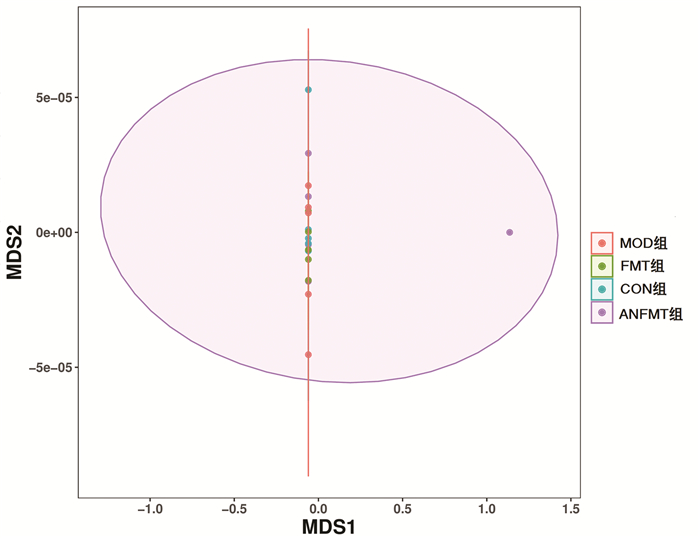
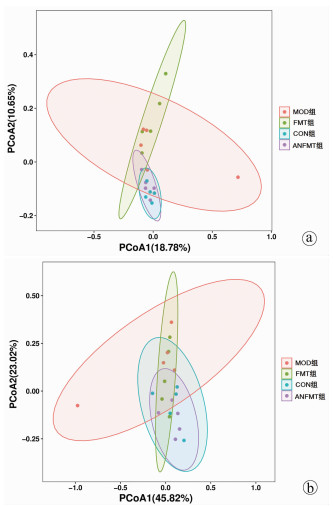
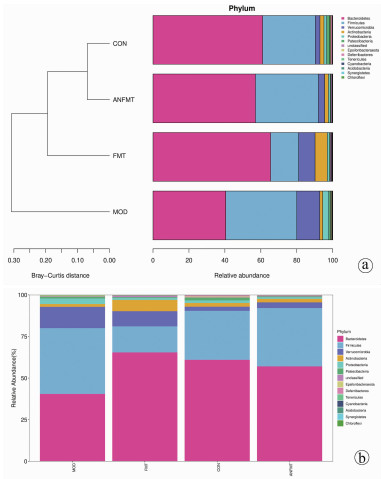
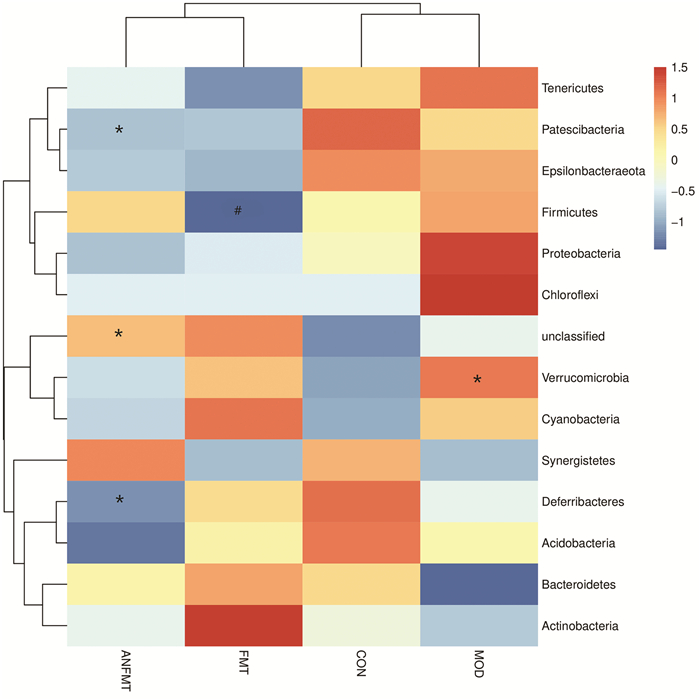
| [1] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019. 01.007.
中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/ j.issn.1001-5256.2019. 01.007.
|
| [2] |
CHEN Y, GUO J, QIAN G, et al. Gut dysbiosis in acute-on-chronic liver failure and its predictive value for mortality[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(9): 1429-1437. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12932. |
| [3] |
MINEMURA M, SHIMIZU Y. Gut microbiota and liver diseases[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(6): 1691-1702. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1691. |
| [4] |
CLEMENTE JC, URSELL LK, PARFREY LW, et al. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view[J]. Cell, 2012, 148(6): 1258-1270. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035. |
| [5] |
WANG KX, ZHENG C, ZHANG JH, et al. Clinical effect of Qingre Jiedu Liangxue prescription in treatment of mice with acute-on-chronic liver failure and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2765-2771. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.025. |
| [6] |
ZHANG YC, BI YZ, FANG X, et al. Protective effect of probiotics in rats with acute- on- chronic liver failure and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1570-1575. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07. |
| [7] |
WANG WW, ZHANG Y, HUANG XB, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation prevents hepatic encephalopathy in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic dysfunction[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(38): 6983-6994. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.6983. |
| [8] |
CUI B, FENG Q, WANG H, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation through mid-gut for refractory Crohn's disease: Safety, feasibility, and efficacy trial results[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(1): 51-58. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12727. |
| [9] |
ROUND JL, MAZMANIAN SK. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2009, 9(5): 313-323. DOI: 10.1038/nri2515. |
| [10] |
QIN N, YANG F, LI A, et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7516): 59-64. DOI: 10.1038/nature13568. |
| [11] |
MOREAU R, JALAN R, GINES P, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(7): 1426-1437, 1437. e1-9. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.042. |
| [12] |
BAJAJ JS, FAGAN A, SIKAROODI M, et al. Liver transplant modulates gut microbial dysbiosis and cognitive function in cirrhosis[J]. Liver Transpl, 2017, 23(7): 907-914. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24754. |
| [13] |
BAJAJ JS, IDILMAN R, MABUDIAN L, et al. Diet affects gut microbiota and modulates hospitalization risk differentially in an international cirrhosis cohort[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(1): 234-247. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29791. |
| [14] |
ACHARYA C, BAJAJ JS. Gut microbiota and complications of liver disease[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2017, 46(1): 155-169. DOI: 10.1016/j.gtc.2016.09.013. |
| [15] |
DAVIS BC, BAJAJ JS. The human gut microbiome in liver diseases[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2017, 37(2): 128-140. DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1602763. |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
ZHANG W, GU Y, CHEN Y, et al. Intestinal flora imbalance results in altered bacterial translocation and liver function in rats with experimental cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 22(12): 1481-1486. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32833eb8b0. |
| [18] |
PENG JH, CUI T, SUN ZL, et al. Effects of puerariae radix extract on endotoxin receptors and TNF-α expression induced by gut-derived endotoxin in chronic alcoholic liver injury[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2012, 2012: 234987. DOI: 10.1155/2012/234987. |
| [19] |
BILZER M, ROGGEL F, GERBES AL. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease[J]. Liver Int, 2006, 26(10): 1175-1186. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01342.x. |
| [20] |
TAKEUCHI O, AKIRA S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation[J]. Cell, 2010, 140(6): 805-820. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.022. |
| [21] |
XU L, KITADE H, NI Y, et al. Roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in obesity-associated insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Biomolecules, 2015, 5(3): 1563-1579. DOI: 10.3390/biom5031563. |
| [22] |
WIEST R. Bacterial translocation and alterations of the digestive system[M]//GINÈS P, KAMATH P, ARROYO V. Chronic liver failure. Clinical Gastroenterology. Humana Press, 2011: 189-218.
|
| [23] |
MA HD, WANG YH, CHANG C, et al. The intestinal microbiota and microenvironment in liver[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2015, 14(3): 183-191. DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.10.013. |
| [24] |
YANG Y, JOBIN C. Microbial imbalance and intestinal pathologies: connections and contributions[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2014, 7(10): 1131-1142. DOI: 10.1242/dmm.016428. |








 本站查看
本站查看





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: