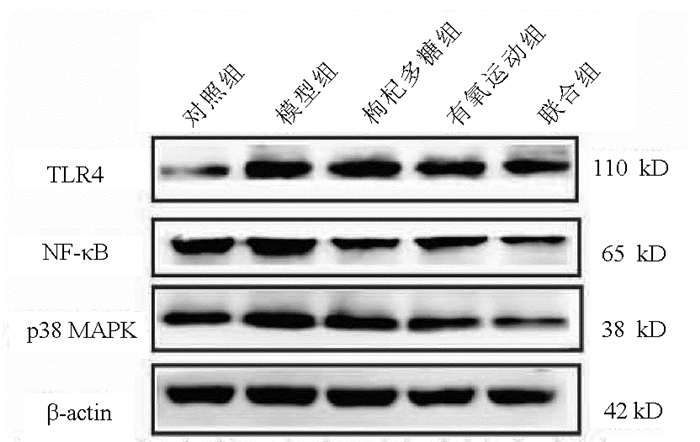
| [1] |
LU XL, JIANG YY, CAO Q. The role of oxidative stress and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(4): 924-927. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.048. |
| [2] |
BOECKMANS J, NATALE A, ROMBAUT M, et al. Flow cytometric quantification of neutral lipids in a human skin stem cell-derived model of NASH[J]. MethodsX, 2020, 7: 101068. DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2020.101068. |
| [3] |
NSEIR W, MAHAMID M. Statins in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis: Updated review[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2013, 15(3): 305. DOI: 10.1007/s11883-012-0305-5. |
| [4] |
XIAO J, LIONG EC, CHING YP, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect rat liver from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-induced injury[J]. Nutr Diabetes, 2013, 3: e81. DOI: 10.1038/nutd.2013.22. |
| [5] |
JIA L, LI W, LI J, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide attenuates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis by up-regulating SIRT1 expression and deacetylase activity[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 36209. DOI: 10.1038/srep36209. |
| [6] |
XIAO J, XING F, HUO J, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides therapeutically improve hepatic functions in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis rats and cellular steatosis model[J]. Sci Rep, 2014, 4: 5587. DOI: 10.1038/srep05587. |
| [7] |
TAKAHASHI H, KOTANI K, TANAKA K, et al. Therapeutic approaches to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Exercise intervention and related mechanisms[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2018, 9: 588. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00588. |
| [8] |
GUO YQ, WU Q, WU YT, et al. Effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide and aerobic exercise on rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its mechanism[J]. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ(Med Sci), 2020, 40(1): 30-36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2020.01.005. 郭怡琼, 吴琼, 吴雅婷, 等. 枸杞多糖和有氧运动对大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝的干预效果及其机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(1): 30-36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115. 2020.01.005.
|
| [9] |
NAKAMURA A, TERAUCHI Y. Lessons from mouse models of high-fat diet-induced NAFLD[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2013, 14(11): 21240-21257. DOI: 10.3390/ijms141121240. |
| [10] |
GONG XW, XU YJ, YANG QH, et al. Effect of soothing gan (liver) and invigorating pi (spleen) recipes on TLR4-p38 MAPK pathway in kupffer cells of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis rats[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2019, 25(3): 216-224. DOI: 10.1007/s11655-018-2829-6. |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
YIMIN, FURUMAKI H, MATSUOKA S, et al. A novel murine model for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis developed by combination of a high-fat diet and oxidized low-density lipoprotein[J]. Lab Invest, 2012, 92(2): 265-281. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2011.159. |
| [13] |
ESTES C, RAZAVI H, LOOMBA R, et al. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(1): 123-133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29466. |
| [14] |
ESTES C, ANSTEE QM, ARIAS-LOSTE MT, et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016-2030[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(4): 896-904. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036. |
| [15] |
BENEDICT M, ZHANG X. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An expanded review[J]. World J Hepatol, 2017, 9(16): 715-732. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i16.715. |
| [16] |
DENG Y, TANG K, CHEN R, et al. Effects of Shugan-Jianpi recipe on the expression of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in the hepatocytes of NAFLD rats[J]. Medicines (Basel), 2018, 5(3). DOI: 10.3390/medicines5030106. |
| [17] |
RECTOR RS, UPTERGROVE GM, MORRIS EM, et al. Daily exercise vs. caloric restriction for prevention of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the OLETF rat model[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2011, 300(5): g874-g883. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00510.2010. |
| [18] |
YANG QH, XU YJ, LIU YZ, et al. Effects of Chaihu-Shugan-San and Shen-Ling-Bai-Zhu-San on p38 MAPK pathway in Kupffer cells of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2014, 2014: 671013. DOI: 10.1155/2014/671013. |
| [19] |
DONOHOE F, WILKINSON M, BAXTER E, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and obesity-related cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(4). DOI: 10.3390/ijms21041241. |
| [20] |
LUEDDE T, SCHWABE R F. NF-κB in the liver-linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastro Hepat, 2011, 8(2): 108-118. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.213 |
| [21] |
KANG HH, KIM IK, LEE HI, et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces liver fibrosis in mice with diet-induced obesity via TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 2017, 490(2): 349-355. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.047. |
| [22] |
WANG XA, ZHANG R, SHE ZG, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 3 constrains IKKβ/NF-κB signaling to alleviate hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59(3): 870-885. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26751. |
| [23] |
LEE DE, LEE SJ, KIM SJ, et al. Curcumin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through inhibition of O-GlcNAcylation[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(11). DOI: 10.3390/nu11112702. |
| [24] |
MANNE V, HANDA P, KOWDLEY KV. Pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2018, 22(1): 23-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2017.08.007. |









 本站查看
本站查看
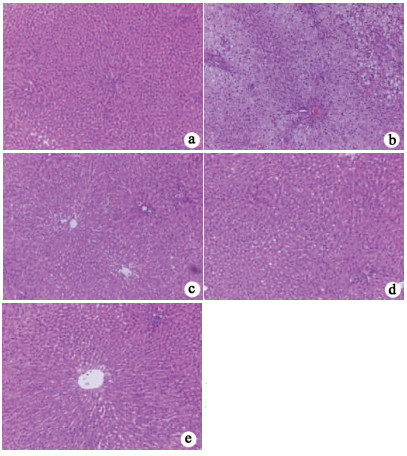




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: