, 88: 15- 19. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2014.10.011. |
| [9] |
MCMILLIN M, GRANT S, FRAMPTON G, et al. FXR-Mediated cortical cholesterol accumulation contributes to the pathogenesis of type A hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 6( 1): 47- 63. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.02.008. |
| [10] |
XUTIAN S, CAO D, WOZNIAK J, et al. Comprehension of the unique characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2012, 40( 2): 231- 244. DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X12500188. |
| [11] |
ZHANG X, YANG Y, ZHANG F, et al. Traditional Chinese medicines differentially modulate the gut microbiota based on their nature(Yao-Xing)[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 85: 153496. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153496. |
| [12] |
WANG N, WANG MG, MAO DW, et al. Clinical efficacy observation of rhubarb decoction in the treatment of type A hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2015, 26( 5): 1169- 1171. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2015.05.053. |
| [13] |
ZHANG GG. Effects of Rhubarb Decoction retention enema on the levels of endotoxin and blood ammonia in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Pract Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 34( 5): 523- 524. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2814.2018.05.013. |
| [14] |
HUANG GC, WANG M, YANG XH, et al. Analysis of specific metabolite profiling of minimal hepatic encephalopathy based on metabolomics analytical plat-forms of GC-TOFMS and UPLC-QTOFMS[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32( 1): 139- 142. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.01.027. |
| [15] |
HUANG GC, WANG M, YANG XH, et al. Effect of Dahuang decoction retention enema on serum metabolite profiling in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy[J]. JCM, 2016, 57( 3): 220- 223. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2016.03.011. |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
ZHANG MH, JIA L, DU H, et al. Dose-effect of thioacetamide on animal model of hepatic encephalopathy in rats[J]. Acad J Guangzhou Med Coll, 2004, 32( 3): 72- 74. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1836.2004.03.022. |
| [18] |
JIA L. ZHANG MH, SU CA, et al. Establishment of a rat model of mild and micro hepatic encephalopathy induced by thioacetamide[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2004, 12( 5): 1207- 1208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3079.2004.05.046. |
| [19] |
ZIMMERMANN C, FERENCI P, PIFL C, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in rats: characterization of an improved model and study of amino acid-ergic neurotransmission[J]. Hepatology, 1989, 9( 4): 594- 601. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840090414. |
| [20] |
MARGOLIS KG, CRYAN JF, MAYER EA. The microbiota-gut-brain axis: from motility to mood[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160( 5): 1486- 1501. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.066. |
| [21] |
TIAN M, ZHENG D, LIU CL. Research progress on the involvement of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of depression[J]. Chin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 6): 658- 660. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.06.34. |
| [22] |
FASULLO M, RAU P, LIU DQ, et al. Proton pump inhibitors increase the severity of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients[J]. World J Hepatol, 2019, 11( 6): 522- 530. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v11.i6.522. |
| [23] |
ZHENG X, CHEN T, ZHAO A, et al. The brain metabolome of male rats across the lifespan[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 24125. DOI: 10.1038/srep24125. |
| [24] |
XIE G, ZHONG W, LI H, et al. Alteration of bile acid metabolism in the rat induced by chronic ethanol consumption[J]. FASEB J, 2013, 27( 9): 3583- 3593. DOI: 10.1096/fj.13-231860. |
| [25] |
MANO N, SATO Y, NAGATA M, et al. Bioconversion of 3beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid into chenodeoxycholic acid by rat brain enzyme systems[J]. J Lipid Res, 2004, 45( 9): 1741- 1748. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M400157-JLR200. |
| [26] |
KIRIYAMA Y, NOCHI H. The biosynthesis, signaling, and neurological functions of bile acids[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9( 6): 232. DOI: 10.3390/biom9060232. |
| [27] |
WU X, LV YG, DU YF, et al. Neuroprotective effects of INT-777 against Aβ1-42-induced cognitive impairment, neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and synaptic dysfunction in mice[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2018, 73: 533- 545. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.06.018. |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
JIA W, XIE G, JIA W. Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15( 2): 111- 128. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.119. |
| [30] |
TAYYAR AT, TAYYAR A, KOZALI S, et al. Evaluation of FGF-19 and β-klotho as biomarkers in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Arch Med Sci, 2019, 15( 1): 113- 119. DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2017.72424. |
| [31] |
AHLUWALIA V, BETRAPALLY NS, HYLEMON PB, et al. Impaired gut-liver-brain axis in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 26800. DOI: 10.1038/srep26800. |
| [32] |
MCMILLIN M, FRAMPTON G, QUINN M, et al. Bile acid signaling is involved in the neurological decline in a murine model of acute liver failure[J]. Am J Pathol, 2016, 186( 2): 312- 323. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.10.005. |
| [33] |
QUINN M, MCMILLIN M, GALINDO C, et al. Bile acids permeabilize the blood brain barrier after bile duct ligation in rats via Rac1-dependent mechanisms[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2014, 46( 6): 527- 534. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2014.01.159. |
| [34] |
MCMILLIN M, FRAMPTON G, QUINN M, et al. Bile acid signaling is involved in the neurological decline in a murine model of acute liver failure[J]. Am J Pathol, 2016, 186( 2): 312- 323. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.10.005. |
| [35] |
MAHMOUDIANDEHKORDI S, ARNOLD M, NHO K, et al. Altered bile acid profile associates with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease-An emerging role for gut microbiome[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2019, 15( 1): 76- 92. DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.07.217. |















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: