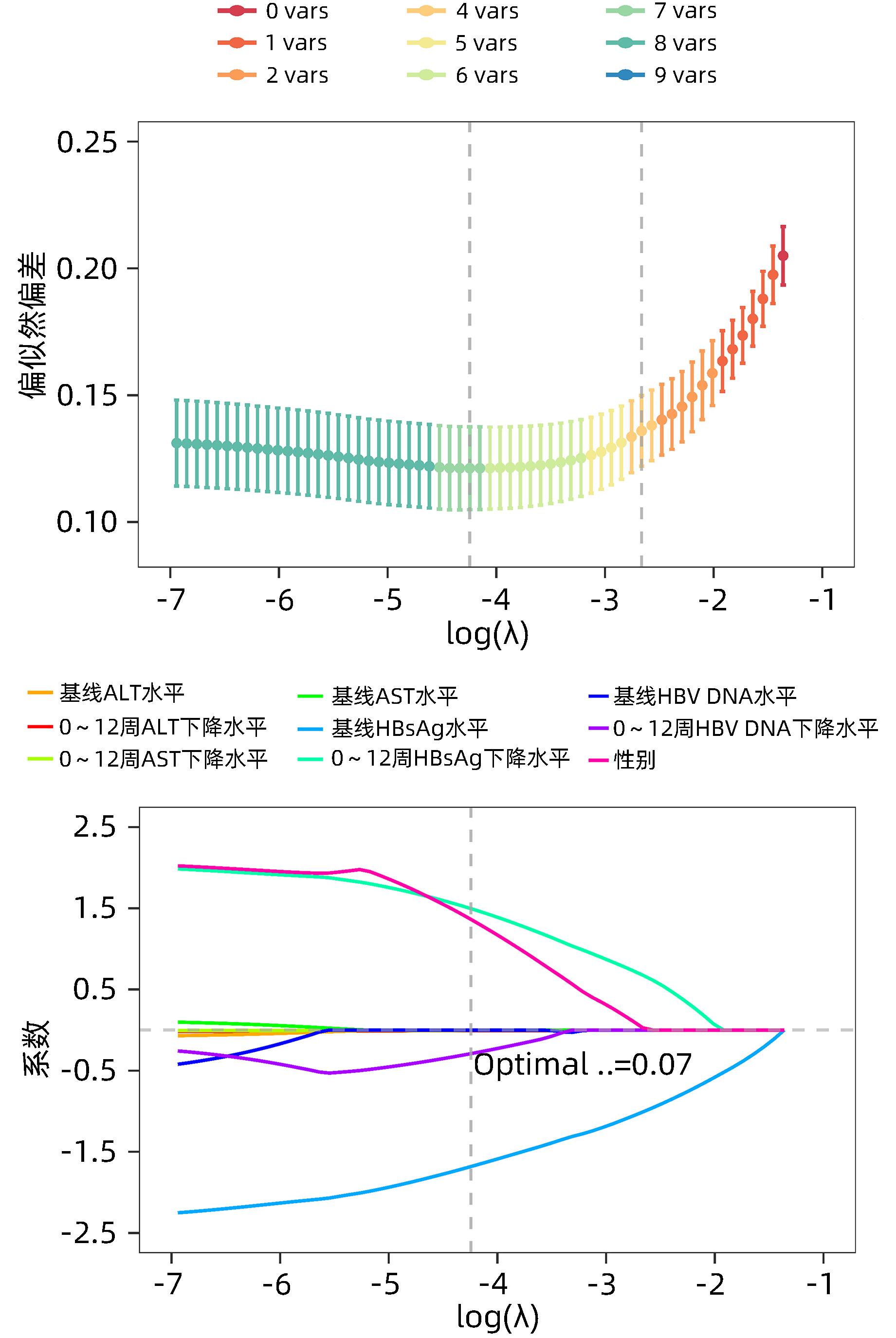
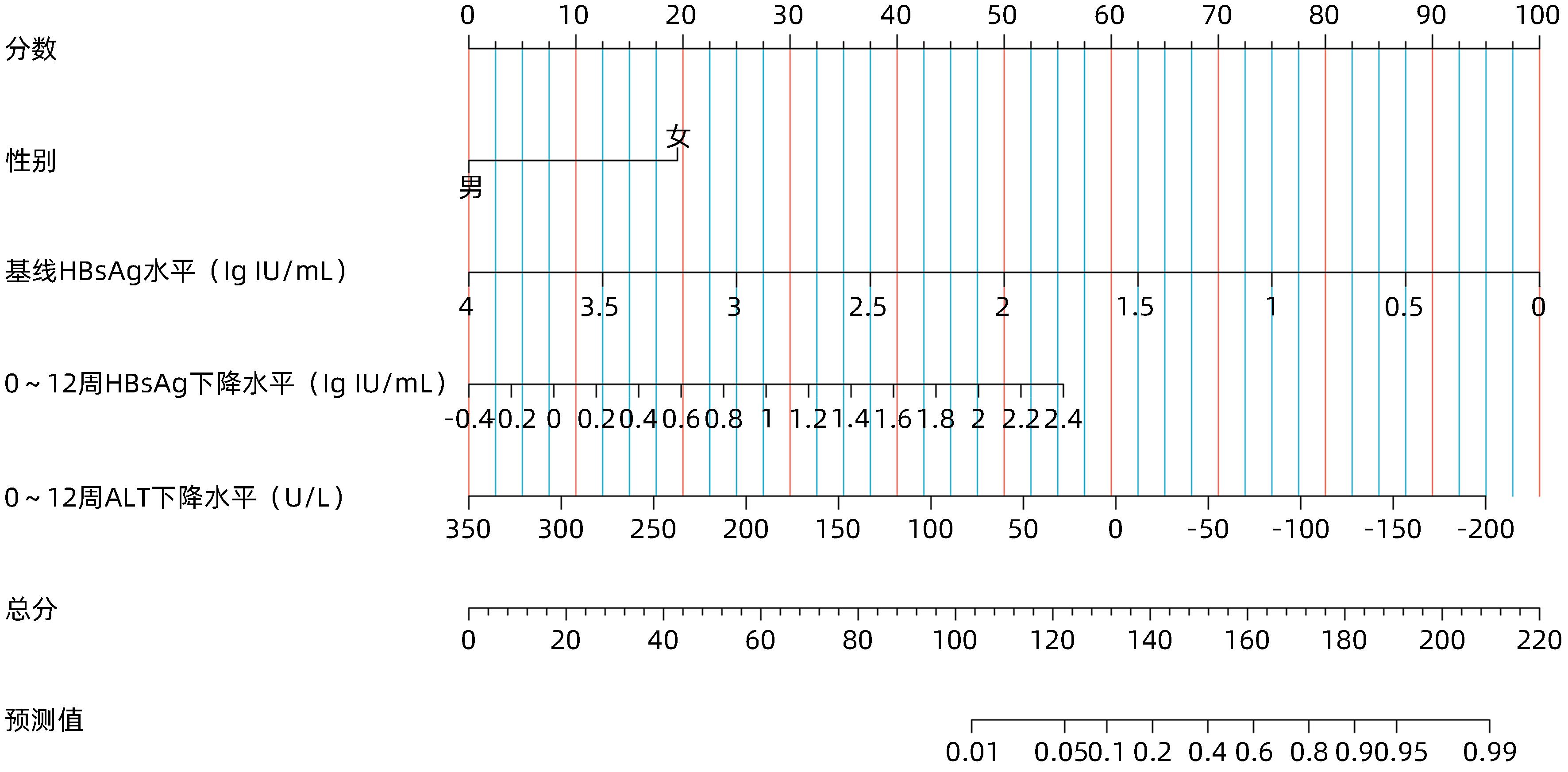
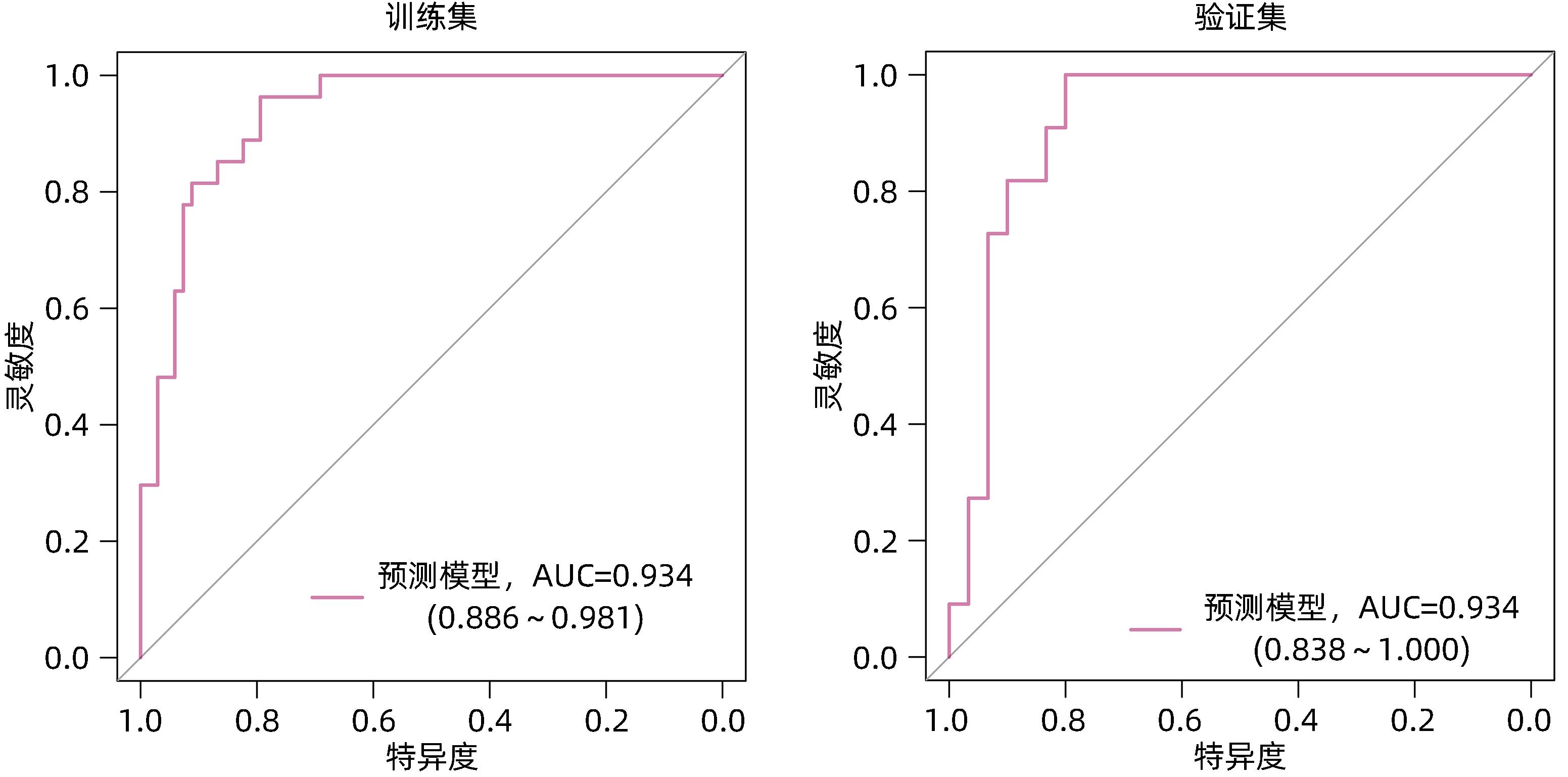
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
ASPINALL EJ, HAWKINS G, FRASER A, et al. Hepatitis B prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care: A review[J]. Occup Med, 2011, 61( 8): 531- 540. DOI: 10.1093/occmed/kqr136. |
| [3] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. The expert consensus on functional cure of chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 30( 12): 1309- 1331. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20221204-00607. |
| [4] |
NGUYEN MH, WONG G, GANE E, et al. Hepatitis B virus: Advances in prevention, diagnosis, and therapy[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2020, 33( 2): e00046- e00019. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00046-19. |
| [5] |
TSENG TC, KAO JH, CHEN DS. Peginterferon α in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2014, 14( 7): 995- 1006. DOI: 10.1517/14712598.2014.907784. |
| [6] |
MIMURA S, FUJITA K, TAKUMA K, et al. Effect of pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B during and 48 weeks after off-treatment follow-up: The limitation of pre-treatment HBsAg load for the seroclearance of HBsAg[J]. Intern Emerg Med, 2021, 16( 6): 1559- 1565. DOI: 10.1007/s11739-020-02622-7. |
| [7] |
KWON H, LOK AS. Hepatitis B therapy[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 8( 5): 275- 284. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.33. |
| [8] |
ALHAMZAWI R, ALI HTM. The Bayesian adaptive lasso regression[J]. Math Biosci, 2018, 303: 75- 82. DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2018.06.004. |
| [9] |
VLACHOGIANNAKOS J, PAPATHEODORIDIS GV. HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B: Why do I treat my patients with pegylated interferon-alfa?[J]. Liver Int, 2014, 34( Suppl 1): 127- 132. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12404. |
| [10] |
SHEPHERD J, JONES J, TAKEDA A, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: A systematic review and economic evaluation[J]. Health Technol Assess, 2006, 10( 28): ⅲ-ⅳ, ⅺ-xiv, 1- 183. DOI: 10.3310/hta10280. |
| [11] |
YE JY, CHEN JL. Interferon and hepatitis B: Current and future perspectives[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 733364. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.733364. |
| [12] |
QIAN JD, ZHAO H, WANG GQ. Current status of the treatment of chronic hepatitis B-related liver fibrosis/cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 12): 2909- 2913. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.12.036. |
| [13] |
LI H, XU WT, DENG BC, et al. Progress in the functional treatment of chronic hepatitis B with nucleos(t)ide analogues and pegylated interferon[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 9): 890- 893. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.04. |
| [14] |
ZHANG WH, ZHANG DZ, DOU XG, et al. Consensus on pegylated interferon alpha in treatment of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2017, 25( 9): 678- 686. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.09.007. |
| [15] |
GUO YF, ZHANG JM. Influencing factors for the functional cure of chronic hepatitis B and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 8): 1721- 1725. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.08.004. |
| [16] |
OMATA M, CHENG AL, KOKUDO N, et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update[J]. Hepatol Int, 2017, 11( 4): 317- 370. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9799-9. |
| [17] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67( 2): 370- 398. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.021. |
| [18] |
LIANG TJ, BLOCK TM, MCMAHON BJ, et al. Present and future therapies of hepatitis B: From discovery to cure[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62( 6): 1893- 1908. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28025. |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
XIE F, XIONG X, YAO CX, et al. Clinical efficacy and influencing factors of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and nucleos(t)ide analogue in chronic hepatitis B patients with low level of hepatitis B virus surface antigen[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis(Electronic Edition), 2022, 16( 4): 247- 253. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2022.04.005. |
| [21] |
CHU JH, HUANG Y, XIE DY, et al. Real-world study on HBsAg loss of combination therapy in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2022, 29( 9): 765- 776. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13722. |
| [22] |
LI MH, ZHANG L, LU Y, et al. Early serum HBsAg kinetics as predictor of HBsAg loss in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B after treatment with pegylated interferonα-2a[J]. Virol Sin, 2021, 36( 2): 311- 320. DOI: 10.1007/s12250-020-00290-7. |
| [23] |
HU P, SHANG J, ZHANG WH, et al. HBsAg loss with peg-interferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B patients with partial response to nucleos(t)ide analog: New switch study[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2018, 6( 1): 25- 34. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2017.00072. |















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: